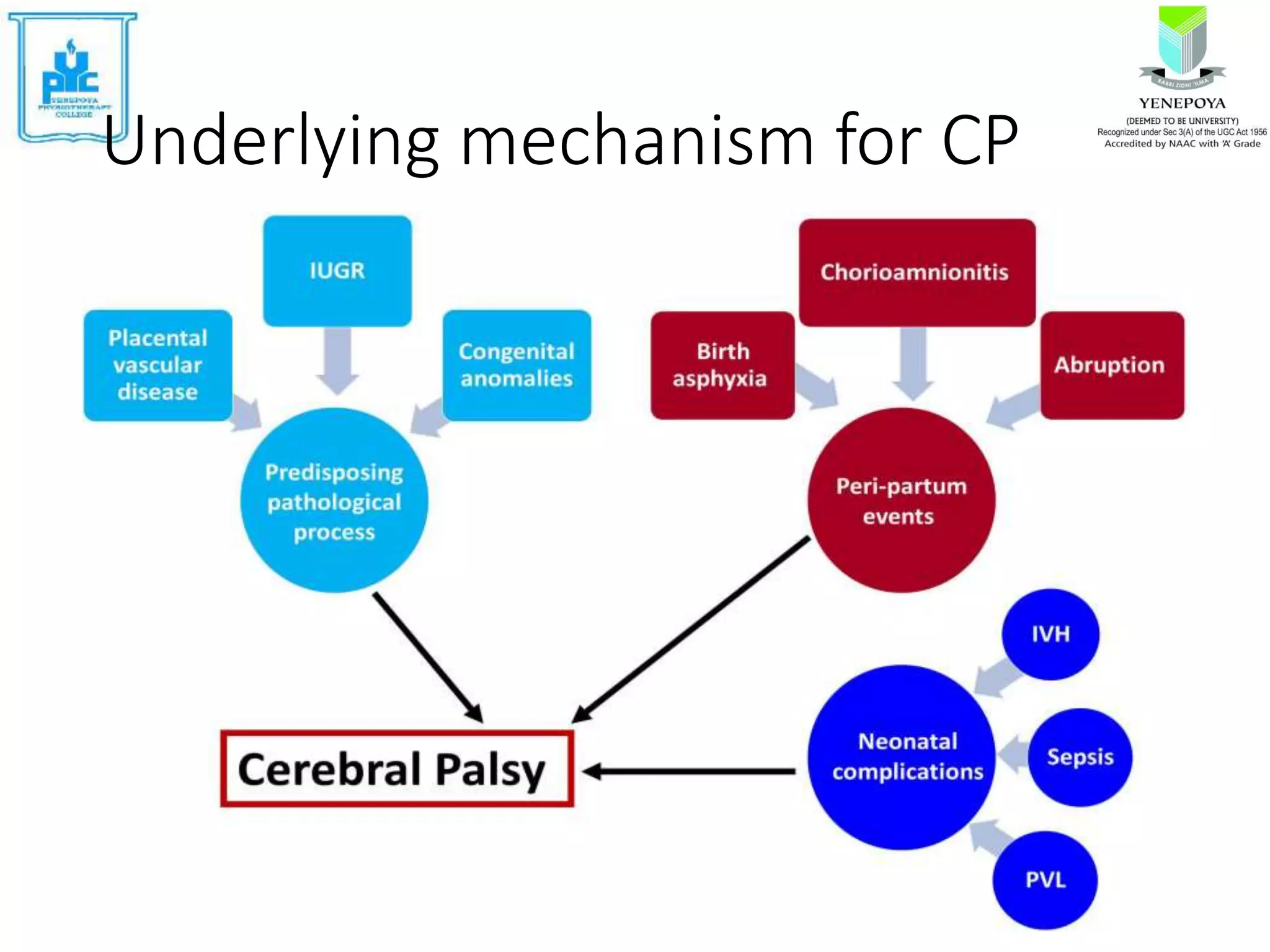
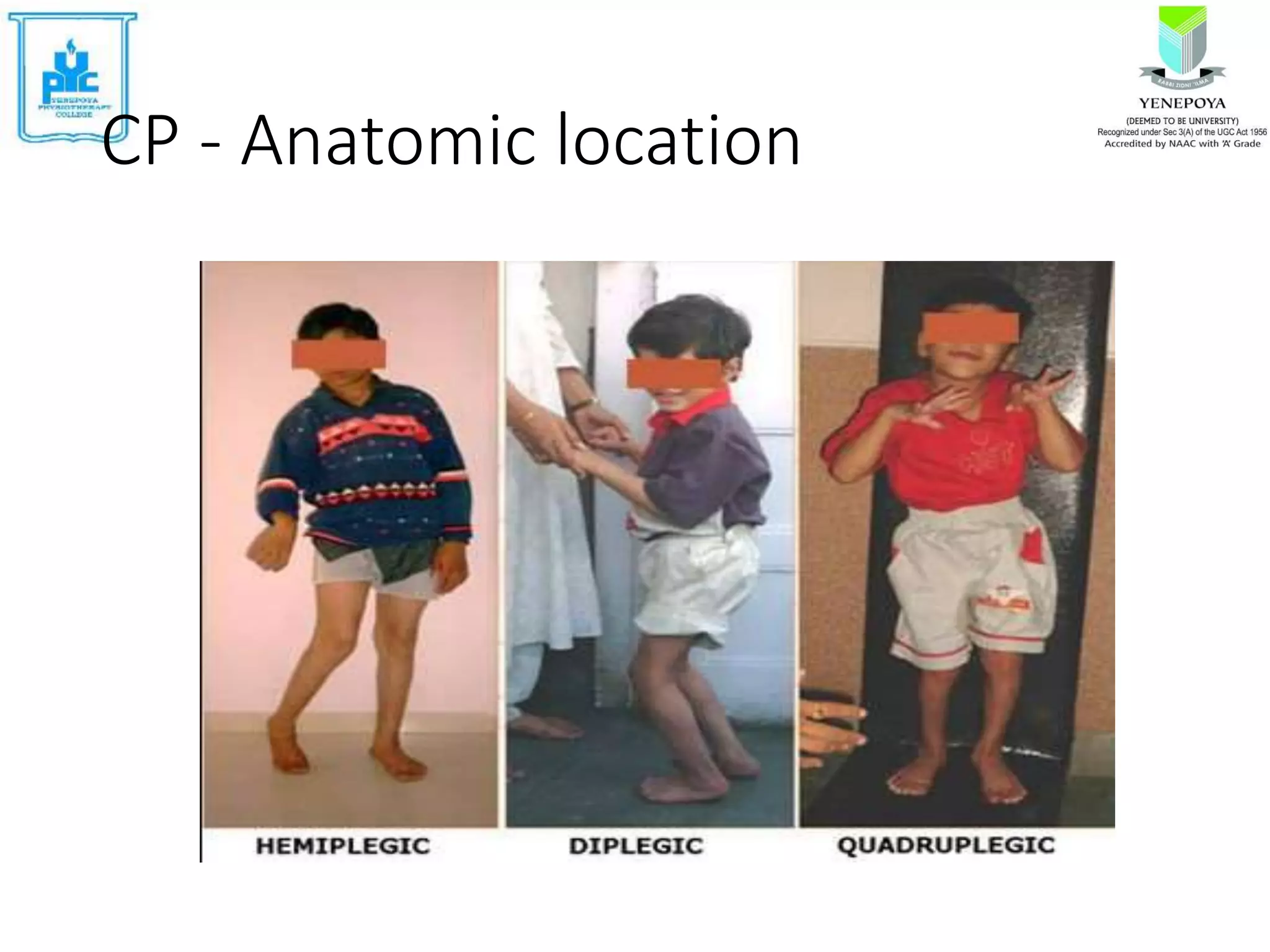
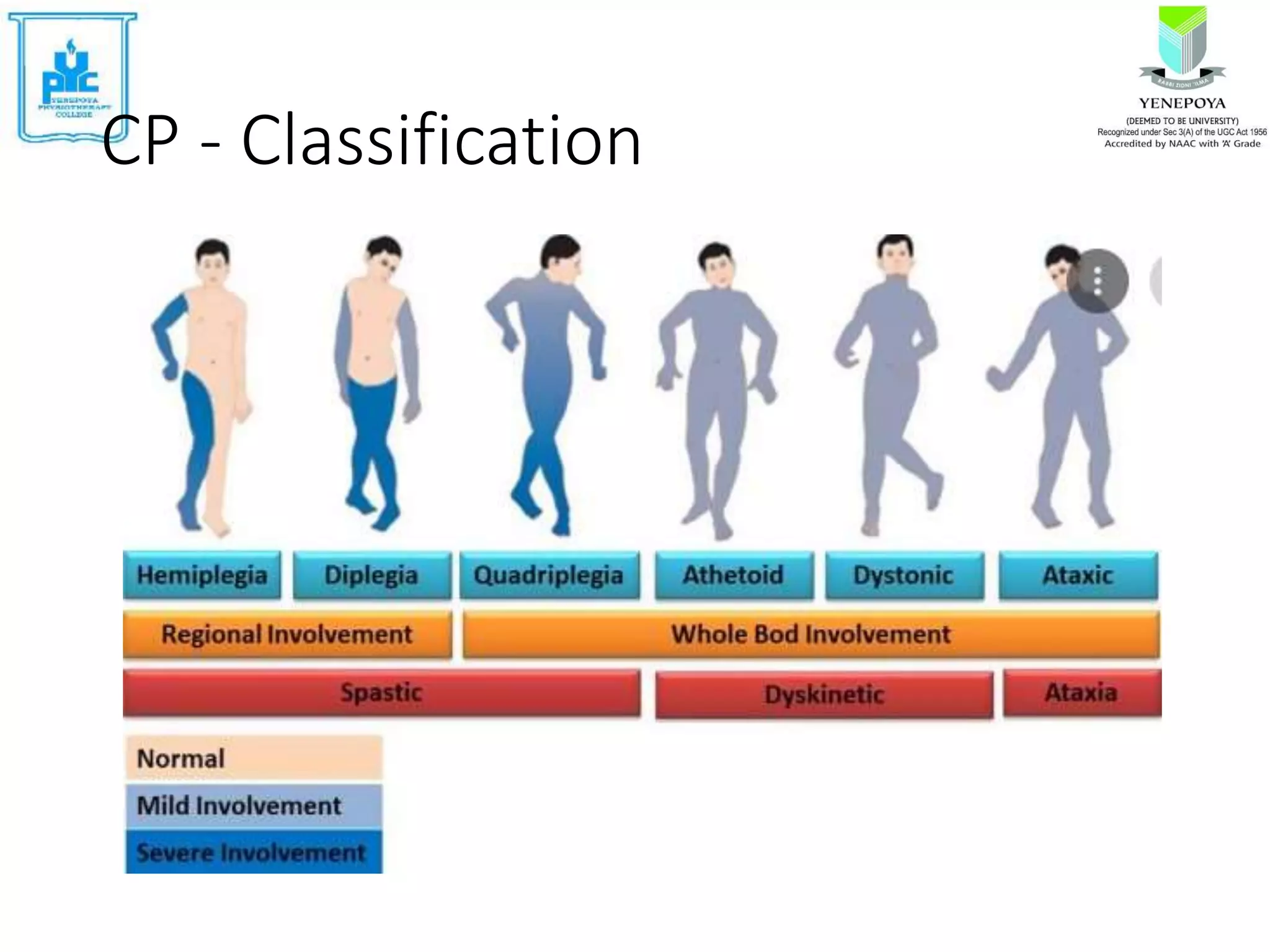
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of disorders that affect movement and posture, caused by non-progressive damage to the developing brain. The motor disorders of CP are often accompanied by disturbances in other functions. CP affects 2-3 per 1000 live births and is a common cause of physical disability in children. Risk factors include problems during pregnancy, labor/delivery, or in the neonatal period. Symptoms include abnormal muscle tone, atypical posture, and delayed motor development. Treatment involves assessing motor skills, imaging, and developing individualized plans to address impairments and promote functional abilities.