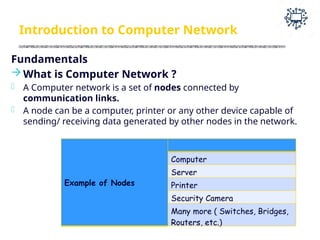
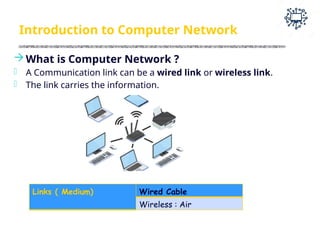
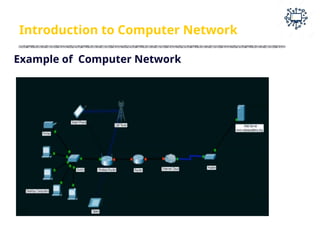
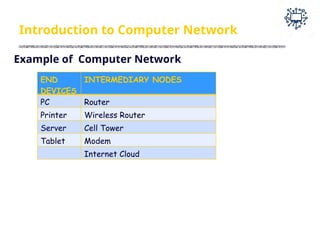
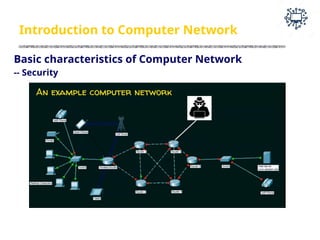
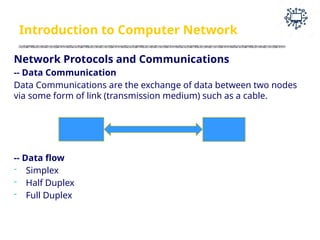
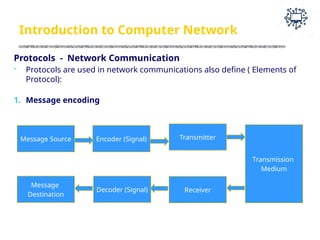
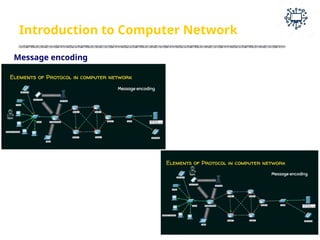
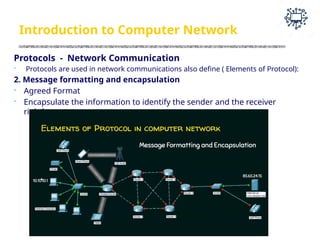
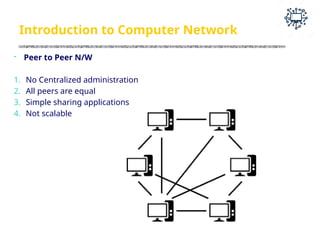
The document outlines the teaching and examination scheme for a Computer Networks course (CSC501) at Thadomal Shahani Engineering College for the academic year 2023-2024. It details the course structure, including contact hours, marking schemes, syllabus modules covering topics such as networking fundamentals, data link layers, network architecture, and protocols, as well as course outcomes relating to network design and protocol analysis. Additional sections address the introduction to computer networks, characteristics, protocols, and communication types including unicast, multicast, and broadcast.