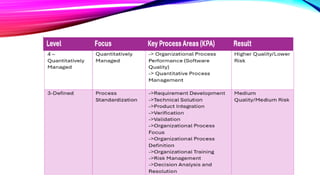
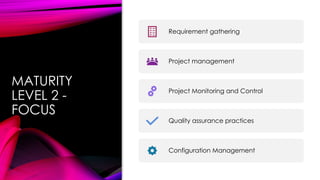
The document outlines the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) for development, detailing various modules on its implementation, appraisal assessments, and process improvement. It emphasizes the advantages of CMMI, such as enhanced quality and efficiency, and discusses specific and generic goals for effectively managing process areas. It includes essential work products for CMMI Level 2, spanning requirements management to configuration management, underscoring the need for structured processes and documentation to support organizational capability enhancement.