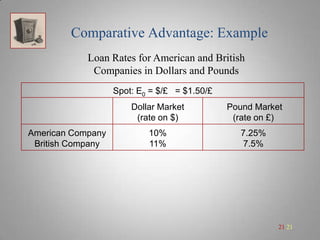
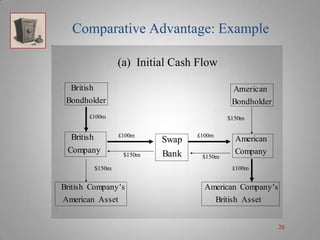
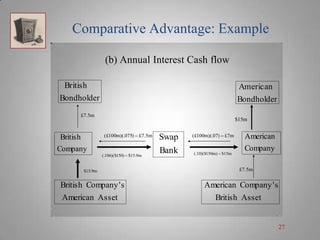
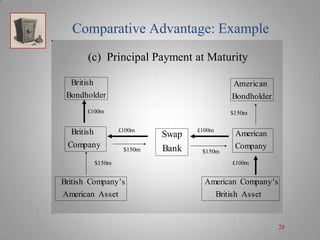
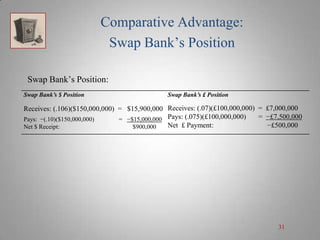
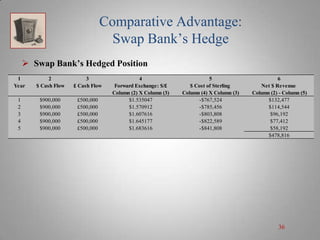
A currency swap allows two companies to exchange loans denominated in different currencies to better meet their financing needs. In the example, a British company borrows dollars and an American company borrows pounds through a swap bank. This allows each to access comparatively better interest rates in the other's local market. The swap bank profits by exploiting small differences in interest rates between the currencies over time. It can hedge its risk and lock in gains by entering forward currency contracts or money market positions. Overall, currency swaps allow companies and banks to benefit from comparative advantages in borrowing costs across currencies.