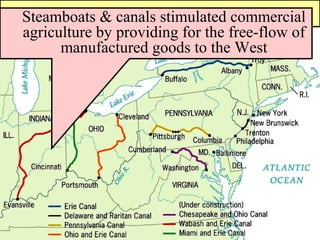
In the 1840s, improved transportation such as steamboats, canals, and the beginning of railroads connected different regions of the US and facilitated the growth of a national market economy. Inventions in agriculture like the cotton gin and mechanical reaper increased productivity on large commercial farms in the South and West. The North specialized in manufacturing to supply the growing agricultural sectors, leading to urbanization and the rise of early factories like the Lowell Mills. However, the US economy remained regionally specialized, with the North industrializing, the South growing cotton, and the West producing wheat and other crops.