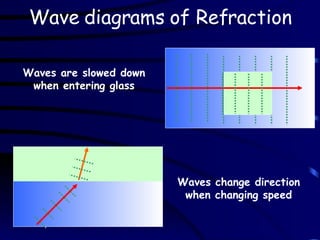
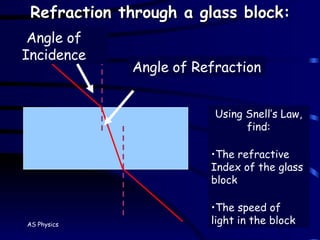
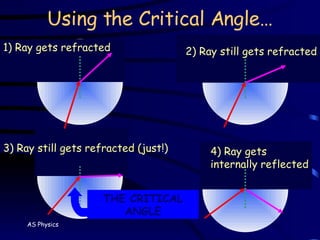
The document discusses refraction and how light behaves when passing from one medium to another with different densities. It defines refraction as light bending or changing speed due to traveling through different mediums. Snell's law is introduced to relate the angle of incidence and refraction based on the refractive indices of the materials. The critical angle is defined as the angle at which total internal reflection occurs, with the refractive index calculated from it. Homework questions ask about using fiber optics instead of copper wires for communication and drawing a diagram showing how signal intensity changes with distance.