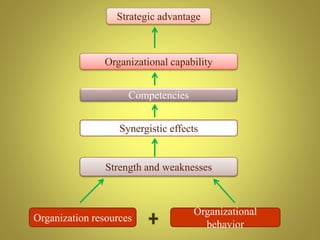
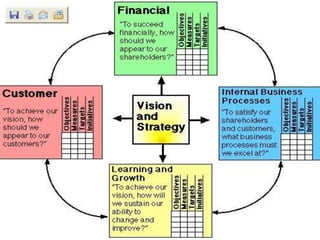
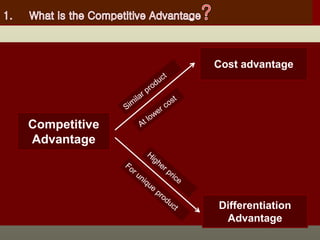
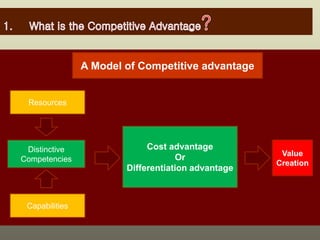
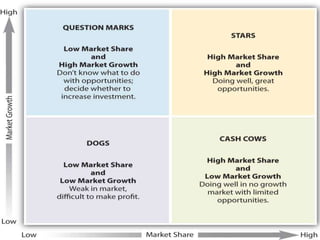
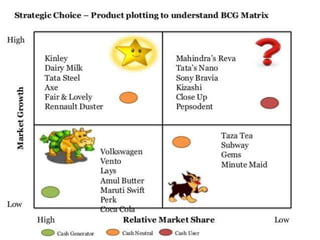
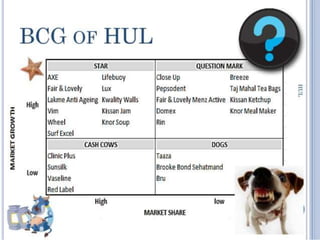
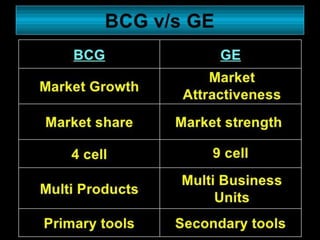
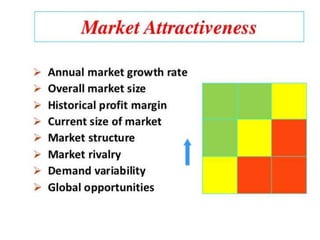
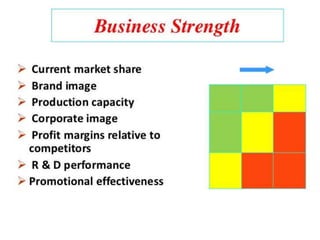
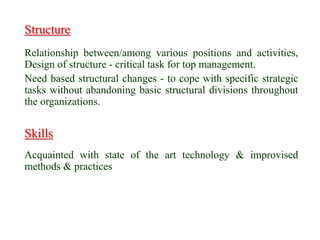
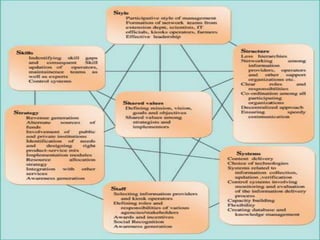
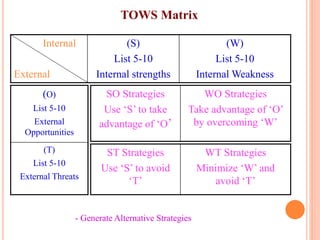
The document outlines the organizational capability profile and strategic advantage framework, detailing the components of organizational strengths, weaknesses, resources, and behavior. It discusses various analytical methods such as SWOT, BCG matrix, GE matrix, and the McKinsey 7S framework for assessing and enhancing organizational performance. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of aligning internal capabilities with external market opportunities to achieve competitive advantage.