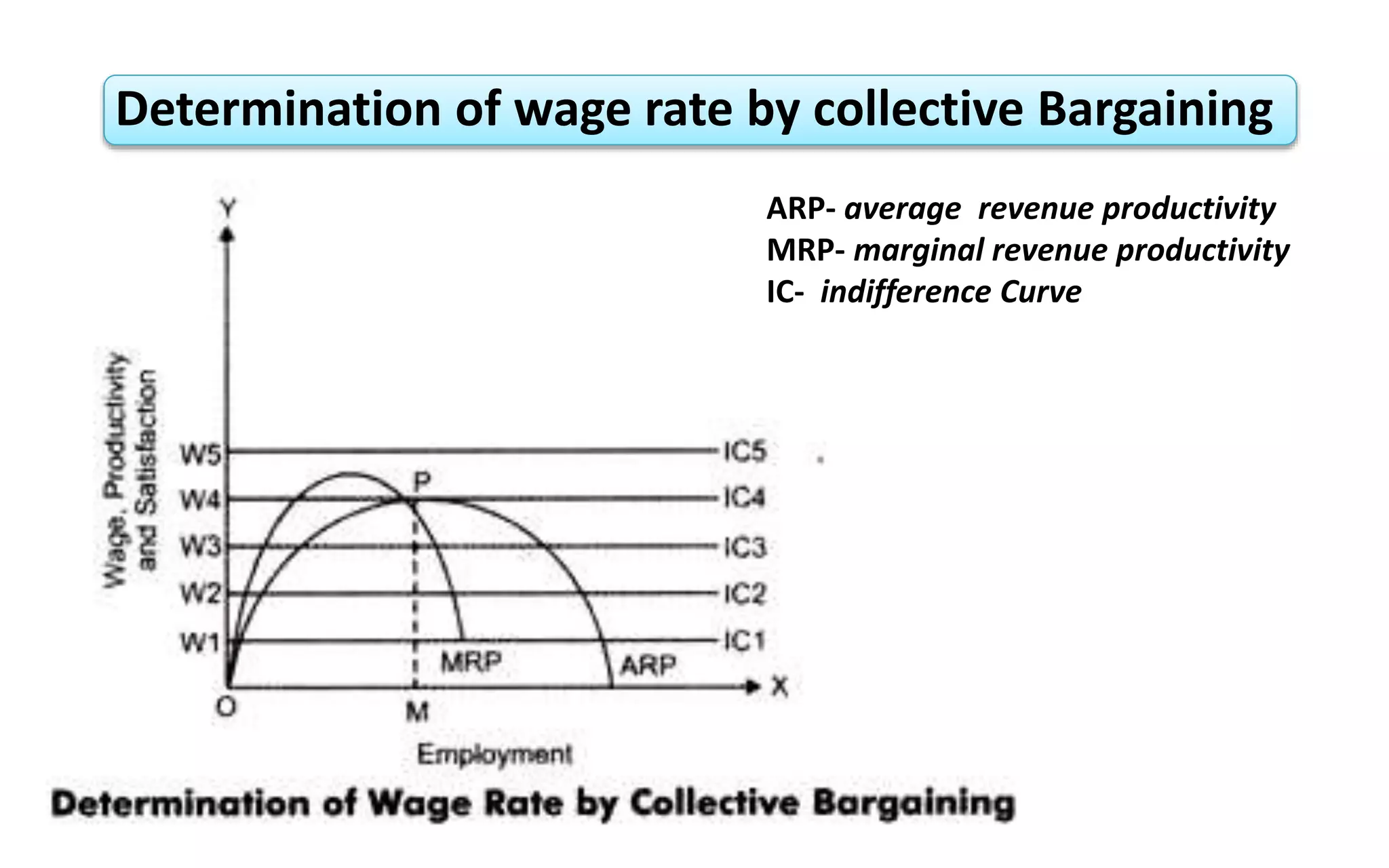
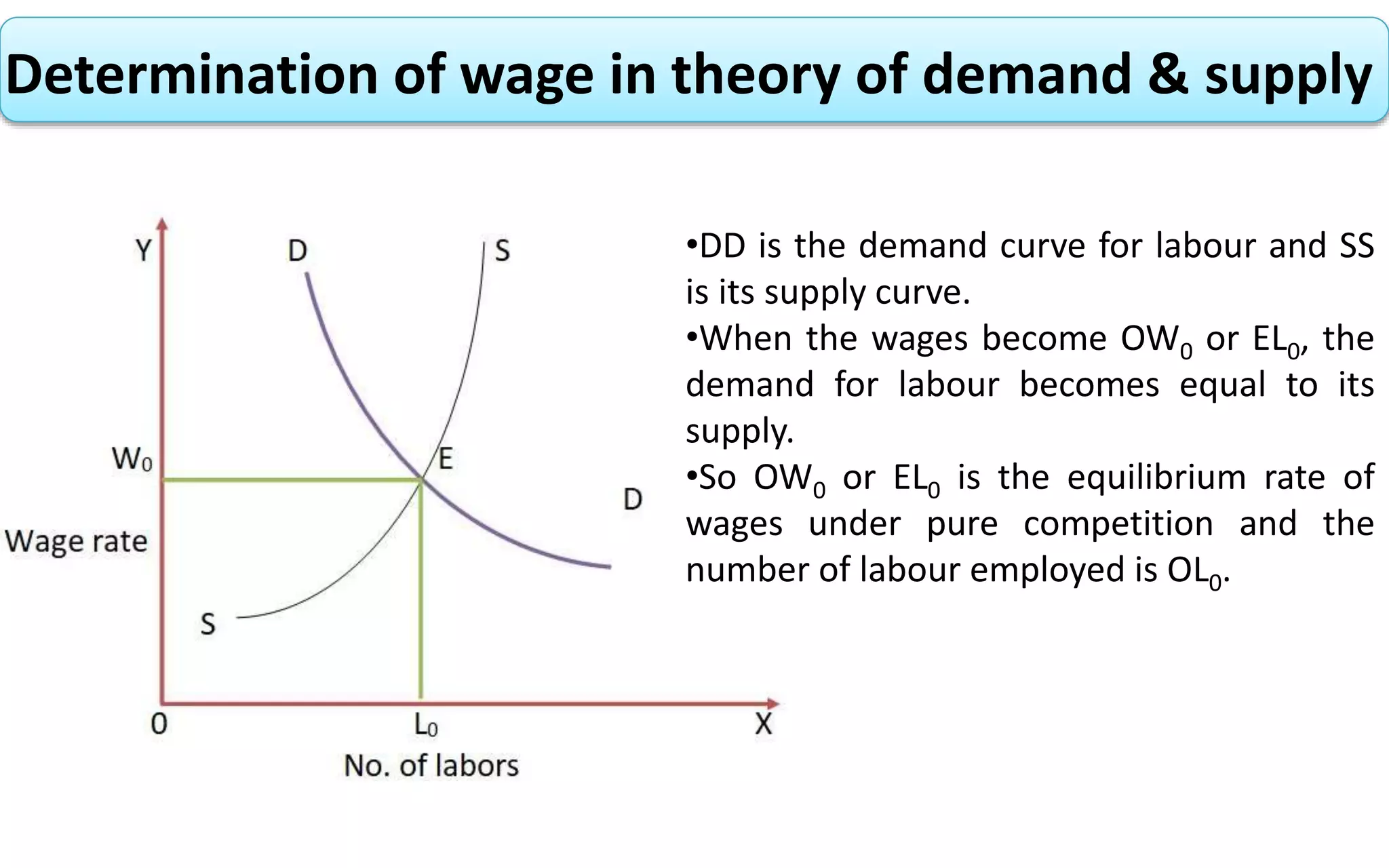
The document presents an overview of wage determination theories, classifying them into classical, neo-classical, and modern categories. It highlights the role of collective bargaining by trade unions in negotiating wages, the impact of labor supply and demand on wage rates, and describes how trade unions seek to enhance wage levels through various means. Additionally, it explains the equilibrium rate of wages based on the interplay between labor demand and supply.