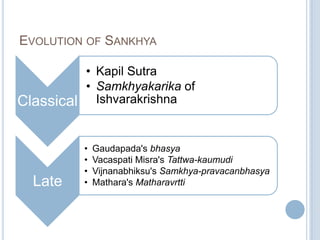
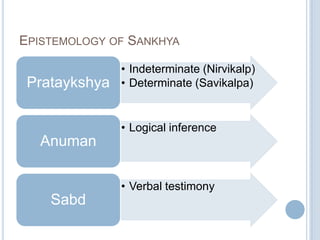
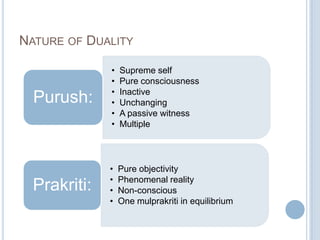
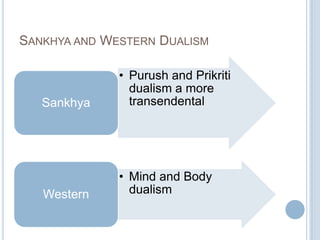
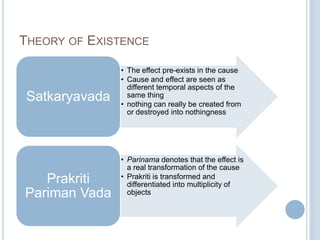
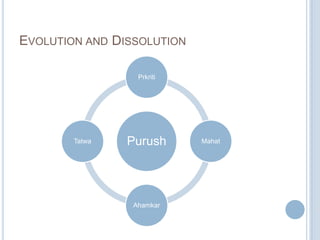
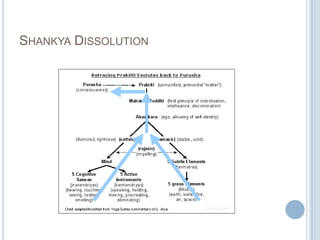
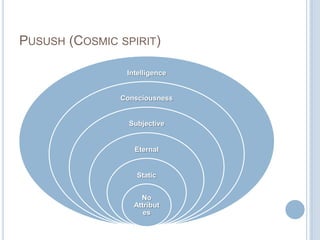
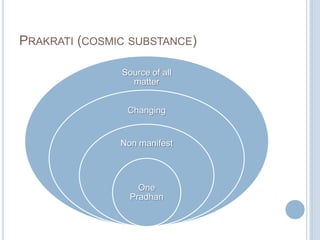
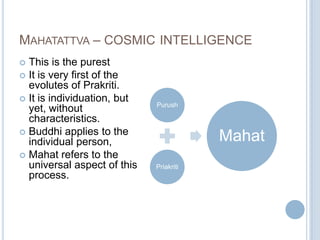
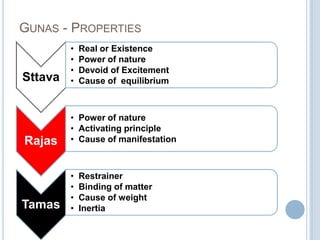
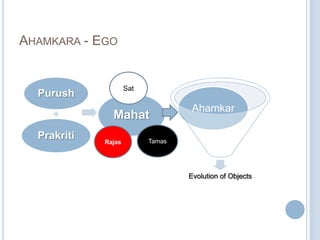
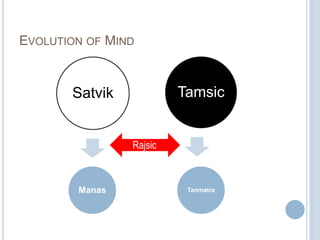
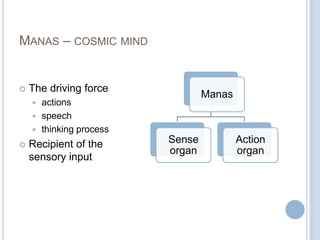
The Sankhya philosophy is one of the oldest schools of Hindu philosophy that sought to explain the process of cosmic evolution through rational analysis and principles of energy transformation. It was founded by Kapila around 1000 BC and enumerates twenty-five principles or categories by which the universe evolves from a primordial state through stages of increasing complexity. Key aspects of Sankhya include the distinction between purusha (consciousness) and prakriti (matter), the three gunas (qualities) that characterize prakriti, and the evolution of the cosmos from subtle elements to grosser ones and its eventual dissolution back to an unmanifest state.






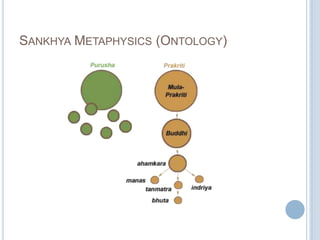
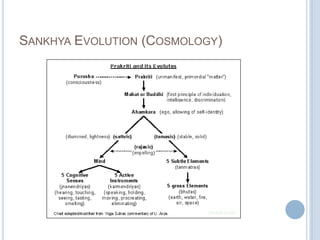
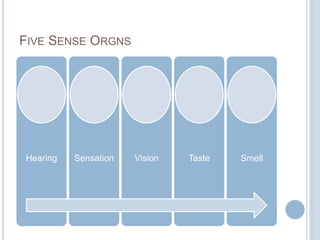
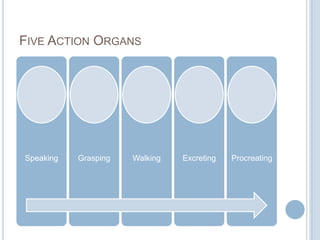
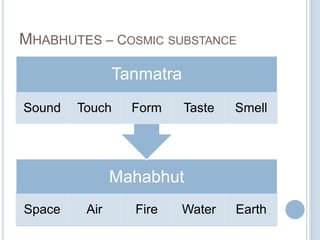

![SANKHYA CATEGORIES (TATWA)
avyakta (unmanifest)
(1) Purusha
(2)Prakriti (Mulaprakriti)
vyakta (manifest) (3) Buddhi [Intellect]
taijasa or rajas mode of Ahamkara
(4) Ahamkara [Ego or "I"-ness]
vaikriti or sattwa mode of Ahamkara
Manas
(5)
Buddhindriyas
Sense-powers
(6-10)
Mind or
Psyche
hearing
touching
seeing
bhutadi or tamas mode of
Ahamkara
Karmendriyas Tanmatras
Bhutas
Action-powers Subtle Matter Gross
(11-15)
(16-20)
Elements
visible tattwas
(21-25)
speaking
sound
space
grasping
touch
air
walking
form
fire
tasting
smelling
excreting
generating
taste
smell
water
earth](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cfakepathsamkhyaphilosophy-100621061538-phpapp02/85/Samkhya-philosophy-27-320.jpg)

