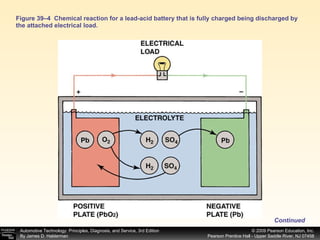
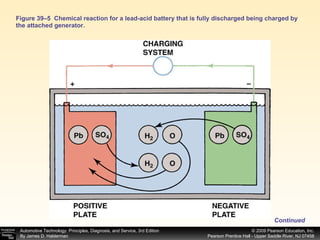
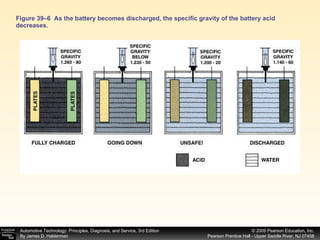
A battery works by a chemical reaction between lead plates and sulfuric acid electrolyte that produces voltage. During discharge, lead dioxide and lead plates react with sulfuric acid to form lead sulfate, and the electrolyte becomes more water-like. During charging, the reactions reverse as sulfuric acid is returned to the electrolyte and lead dioxide and lead plates are regenerated. A battery provides electrical current through these reversible chemical reactions and maintains voltage in a vehicle's electrical system. Proper charging, maintenance, and testing procedures are required to safely work with batteries.






![BATTERY CONSTRUCTION Most automotive battery cases (container or covers) are constructed of polypropylene, a thin (approx. 0.08 inch [.0 millimeters] thick), strong, and lightweight plastic. Industrial and truck batteries are constructed of a hard, thick, rubber material. Continued Inside the case are six cells (for 12-volt), each with positive and negative plates. Built in the bottom are ribs to support the lead-alloy plates and provide space for sediment to settle. This sediment chamber , prevents spent material from causing a short circuit between the plates at the bottom of the battery. Figure 39–1 Batteries are constructed of plates grouped into cells, installed in a plastic case.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap39-091025182923-phpapp02/85/Chapter-39-8-320.jpg)






















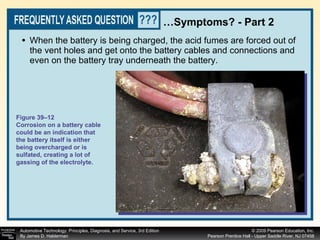




























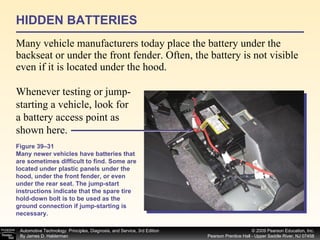
![Procedure for battery electrical drain test using a test light: Figure 39–29 After connecting the shutoff tool, start the engine and operate all accessories. Stop the engine and turn off everything. Connect the ammeter across the shutoff switch in parallel. Wait 20 minutes. This time allows all electronic circuits to “time out” or shut down. Open the switch—all current now will flow through the ammeter. A reading greater than specified (usually greater than 50 milliamperes [0.05 amperes]) indicates a problem that should be corrected. Make certain that all lights, accessories, and ignition are off. Check all vehicle doors to be certain that the interior courtesy (dome) lights are off. Disconnect the negative ( ) battery cable and install a parasitic load tool as shown here. Start the engine, drive vehicle about 10 min, using lights, accessories and radio. Continued](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap39-091025182923-phpapp02/85/Chapter-39-76-320.jpg)