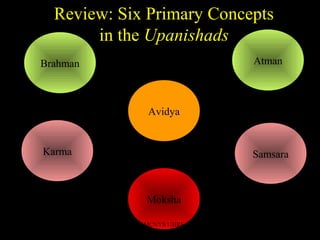
Vedanta refers to the philosophical traditions and sutras that were based on, and aimed to synthesize, the teachings of the Upanishads, Bhagavad Gita, and Brahma Sutras. The document outlines six primary concepts of the Upanishads: Brahman as the ultimate impersonal reality; Atman as the true self; Avidya as ignorance of reality/self; Samsara as the cycle of rebirth fueled by karma; and Moksha as liberation from samsara through realizing the identity of Atman and Brahman. It also discusses the different views of Brahman and debates around its nature.




















!["Bliss [ananda] is Brahman, for
from bliss all beings are born; by
bliss, when born, they live; and into
bliss they enter at their death."
(Taittiriyaka Upanishad, III.6)
SDMCNYS UJIRE 22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vedantaphilosophysdmcnys-181224095633/85/Vedanta-philosophy-sdmcnys-22-320.jpg)




![Tat Tvam Asi
“Thou [Atman] art That [Brahman]”
(Chandogya Upanishad, VI)
A famous and controversial passage from
the Upanishads.
Atman and Brahman are identical?
Atman and Brahman are united in some
way without being entirely identical?
SDMCNYS UJIRE 27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vedantaphilosophysdmcnys-181224095633/85/Vedanta-philosophy-sdmcnys-27-320.jpg)