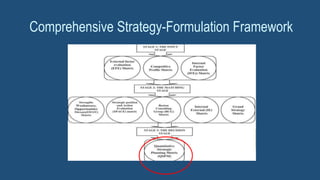
This document discusses Quantitative Strategic Planning Matrix (QSPM), a high-level strategic management approach for evaluating alternative strategies. It describes QSPM as falling within the third stage of strategic formulation, which involves comparing strategies. The document outlines the steps to develop a QSPM, including identifying strategic factors, formulating strategies, assigning weights and attractiveness scores, and calculating total scores to determine the most attractive strategy. It also notes limitations and advantages of the QSPM approach.