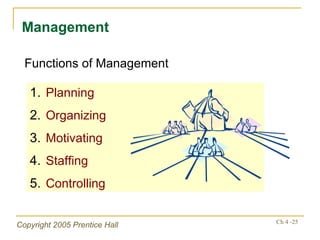
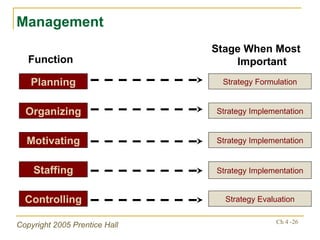
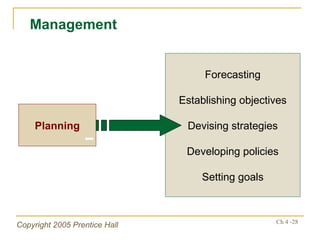
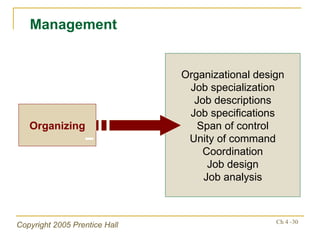
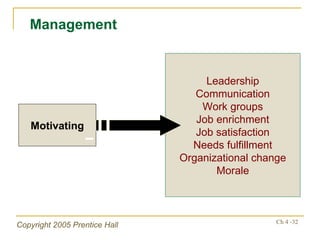
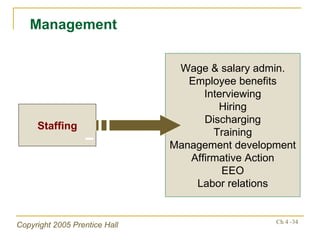
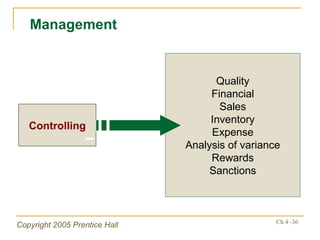
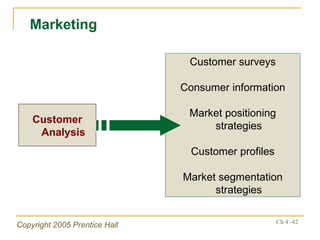
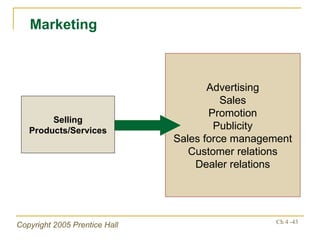
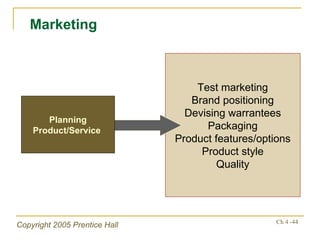
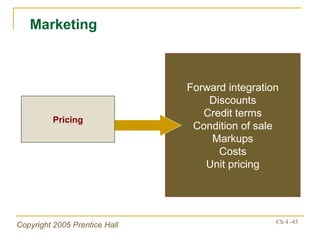
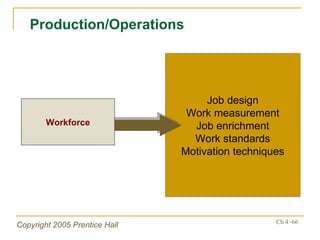
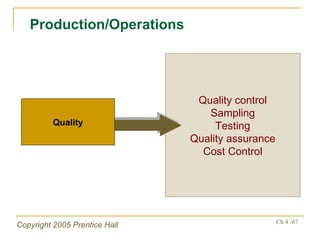
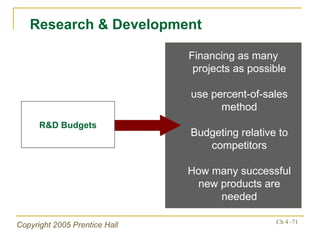
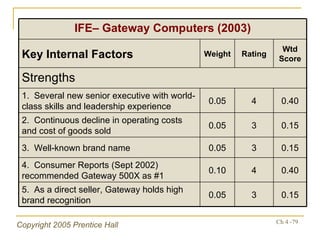
The document outlines key topics from Chapter 4 of a strategic management textbook, including:
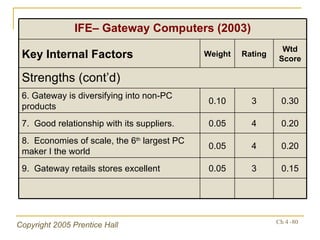
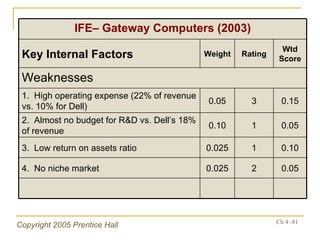
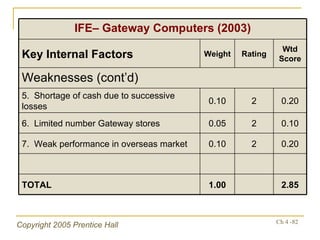
- The internal audit process examines functional business areas to understand strengths and weaknesses
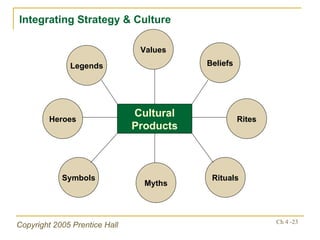
- Culture and strategy must be integrated, as culture can inhibit strategic changes if not aligned
- Resource-based view argues that internal resources are more important than external factors for competitive advantage
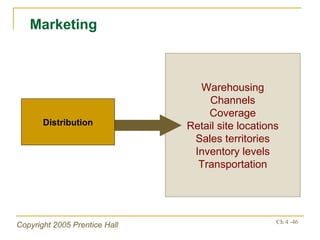
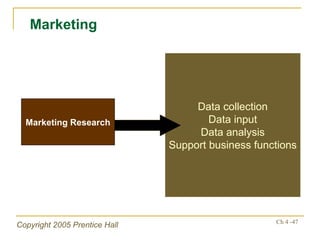
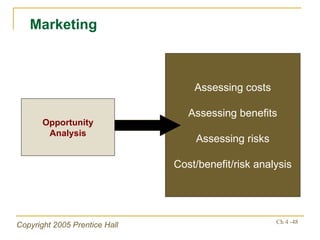
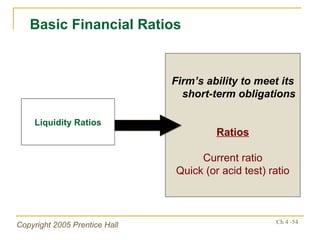
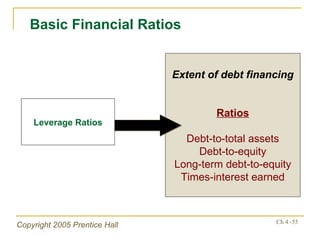
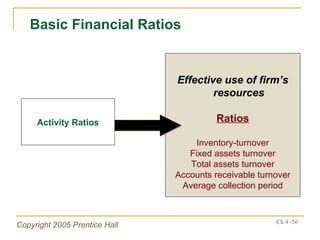
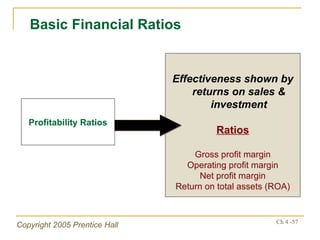
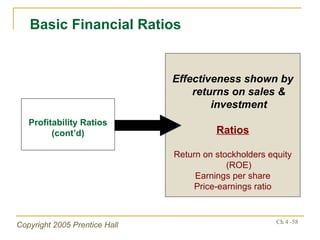
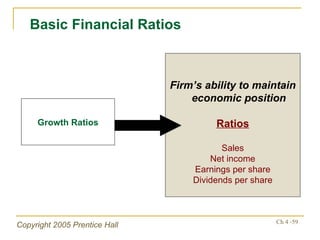
- Financial ratios and other metrics are used to evaluate performance across marketing, production, R&D, and other functions