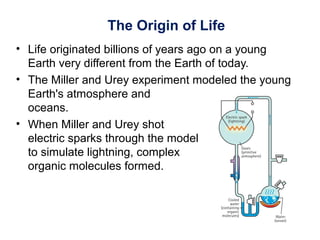
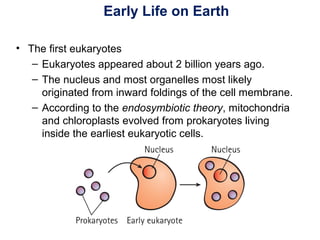
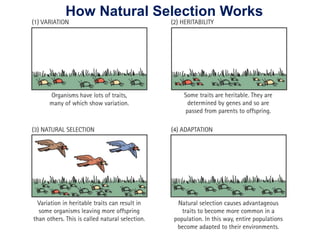
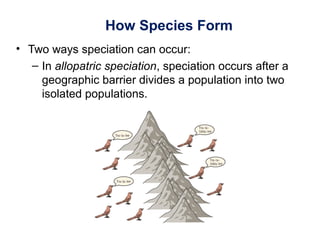
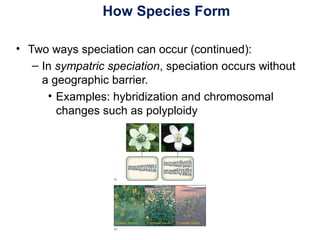
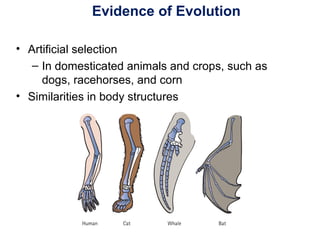
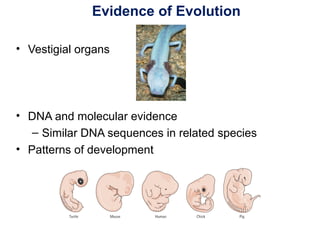
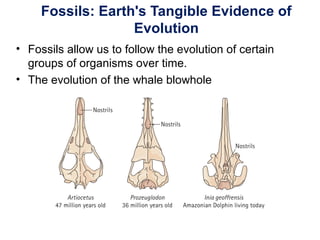
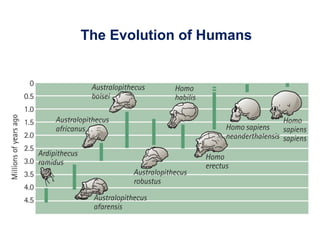
The document outlines the evolution of life, addressing key topics such as the origin of life on Earth, evidence of evolution, and natural selection, while also discussing the evolution of humans and antibiotic-resistant bacteria. It covers the transition from early prokaryotic life through the evolution of eukaryotes, Darwin's theory of natural selection, and various reproductive barriers in species formation. Additionally, it provides historical examples like the peppered moth and emphasizes the importance of responsible antibiotic use to combat resistance.