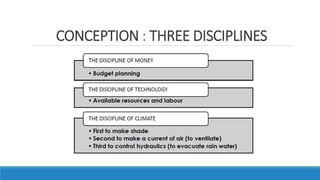
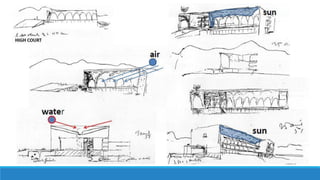
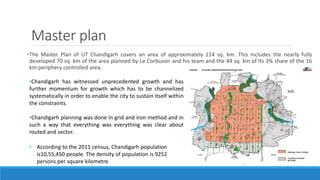
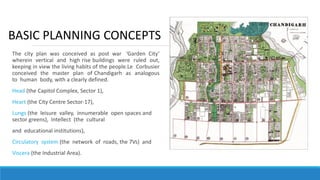
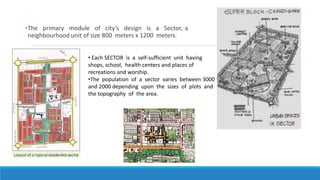
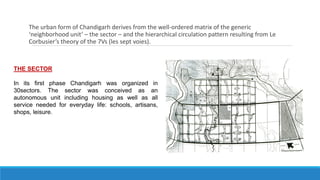
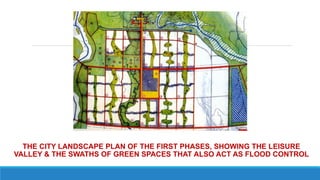
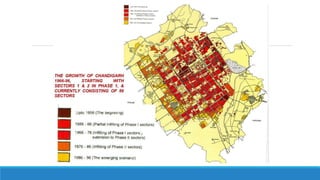
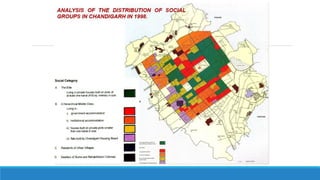
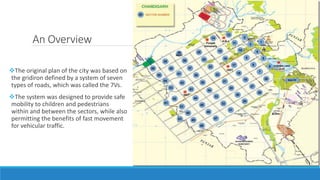
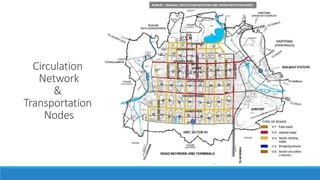
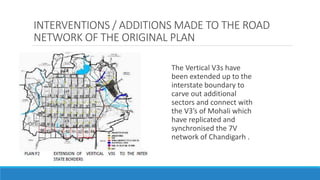
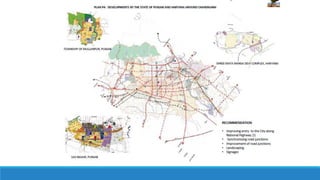
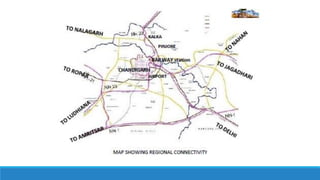
Chandigarh was established as the new capital of the Indian states of Punjab and Haryana after partition. [1] Le Corbusier was commissioned to design the master plan for Chandigarh based on modernist planning principles. [2] He organized the city into sectors with open green spaces, prioritizing pedestrian mobility over vehicles. [3] Key features include the Capitol Complex with important buildings separated by plazas, and the city center in Sector 17.