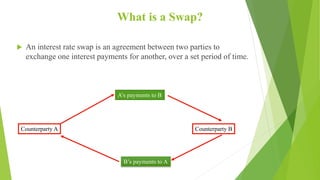
An interest rate swap is an agreement between two parties to exchange interest payments, typically with one party paying a fixed rate and the other a floating rate. There are four main types of swaps: interest rate swaps, currency swaps, cross-currency swaps, and credit default swaps. Swaps are used for portfolio management, speculation, corporate finance, risk management, and setting rates for bond issuances. The primary risks of interest rate swaps are interest rate risk and credit risk.