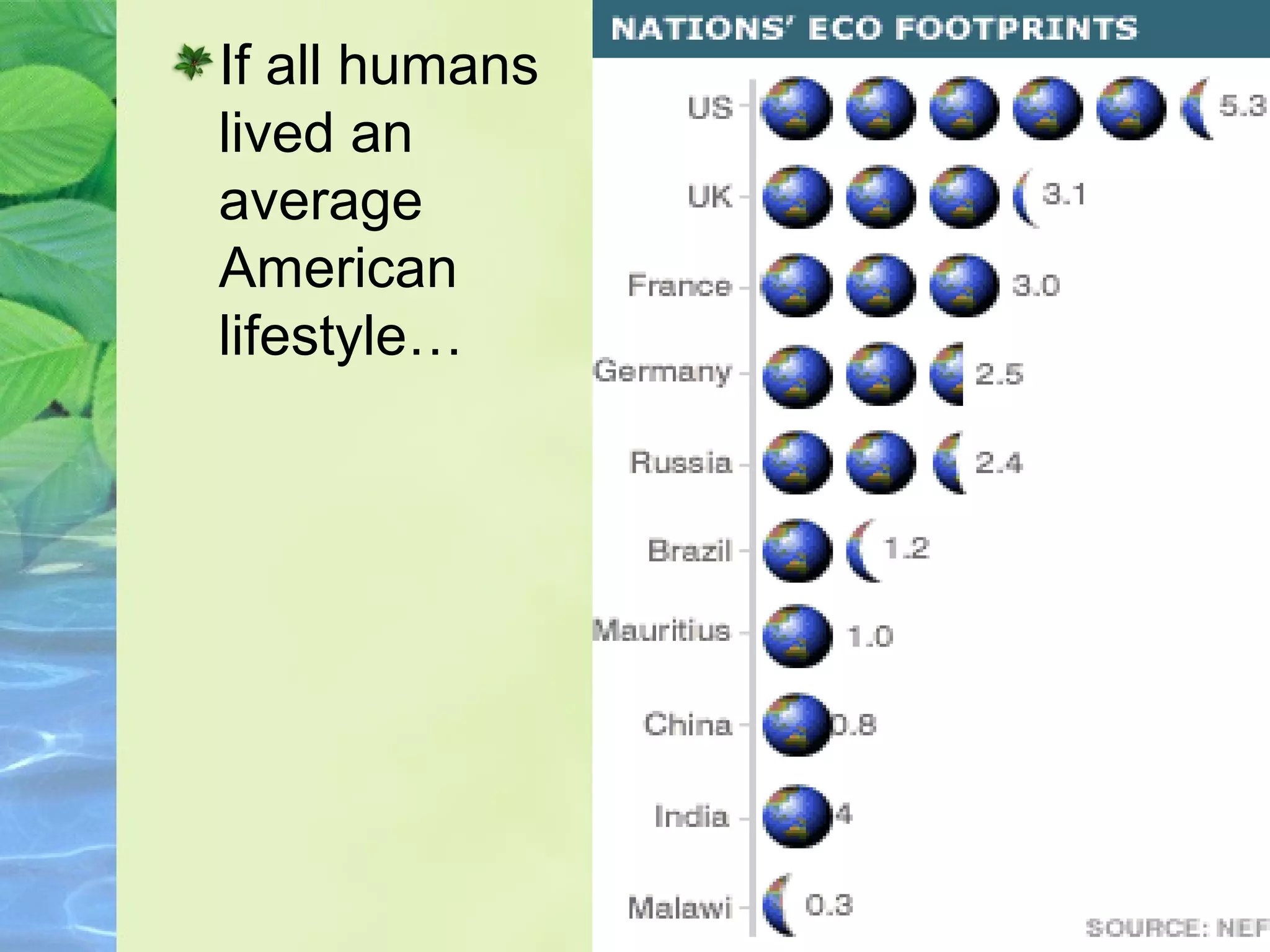
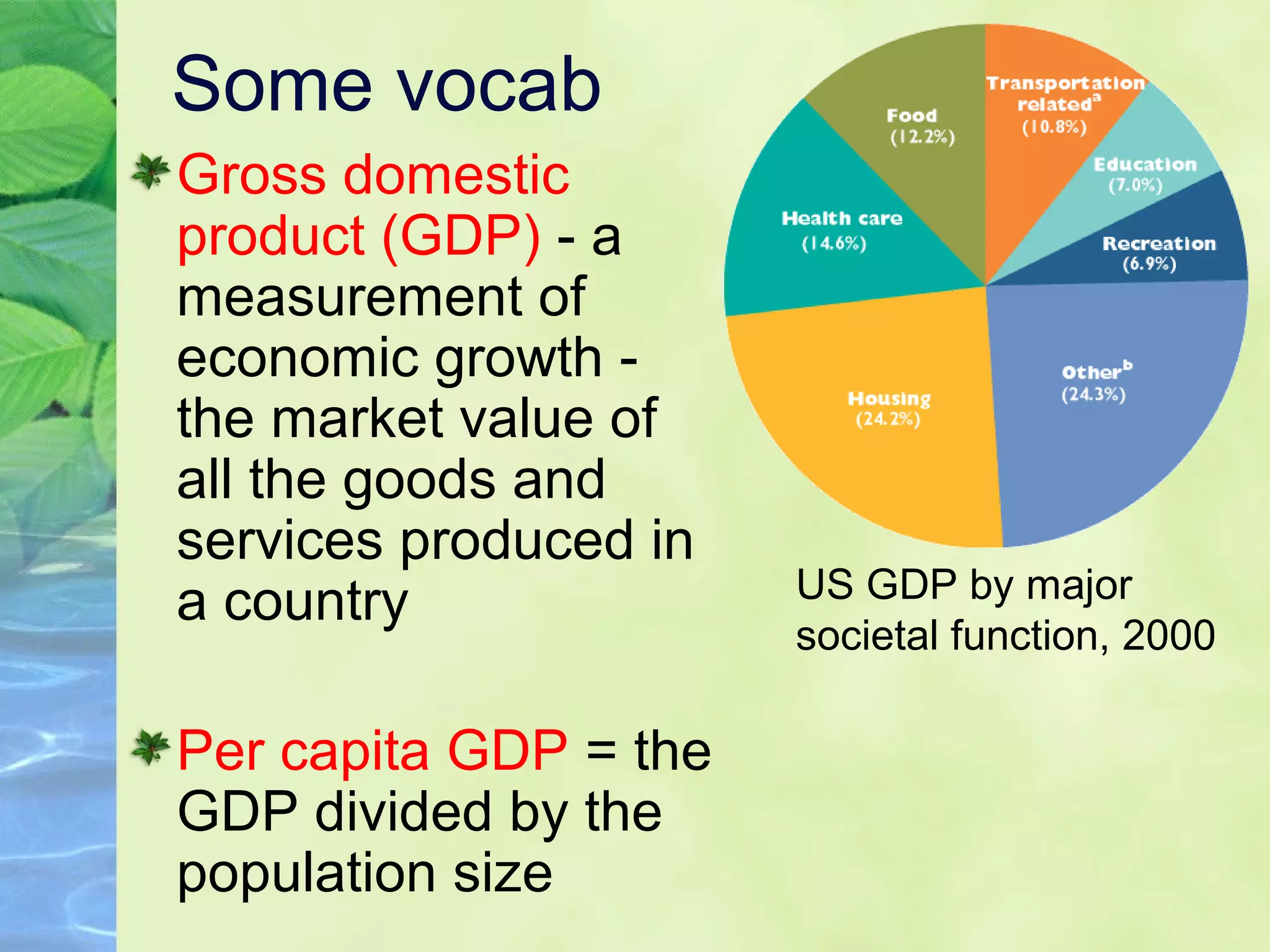
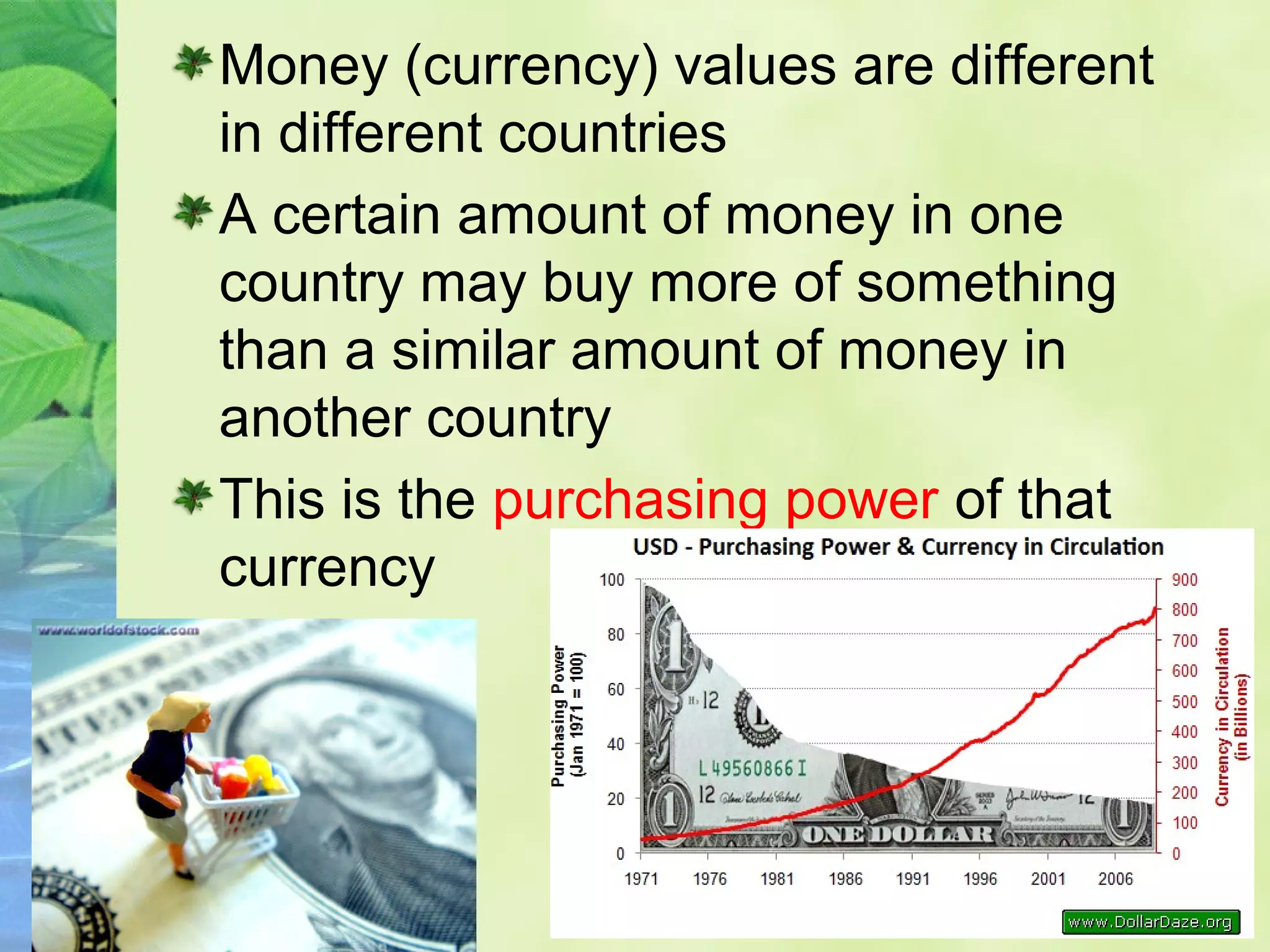
This document discusses the fragility and importance of Earth as humanity's home. It describes Earth as alone in space, sustaining life through delicate systems powered by immense energies. Though wayward and unpredictable, Earth nourishes, enlivens and enriches us greatly. The authors argue that given Earth's precious role in supporting all life, it is worth protecting with love and care.