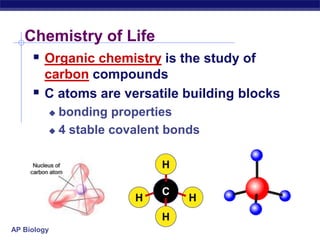
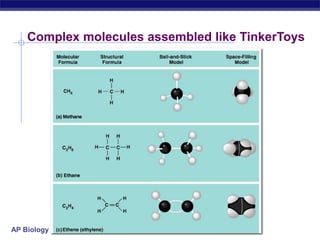
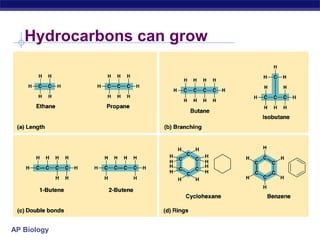
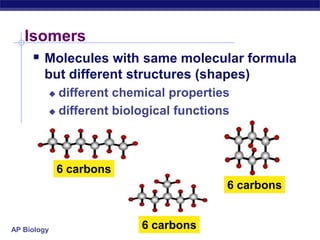
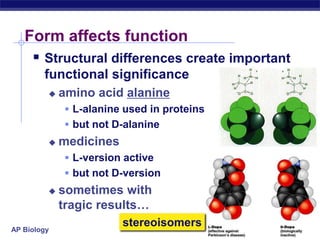
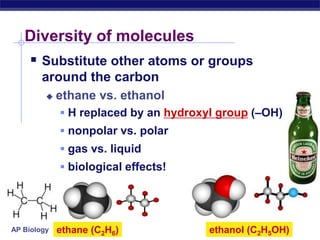
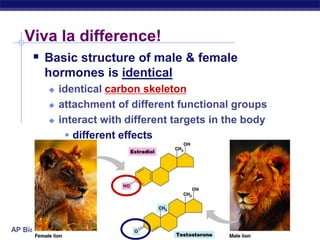
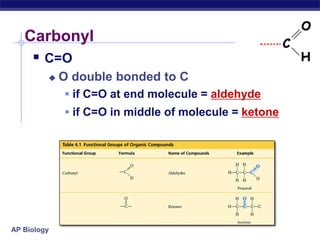
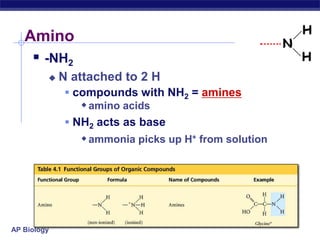
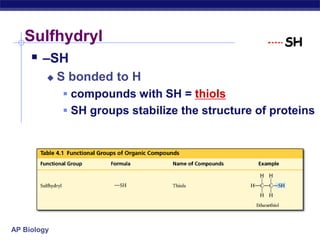
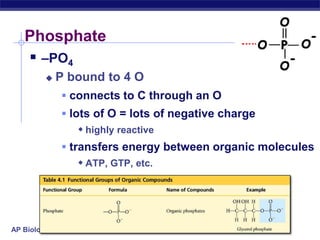
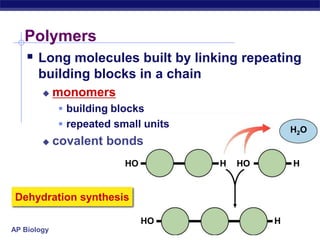
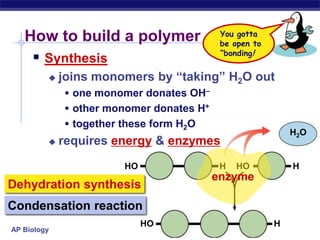
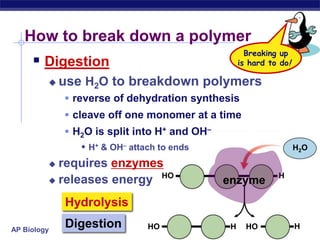
The document summarizes key points about carbon chemistry and its importance in life. It notes that all of life is built on carbon, with cells composed of around 72% water and 25% carbon compounds like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Organic chemistry studies carbon compounds, which are versatile building blocks that can form complex molecules through bonding. These molecules include hydrocarbons, isomers with different structures and properties, and functional groups that influence reactivity and solubility. Macromolecules like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids are formed from smaller organic molecules linking together in polymers through dehydration synthesis.