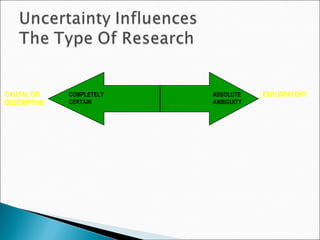
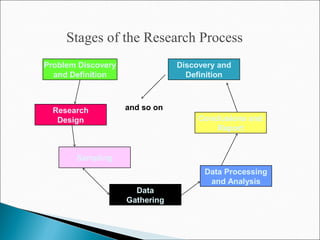
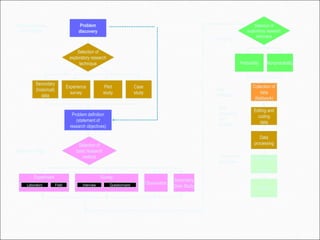
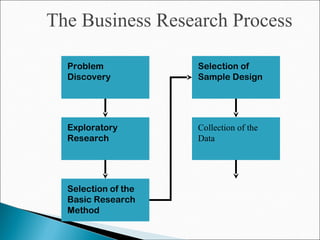
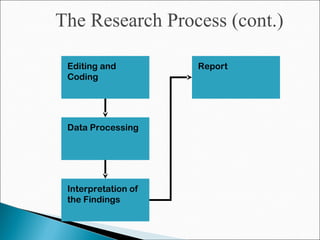
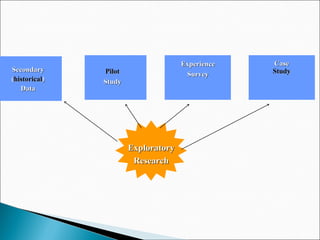
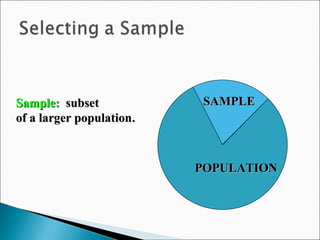
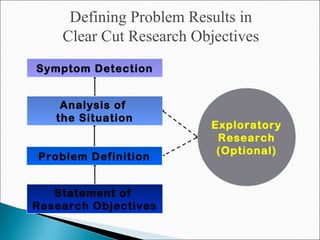
The chapter discusses the business research process, which includes 6 stages: 1) problem discovery and definition, where a business problem or opportunity is identified; 2) research design, developing a framework for investigating the problem; 3) sampling, determining who and how many people to study; 4) data gathering using methods like surveys and experiments; 5) data processing and analysis; and 6) conclusions and reporting of findings. The process is cyclical as conclusions can lead to new problems to study.