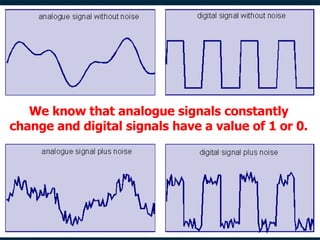
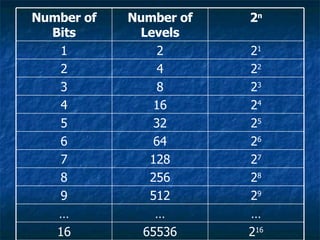
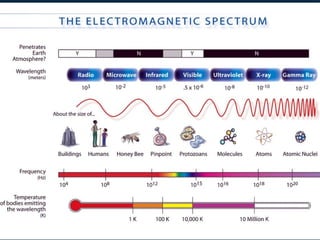
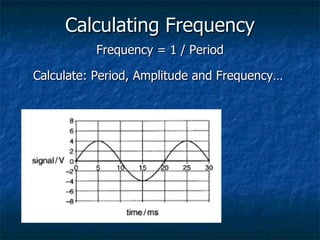
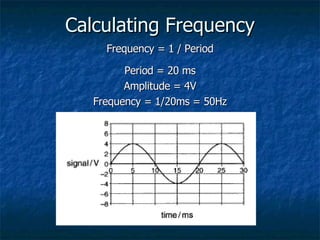
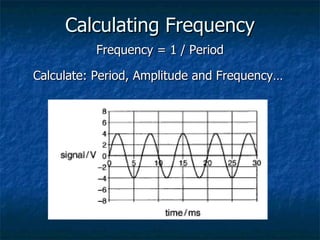
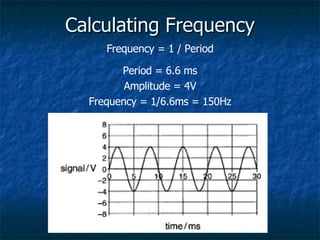
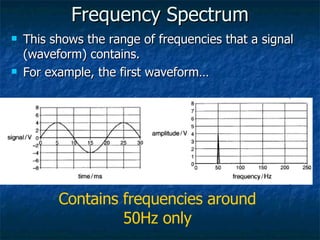
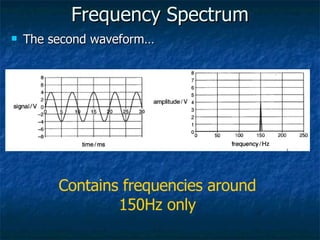
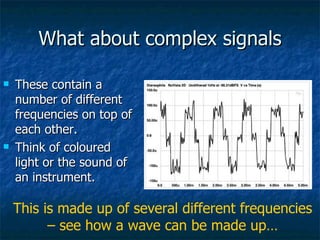
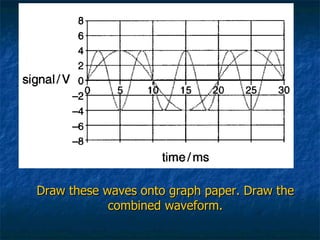
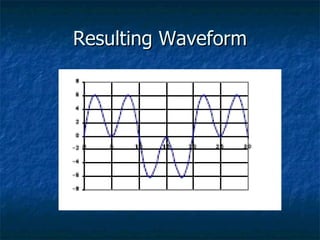
This document discusses how digital signals are transmitted using electromagnetic waves. It explains that digital signals are strings of 1s and 0s representing sampled analogue signals. Electromagnetic waves emitted from a transmitter carry these digital signals by causing electrons in a receiver to vibrate, reproducing the original signal. Key characteristics of signals like amplitude, period, and frequency are defined. Frequency is calculated as the inverse of period and examples are given. A frequency spectrum shows the range of frequencies that make up a signal. Complex signals contain multiple frequencies combined.