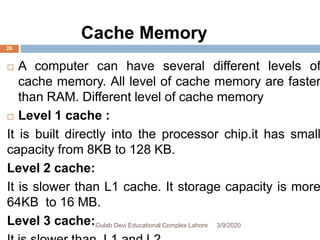
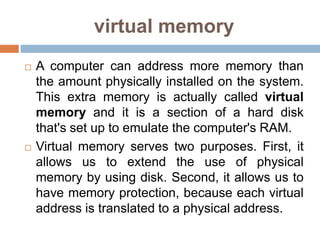
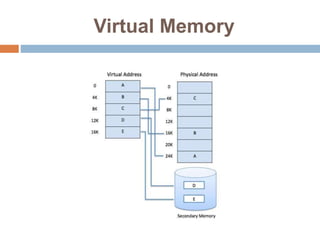
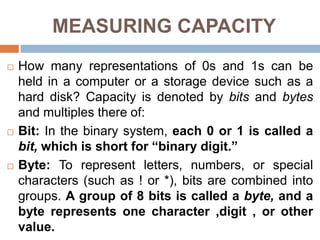
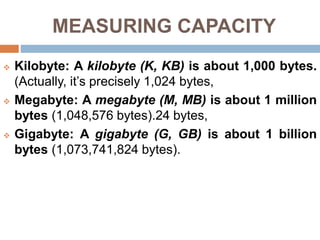
The document outlines various types of storage devices, categorizing them into primary and secondary memory, with a focus on RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read Only Memory) characteristics. It describes the nature of different RAM types, such as static RAM (SRAM), dynamic RAM (DRAM), and their variations, while also detailing secondary memory sources like hard drives and cloud storage options. The capacity of storage is discussed in terms of bits, bytes, and larger units like megabytes and gigabytes.