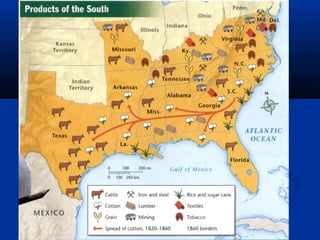
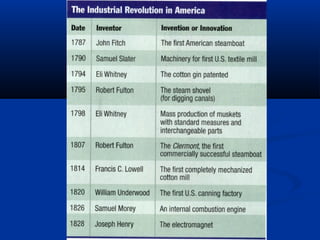
The document discusses the Industrial Revolution and how it transformed the economies of the North and South in the United States during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. The Industrial Revolution saw the rise of factories and mechanized production in the North, while the South's economy remained based on plantation agriculture and slavery. Inventions like the cotton gin further entrenched the South's reliance on the institution of slavery. Figures like Henry Clay promoted the American System to help unify the country's diverging regional economies through internal improvements, tariffs, and a national bank.