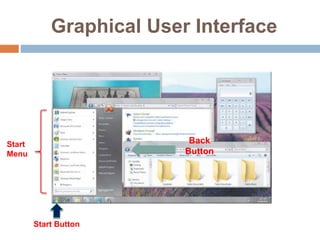
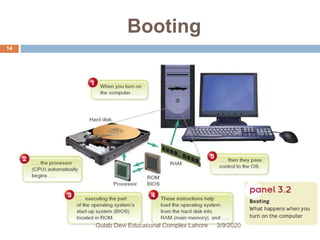
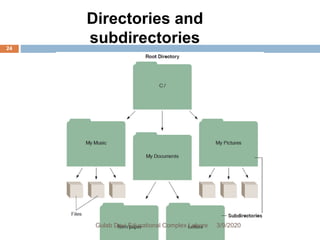
The document discusses the fundamentals and functionalities of operating systems (OS), highlighting their role in managing computer hardware and resources, user interfaces, and multitasking capabilities. It covers key aspects such as booting, CPU and memory management, file management, task management, security measures, and types of operating systems like stand-alone, server, and embedded systems. Additionally, it introduces concepts of device drivers and utilities like file managers and search utilities essential for effective system operation.