This document discusses software engineering and quality assurance. It begins by outlining the uniqueness of software quality assurance and the different environments for which SQA methods are developed.
It then provides an example of a failed software implementation at the Denver International Airport in 1995. The new airport's opening was delayed by 16 months due to failures in their software-based baggage handling system, costing $2 billion.
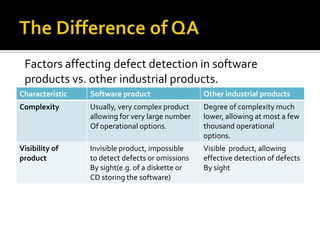
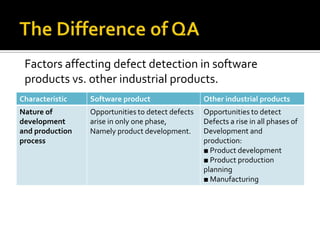
The document identifies three main differences between ensuring quality in software products versus other industrial products: 1) Software is usually more complex with more operational modes; 2) Software is invisible so defects are not easily detectable; 3) Opportunities to detect defects in software are limited to the development phase, unlike other products which have