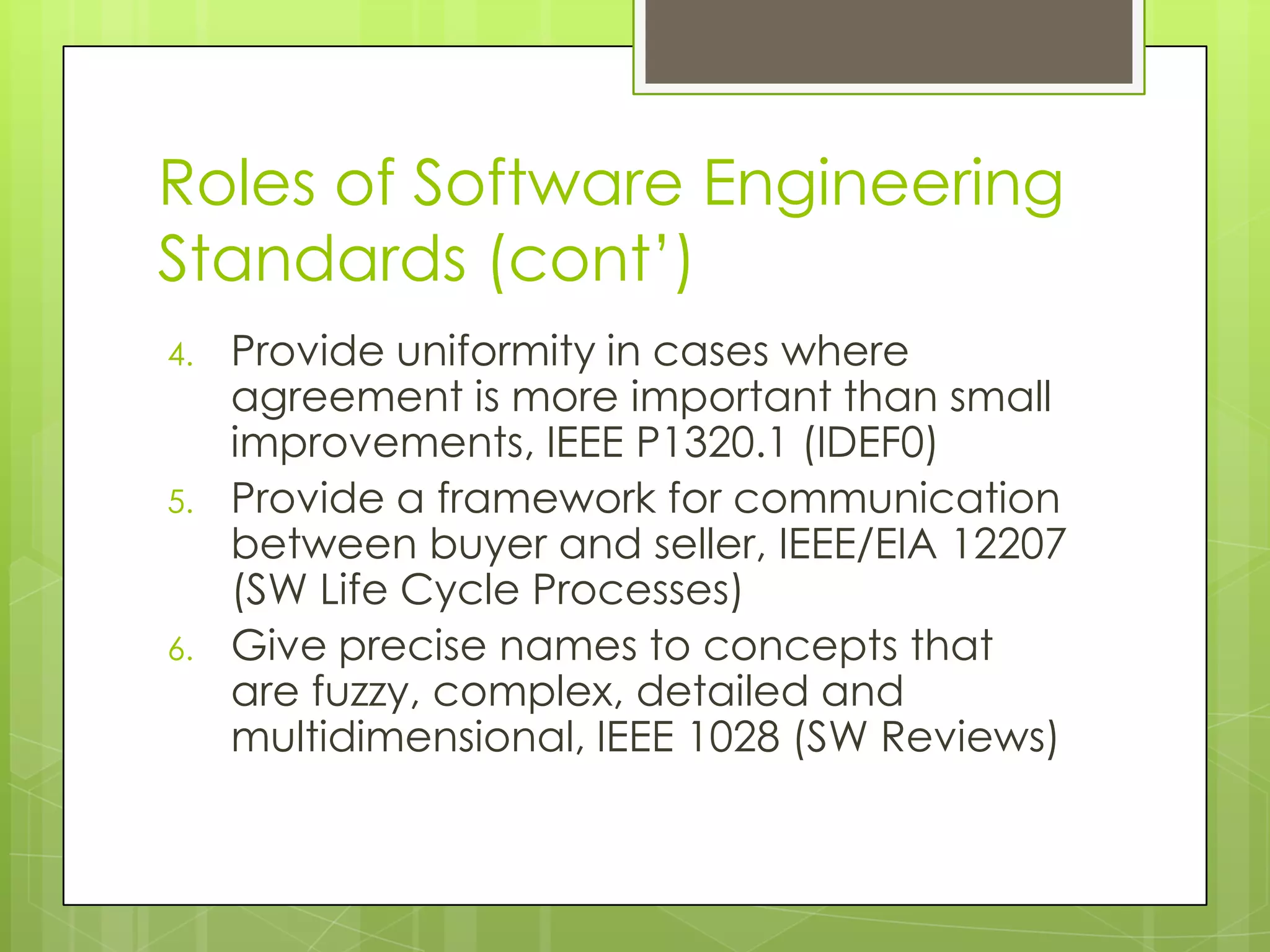
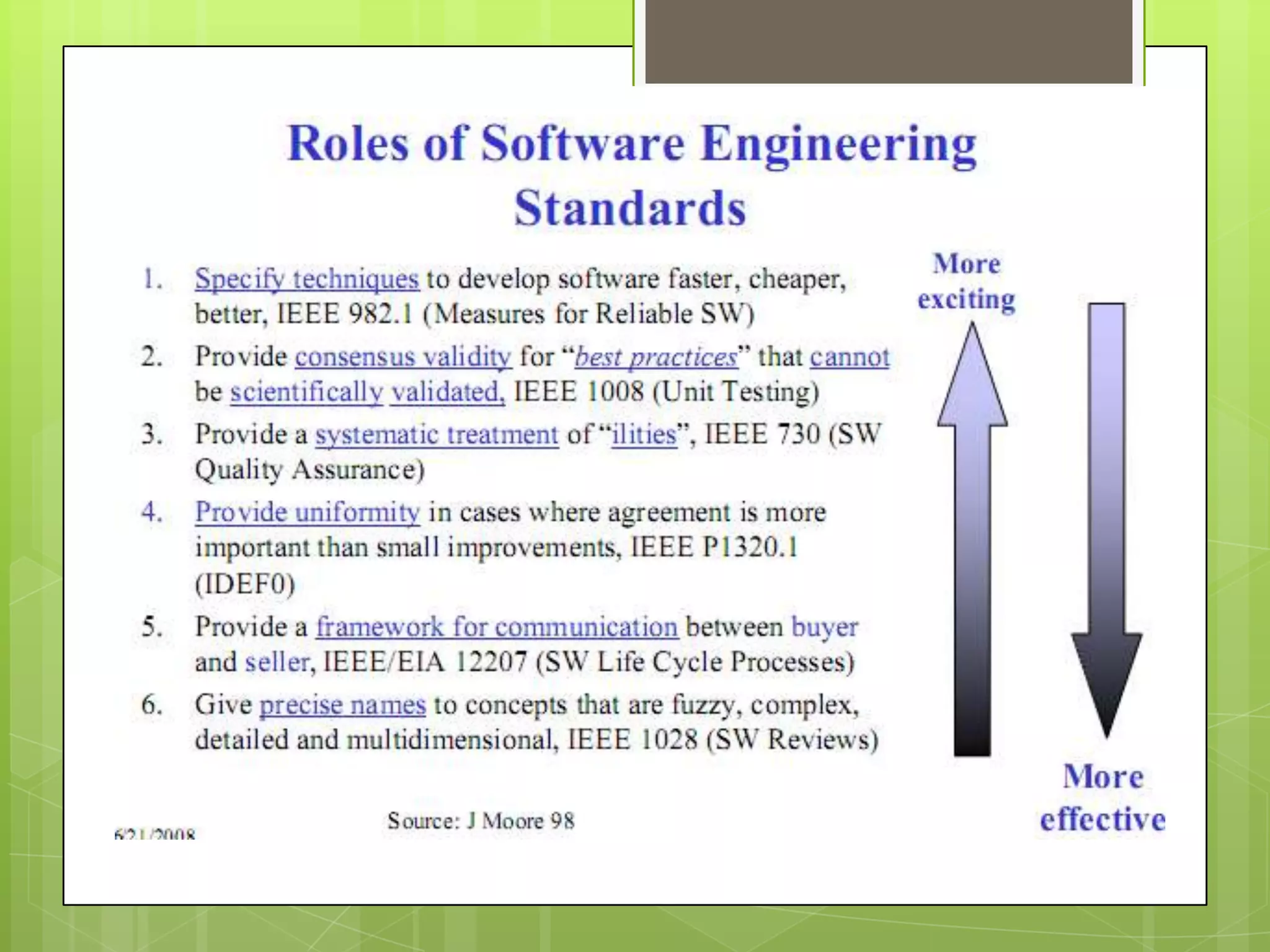
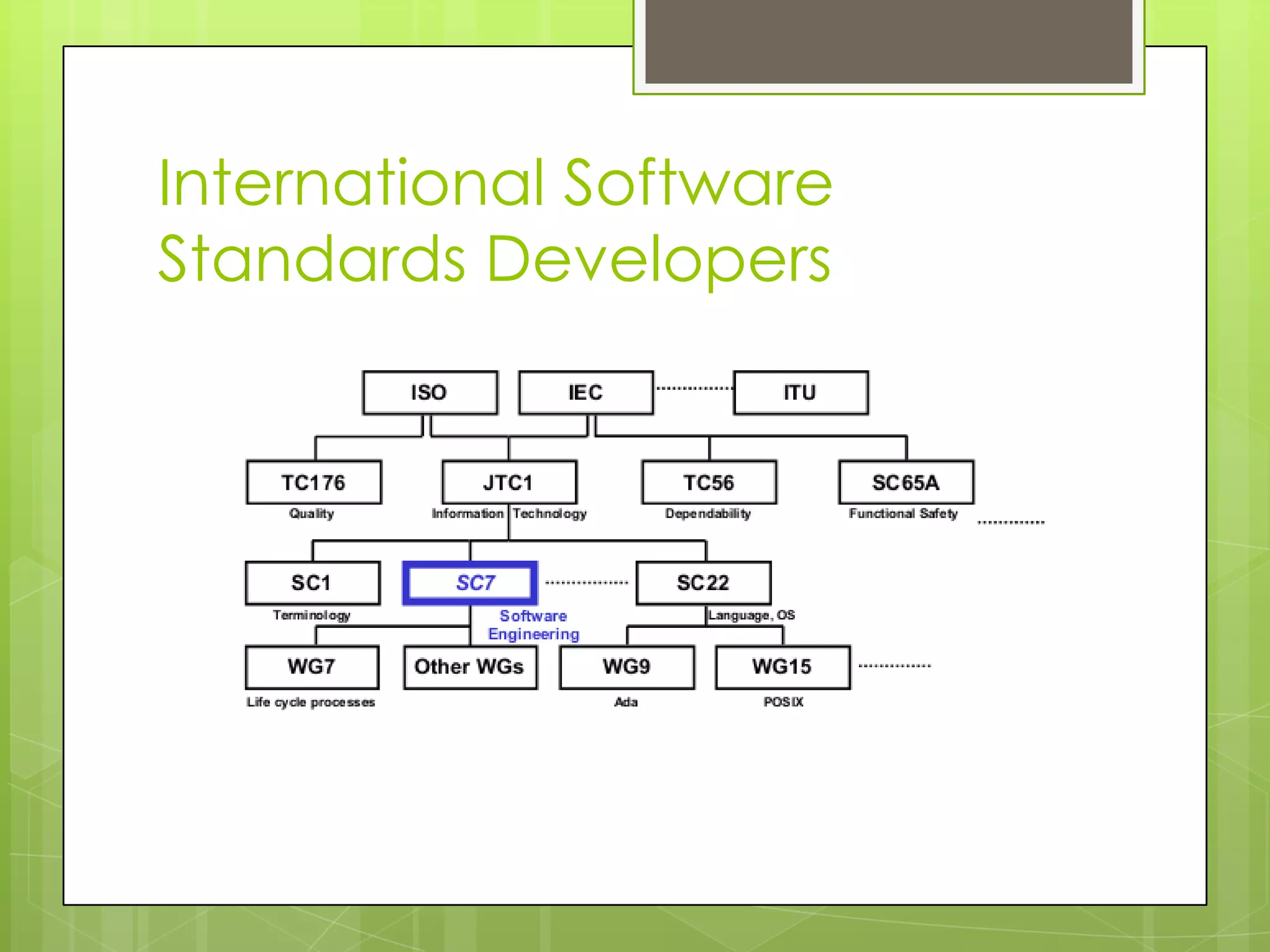
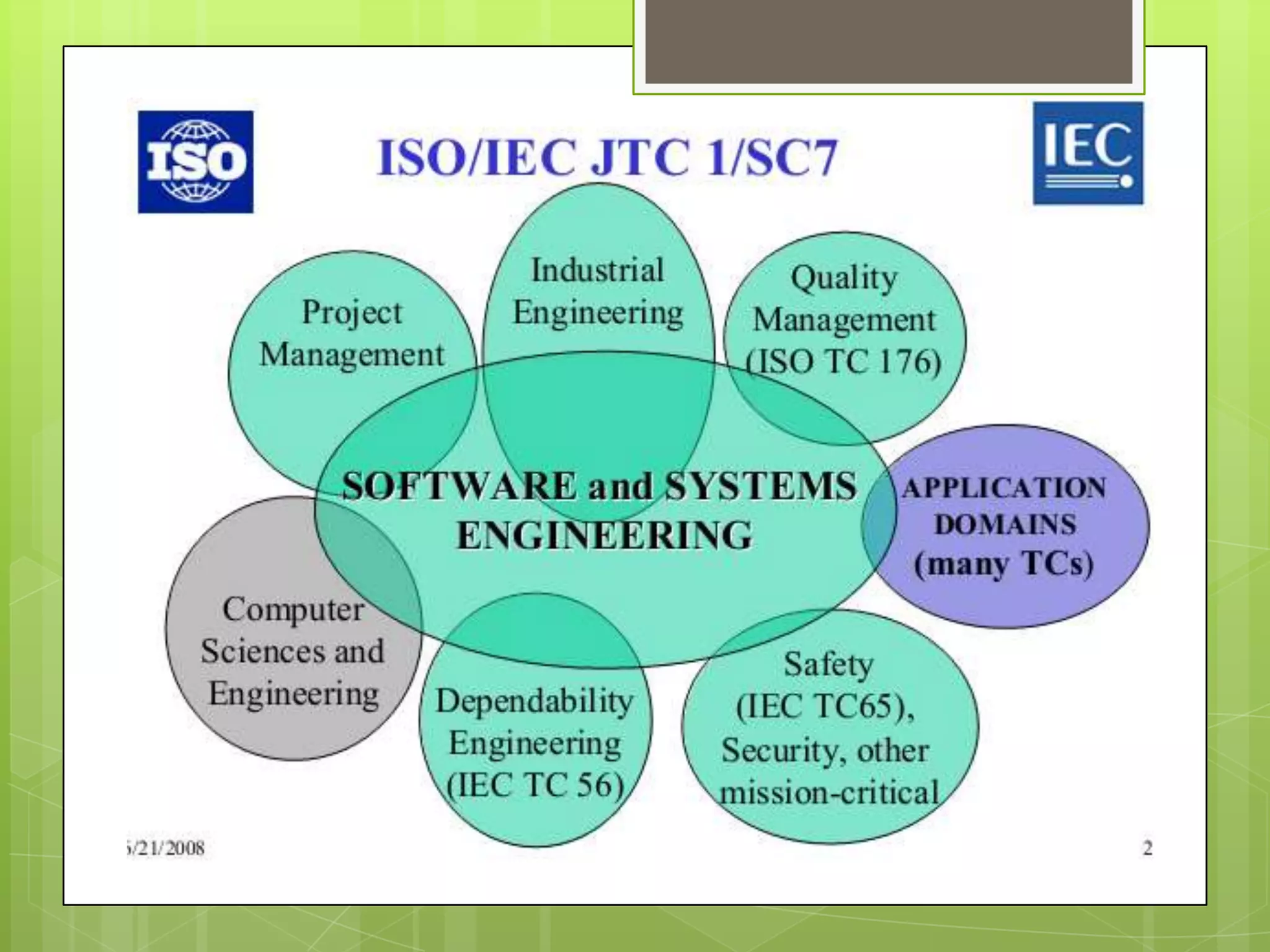
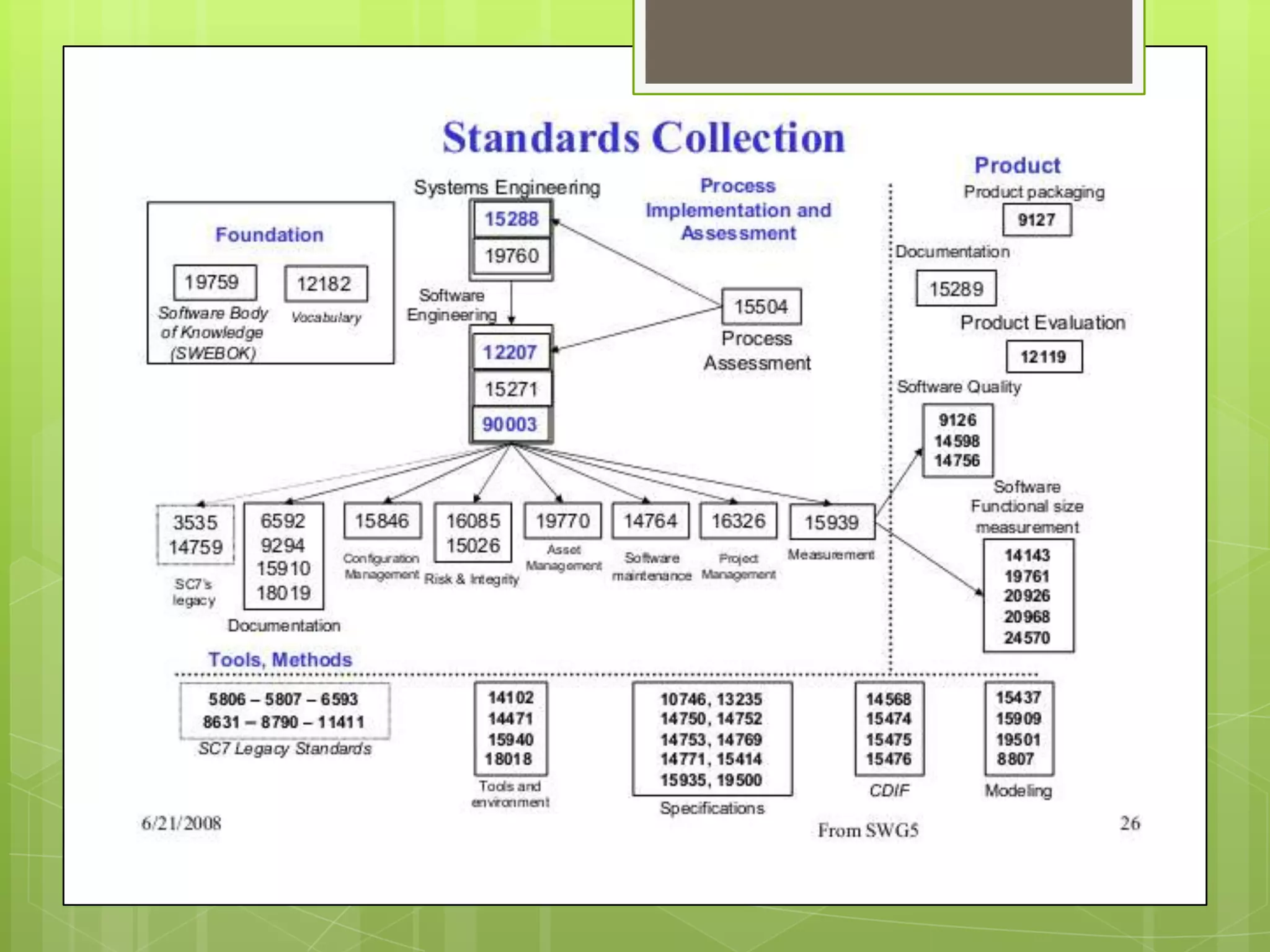
This document discusses software engineering standards. It defines a standard as mandatory requirements that prescribe a disciplined, uniform approach to software development. Standards help specify techniques, provide consensus on best practices, and give precise names to concepts. There are approximately 315 software engineering standards maintained by 46 organizations. Standards cover processes, techniques/tools, and applicability across different domains. Using standards helps establish requirements, define common frameworks, clarify roles, and avoid reinventing proven practices. Sources of standards include organizations, professional groups, governments, and standards bodies like ISO. ISO consolidates existing technology and improves products, business, and buyer protection.