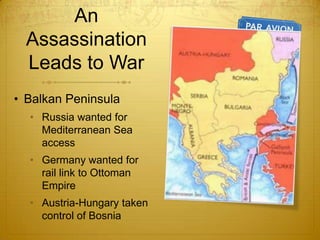
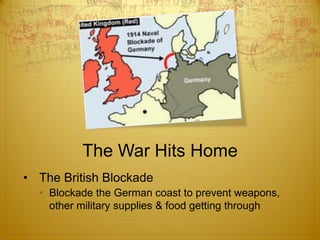
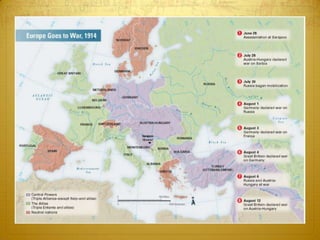
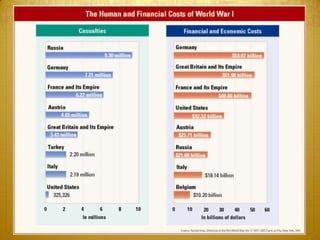
World War I began in 1914 and involved many of the major world powers. Nationalism, imperialism, militarism, and the alliance system all contributed to the outbreak of war. The US initially remained neutral but was drawn into the conflict in 1917 after German submarine attacks and the Zimmerman Telegram. Over 4 million American troops were deployed to Europe. With the addition of American troops and resources, the Allies were finally able to gain the upper hand, leading to the Central Powers' defeat in late 1918.