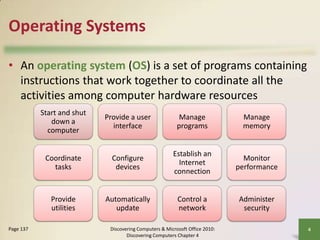
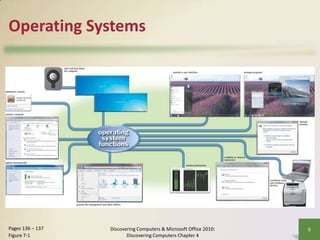
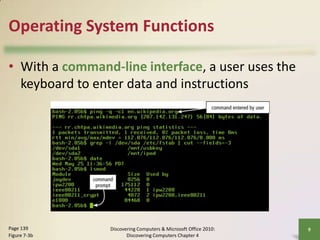
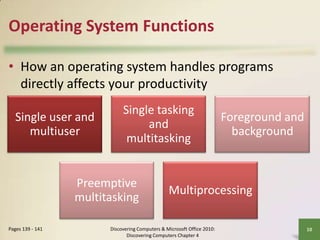
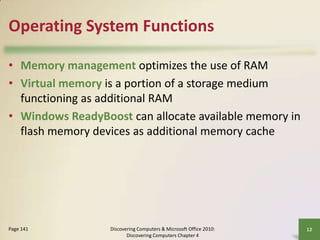
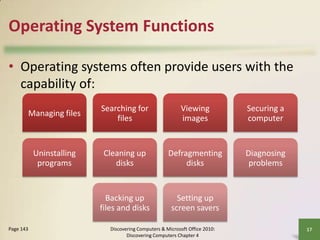
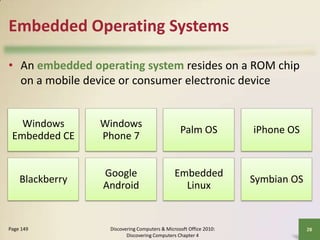
This document defines system software and describes the functions of operating systems and various utility programs. It explains that system software consists of operating systems and utility programs that control computer operations. An operating system coordinates hardware resources, provides a user interface and memory management, and allows connecting to networks. Common operating systems discussed include Windows, Mac OS X, Linux, and server versions for networks. The document also outlines many utility programs that perform functions like file management, backups, virus protection, and media playback.