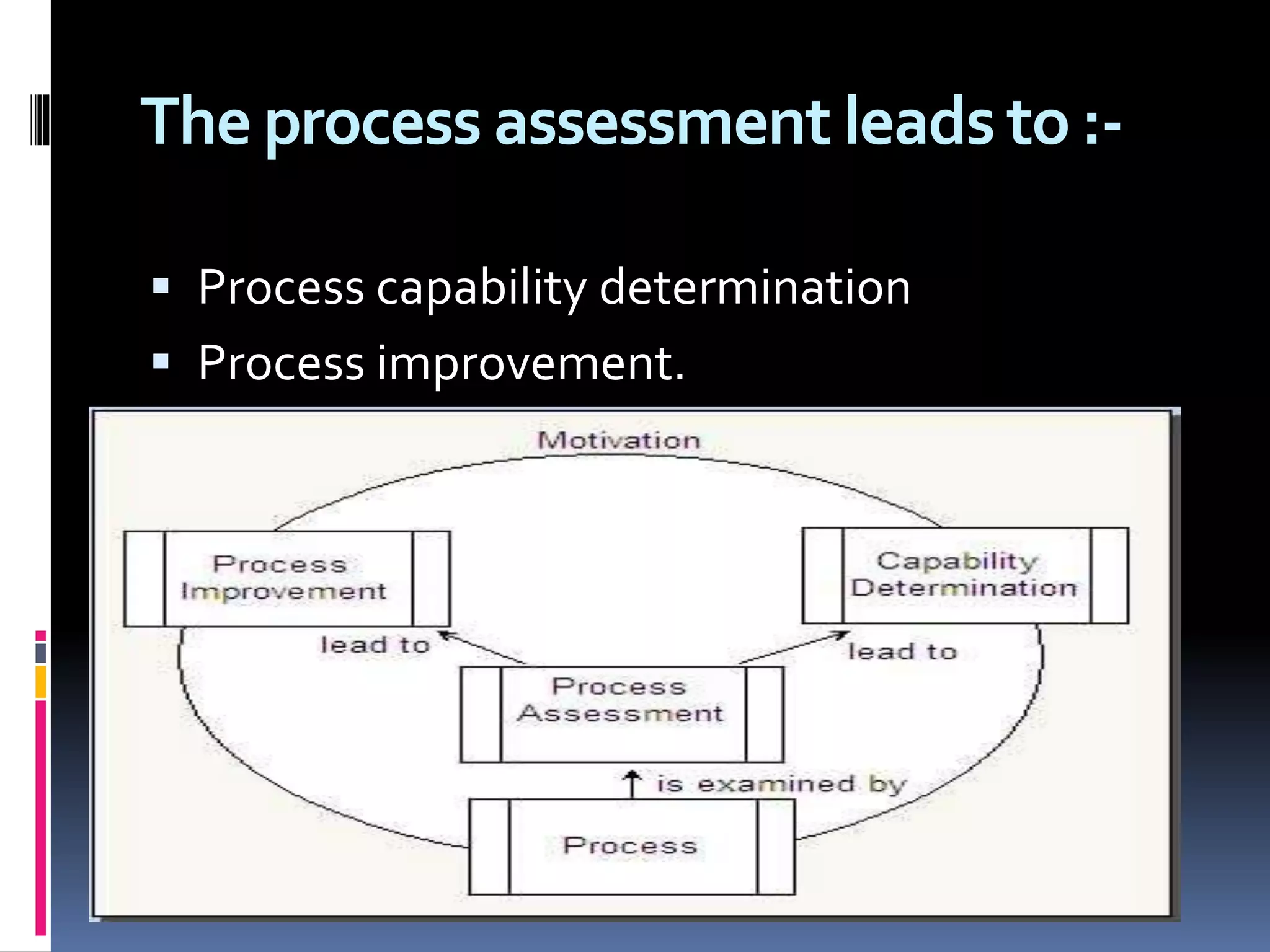
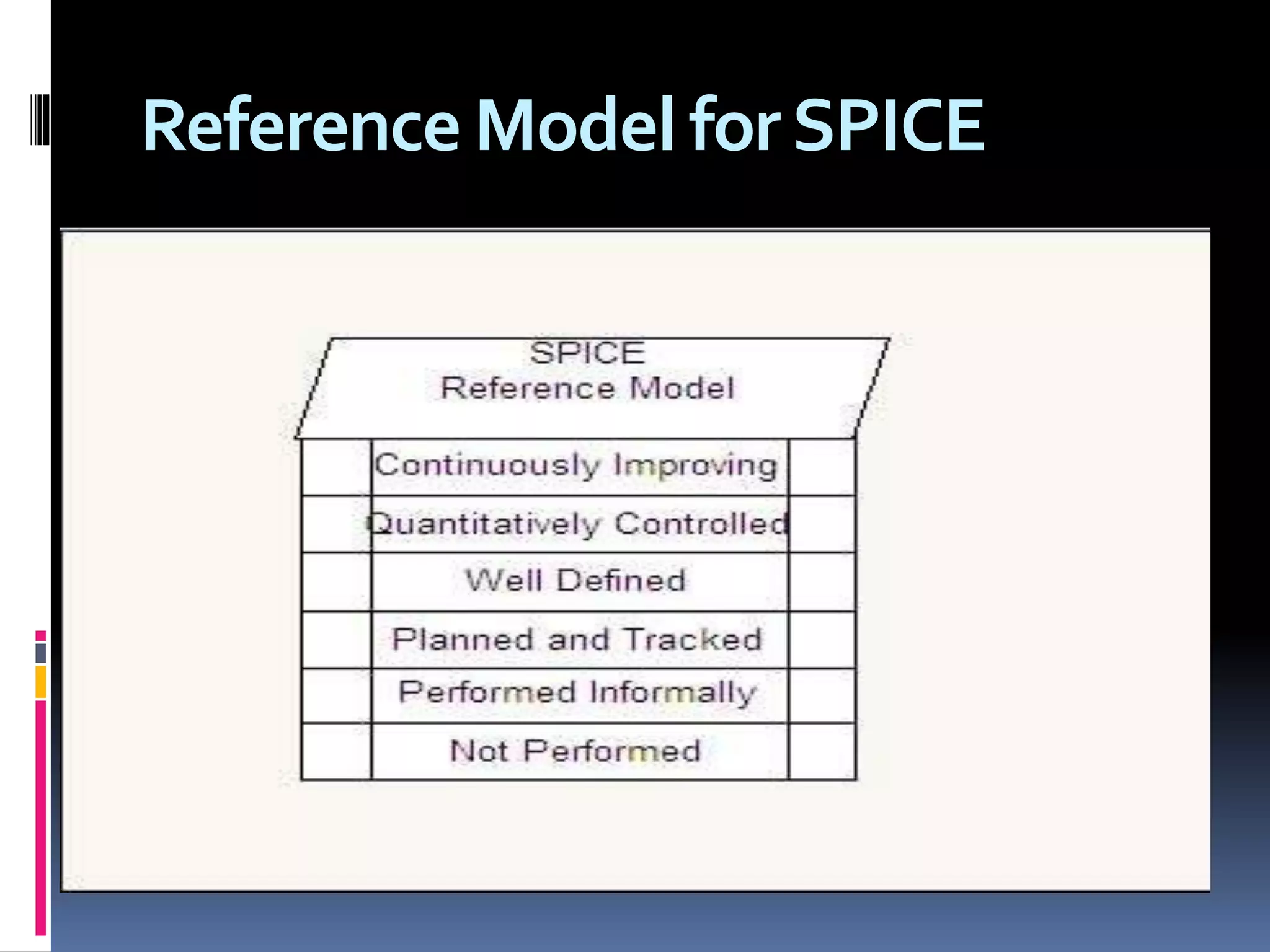
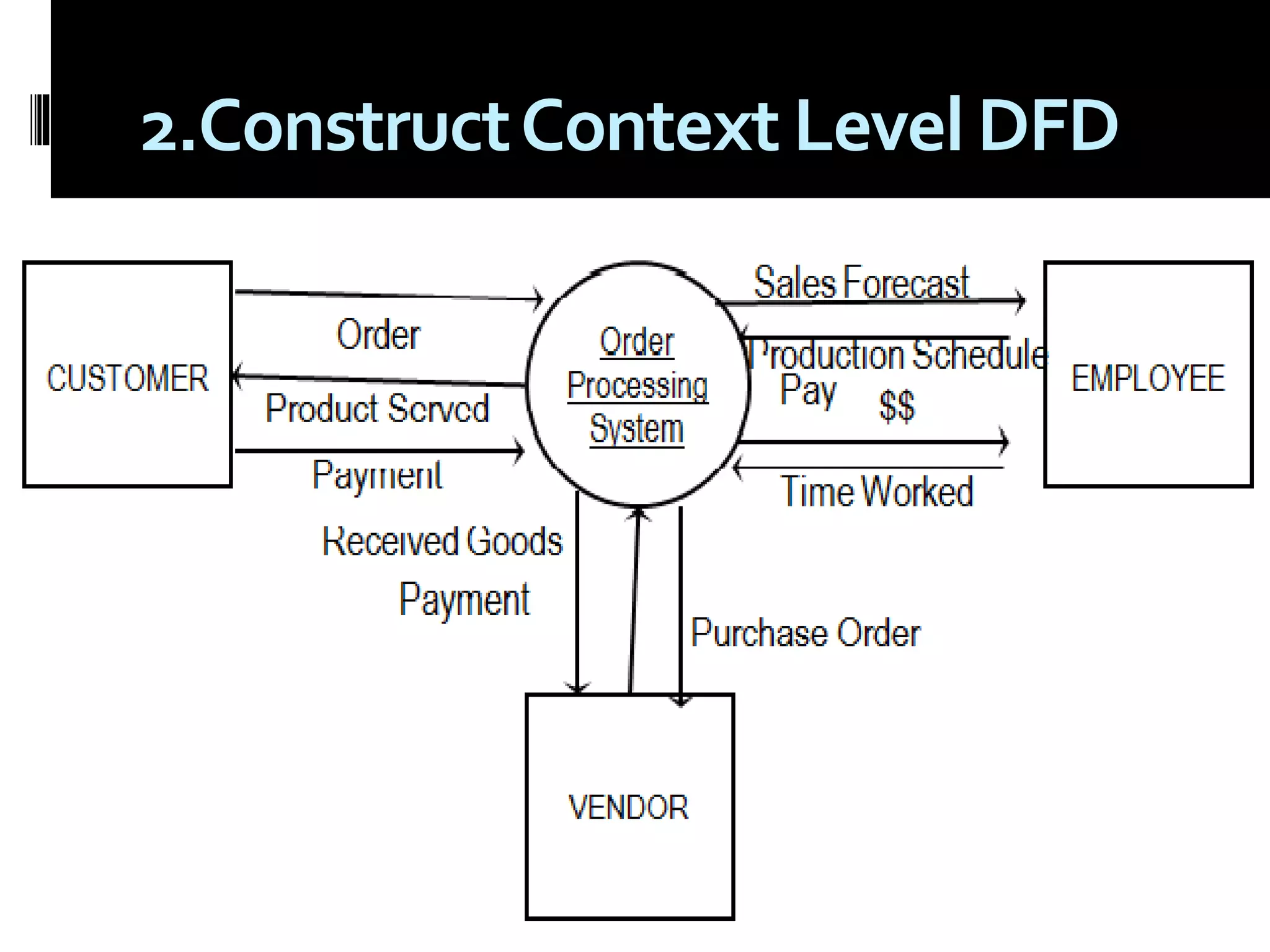
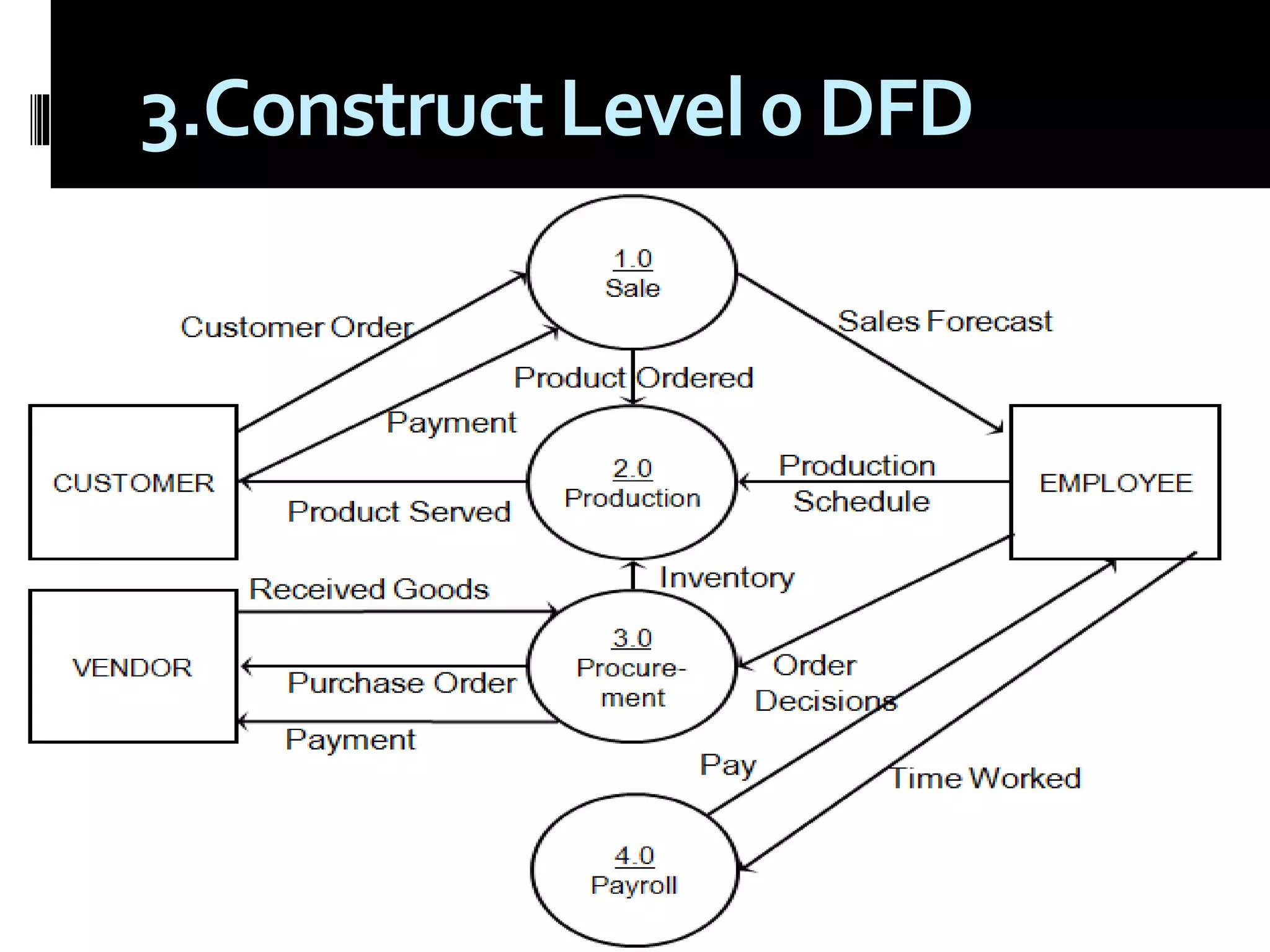
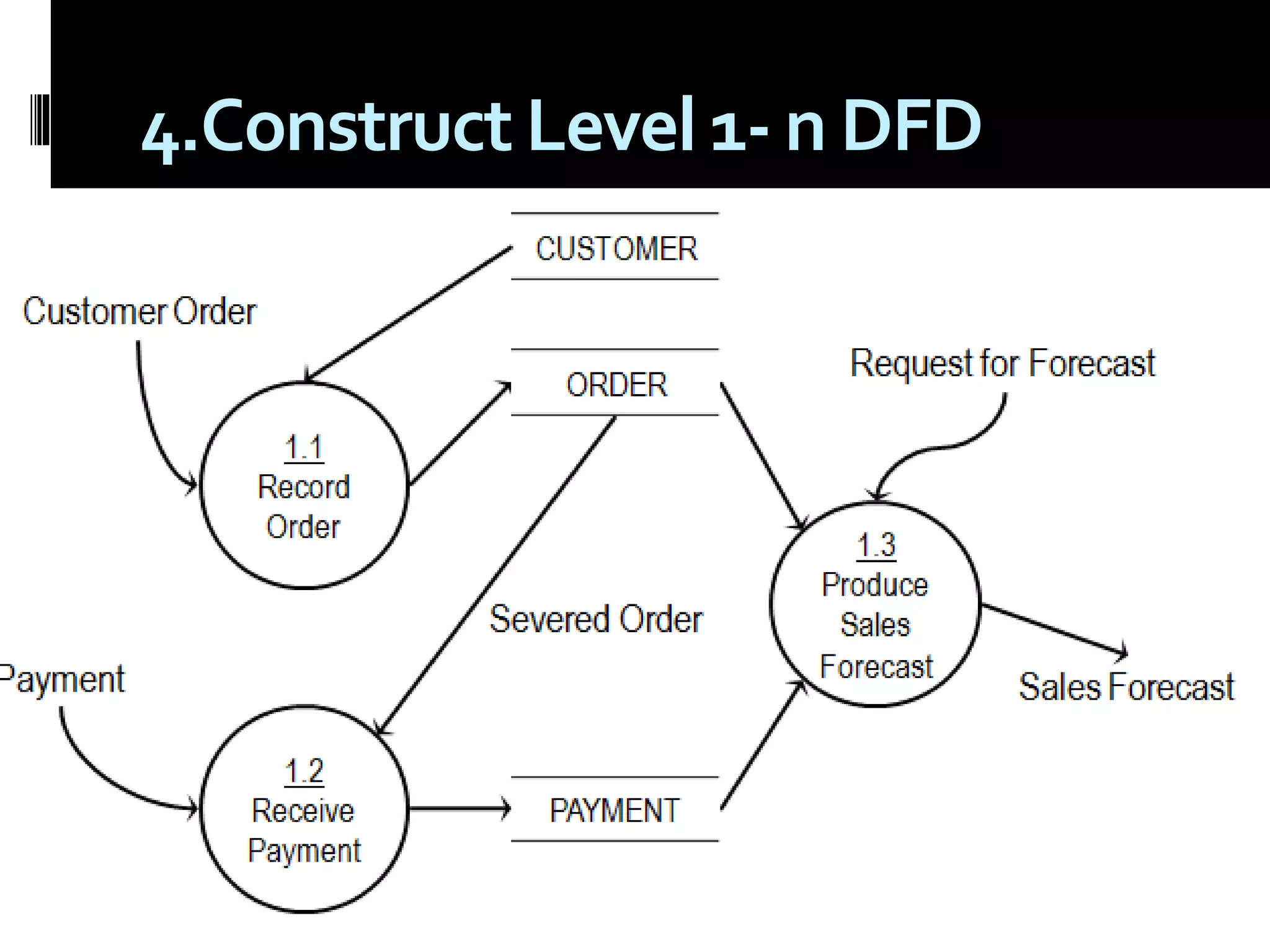
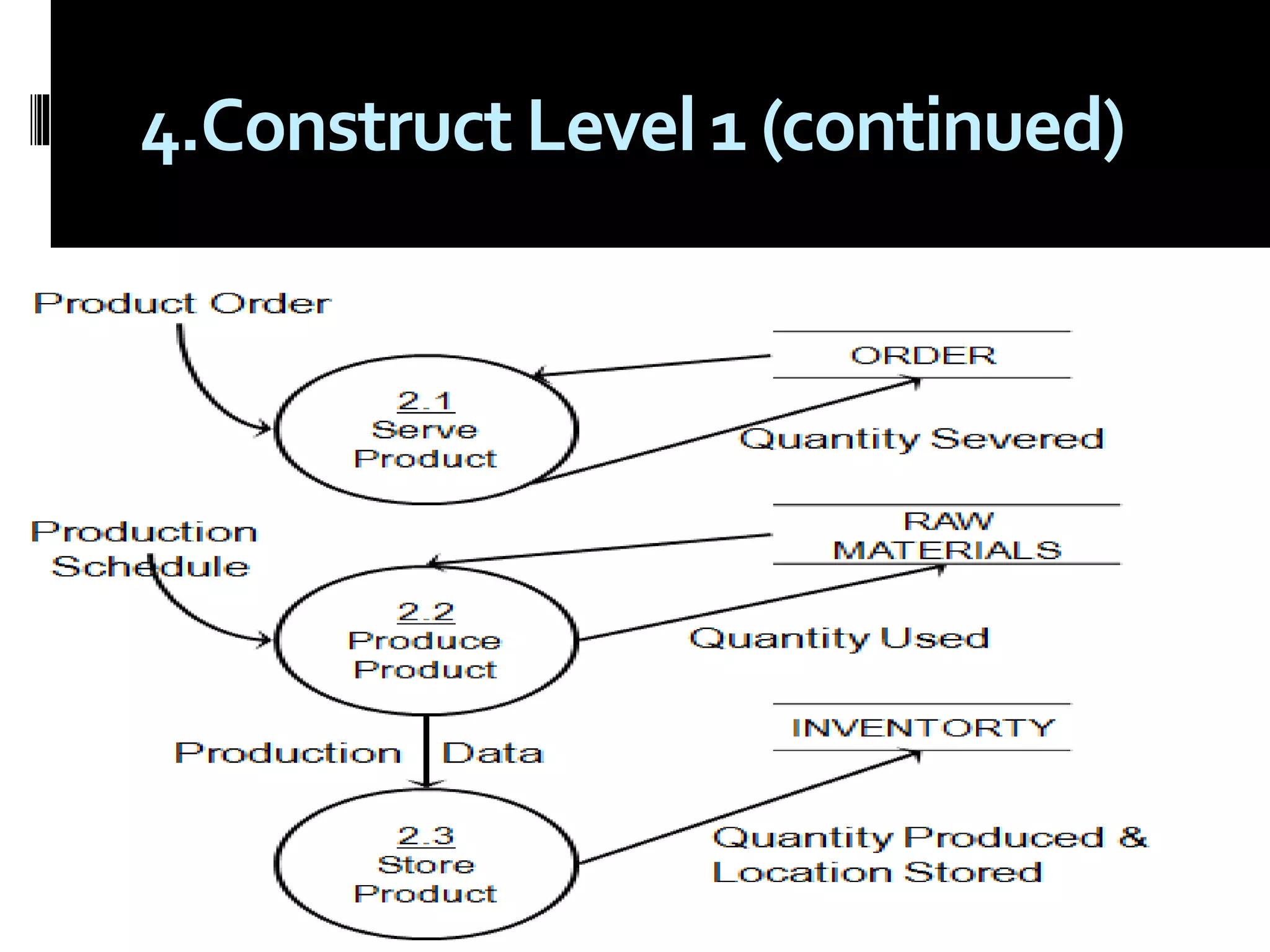
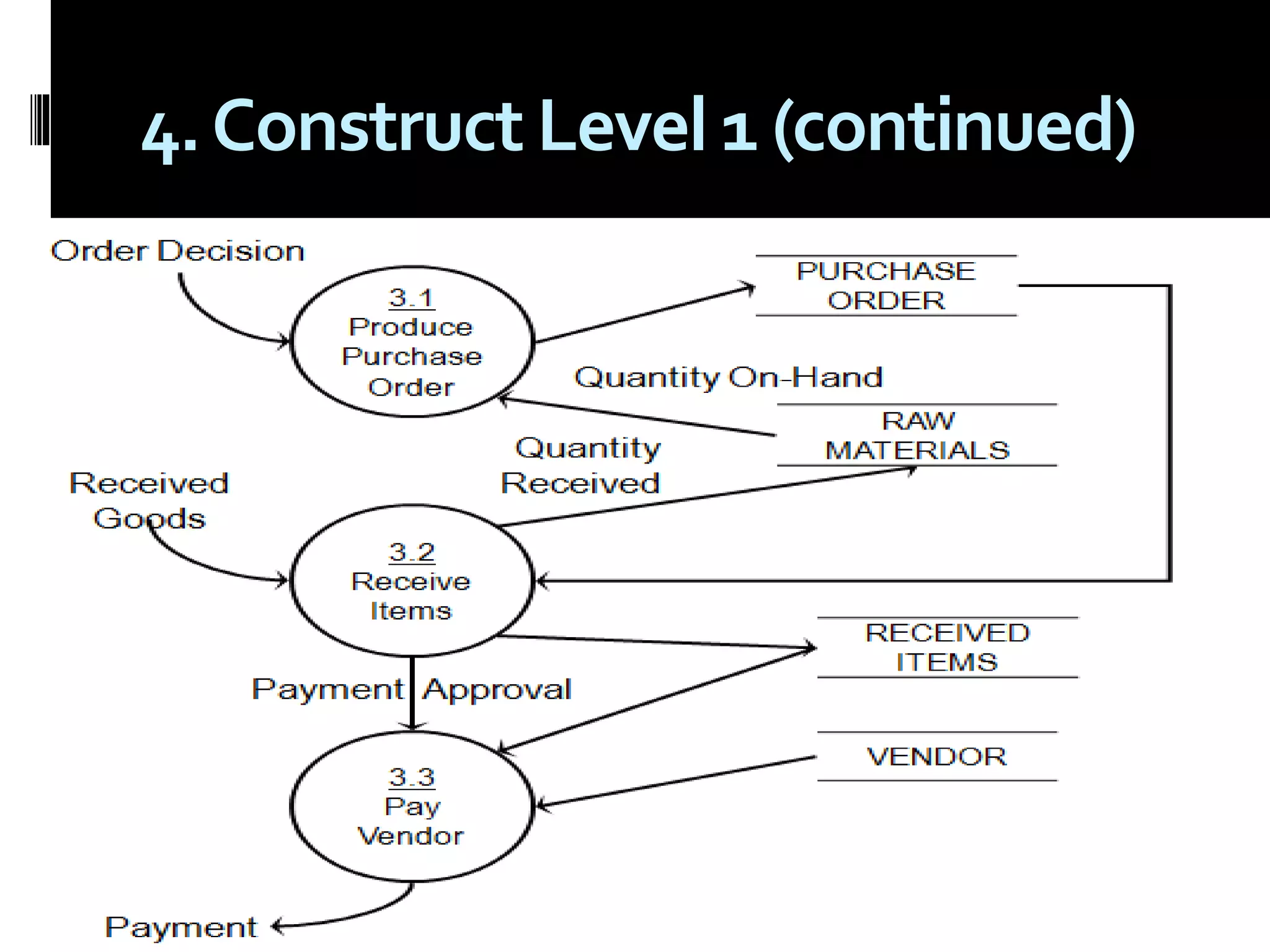
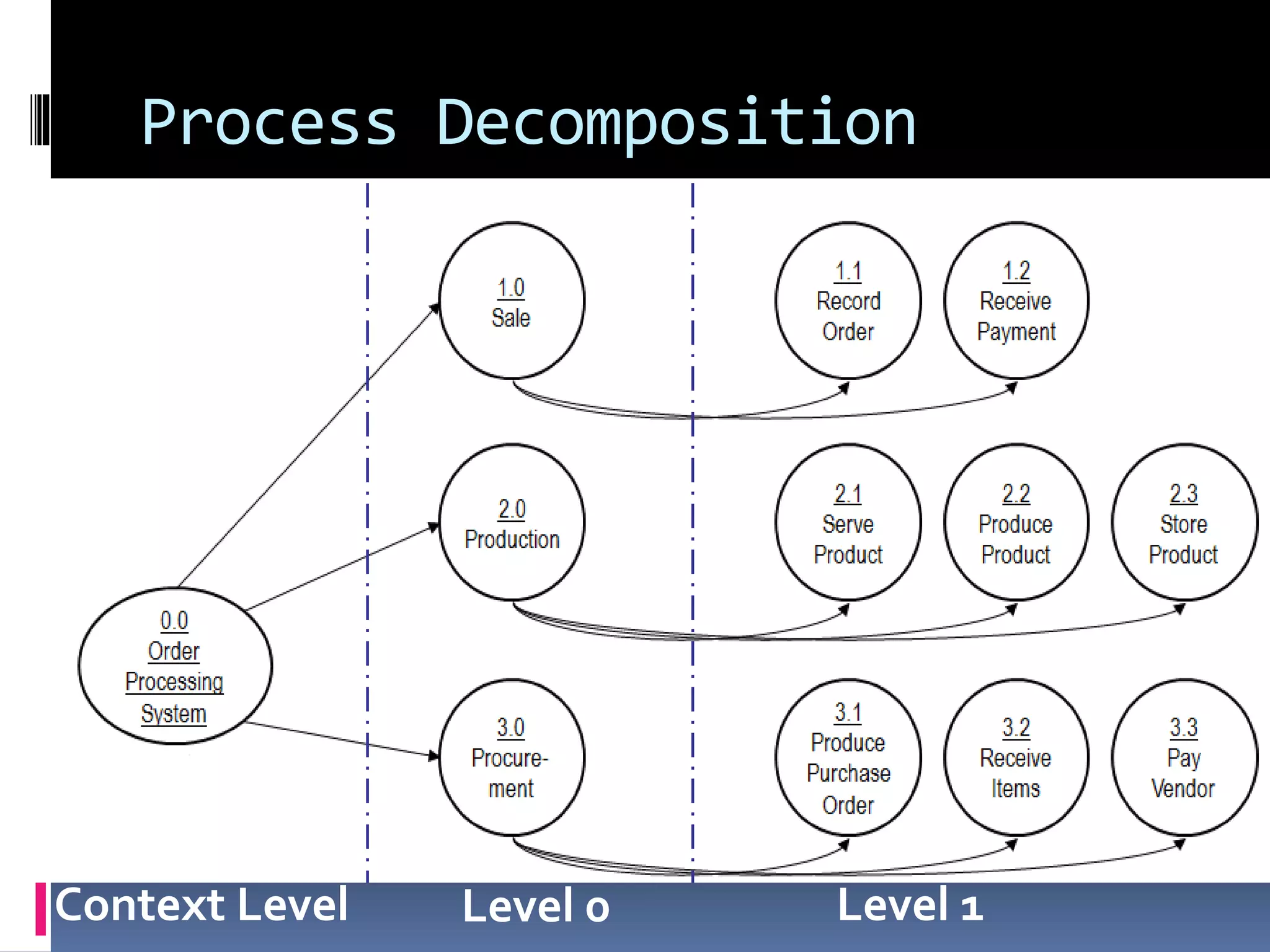
The document discusses process assessment and data flow diagrams. It defines processes and explains that process assessment examines whether software processes are effective and efficient. It outlines different approaches to process assessment including SPICE, ISO 9001:2000, CMMI, and CBA-IPI. Process patterns represent activities in a software development lifecycle. Data flow diagrams graphically show how data moves through a system and can be constructed at different levels of detail. An example creates a data flow diagram for an order processing system.