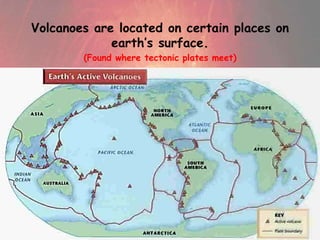
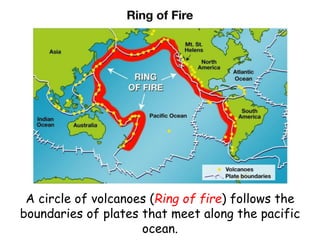
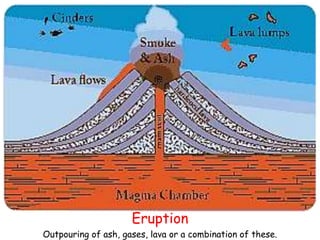
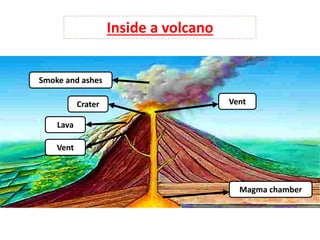
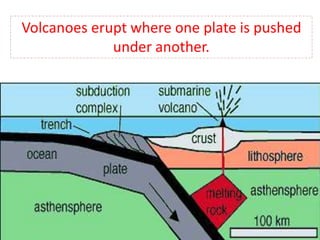
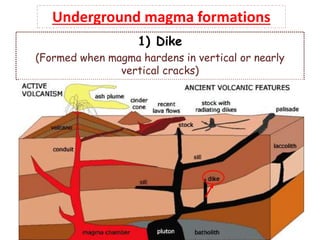
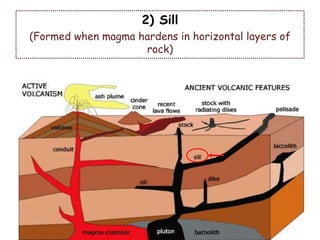
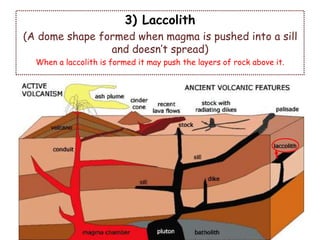
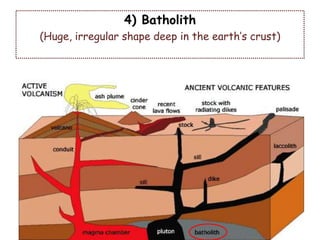
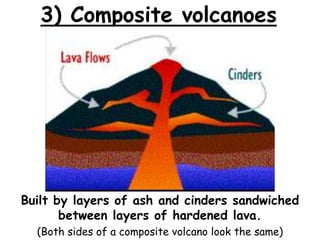
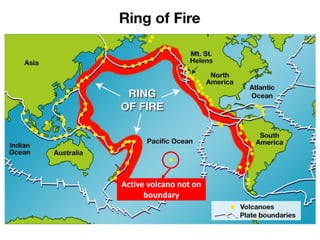
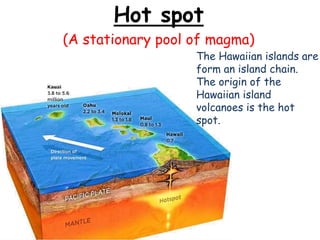
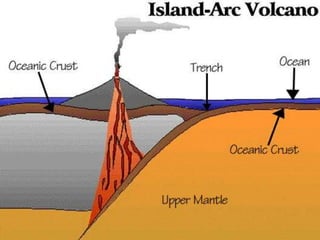
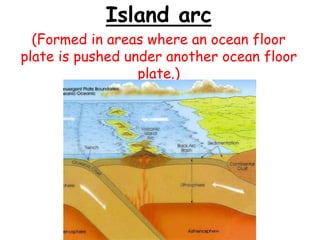
Volcanoes form at boundaries where tectonic plates meet underwater or on land. Eruptions occur when magma travels up from the mantle through the crust and vents on the surface, emitting lava, ash, gases or a combination. Different types of volcanoes include shield volcanoes which erupt fluid lava over large areas, cinder cone volcanoes which throw chunks of hardened lava into the air, and composite volcanoes which build up layers of ash and lava. Volcanoes shape the land by emitting new rock and changing landscapes over thousands of years through eruptions.