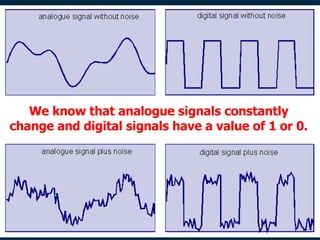
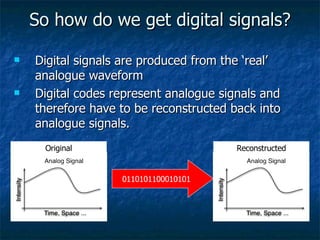
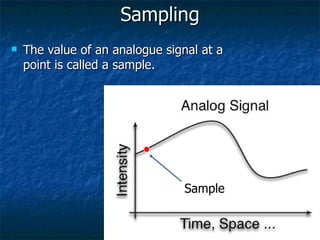
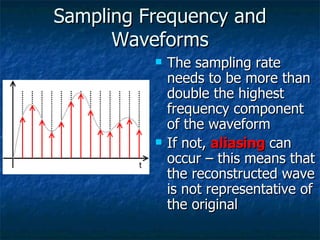
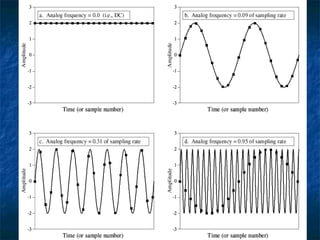
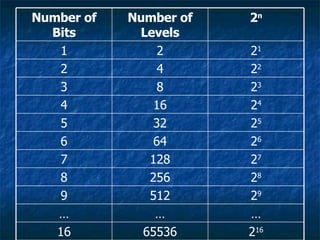
This document discusses how analog signals are converted to digital signals through the process of sampling. It explains that sampling involves taking the value of an analog signal at discrete points in time and converting it to a digital code. The key variables in sampling are the sampling frequency, or how many samples are taken per second, and resolution, or the number of bits used to record each sample value. The sampling frequency needs to be more than double the highest frequency of the analog waveform to avoid aliasing and get an accurate digital reconstruction of the original signal. More bits of resolution provide more possible sample values and a more accurate digital representation.