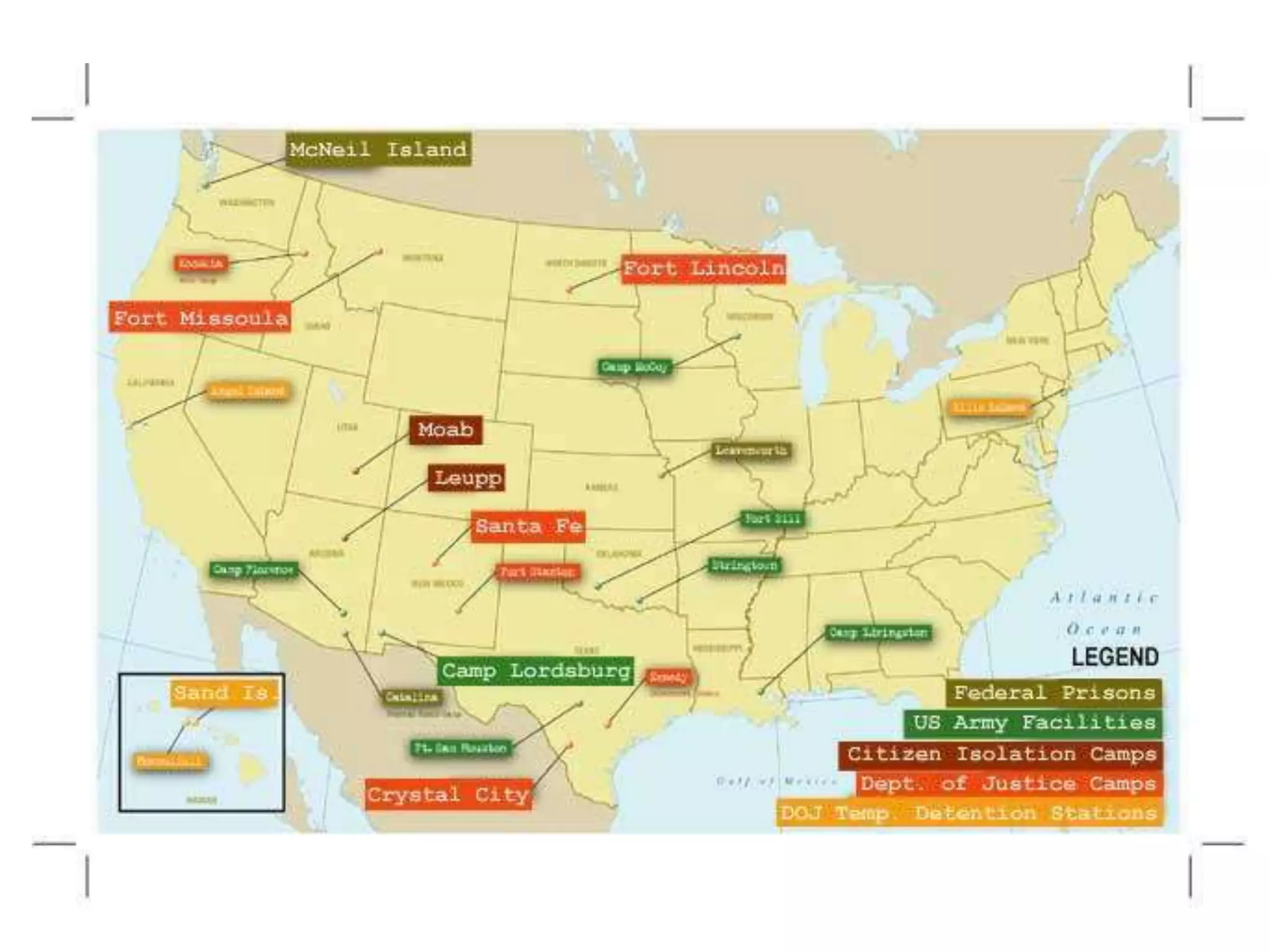
The US mobilized for war by dramatically increasing industrial output, which ended the Great Depression. American workers were much more productive than German and Japanese workers. The US produced over 600,000 vehicles, 88,000 tanks, 7,000 ships, and billions of bullets and other equipment. Over 40 million men were drafted and given basic training. African American soldiers faced segregated facilities, while women took factory jobs at home. Japanese Americans were relocated to internment camps due to racism and fear. Despite discrimination, the US mobilized its diverse population to support the war effort through work, military service, and rationing.