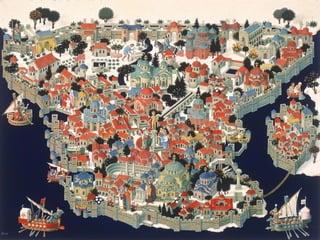
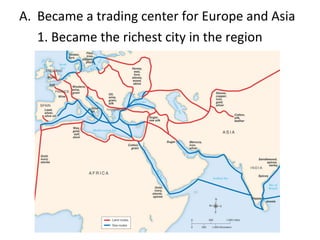
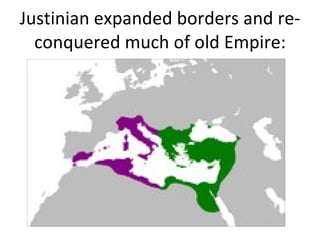
The document summarizes key aspects of the Byzantine Empire and Eastern Orthodox Church. It describes Constantinople as the wealthy capital city with advanced infrastructure. Emperor Justinian rebuilt the city after a rebellion and established new laws and expanded the empire's borders. The Eastern Orthodox Church was the dominant religion and viewed the emperor as both religious and political leader, in contrast to the growing power of the Pope in the Western Church, leading to a final split between the two in 1054.