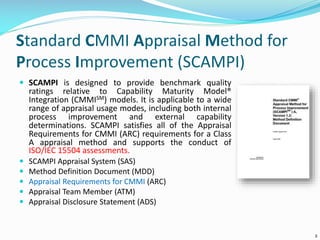
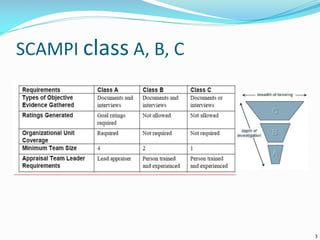
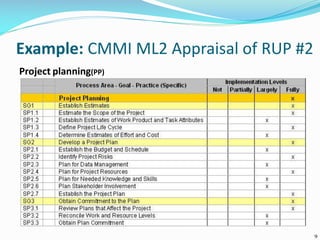
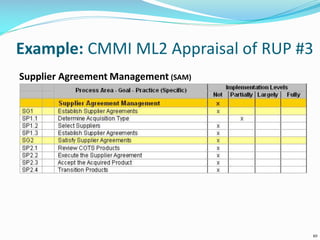
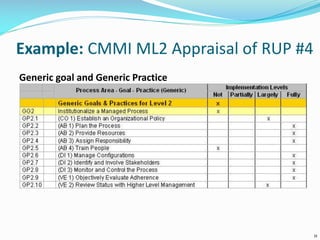
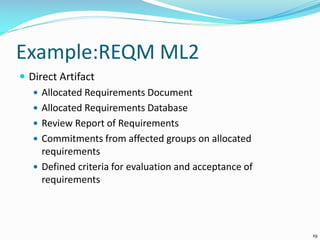
The document discusses the Standard CMMI Appraisal Method for Process Improvement (SCAMPI). SCAMPI is designed to provide benchmark quality ratings relative to the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) and satisfies requirements for a Class A appraisal method. The document provides examples of using SCAMPI to conduct appraisals at Maturity Level 2, including rating process attributes, examples assessing process areas, and scoring. Key practices and artifacts considered for requirements management are also outlined.