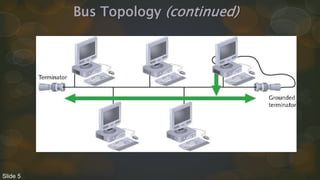
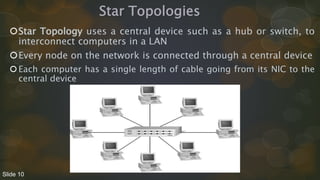
This document discusses various network topologies including physical and logical topologies. It describes the key characteristics of bus, star, ring, point-to-point and mesh topologies. It also covers token ring networks and how data travels on different physical topologies like bus, star and ring. Logical topologies like bus and ring are described along with baseband and broadband signaling.