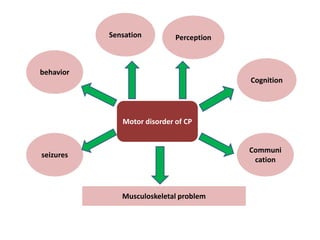
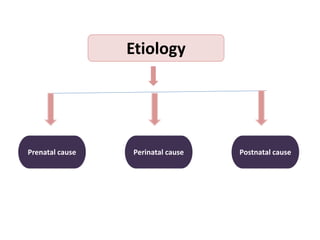
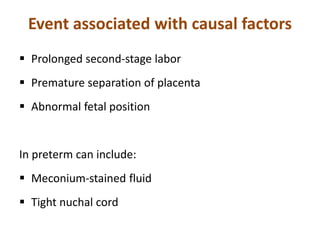
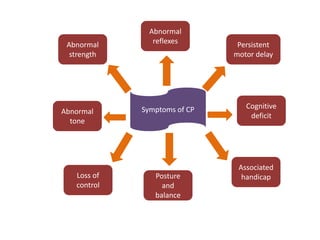
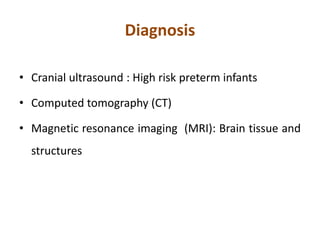
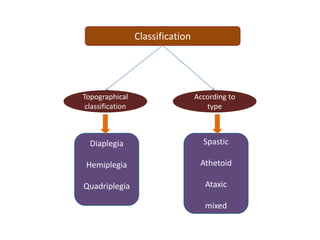
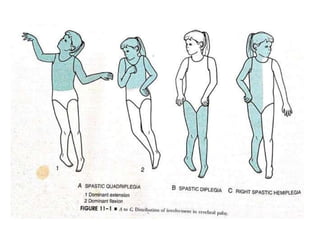
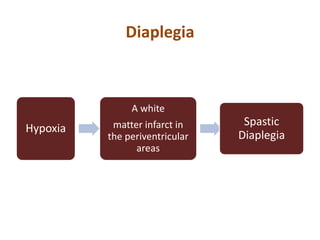
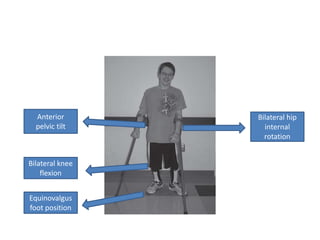
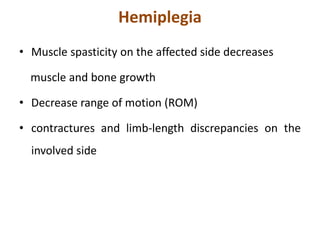
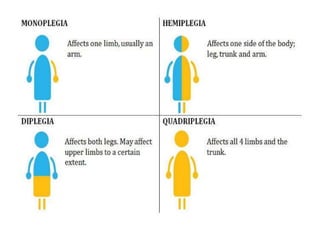
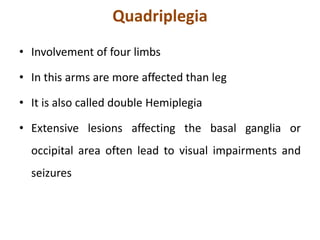
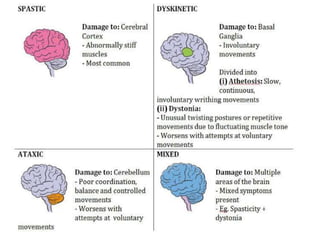
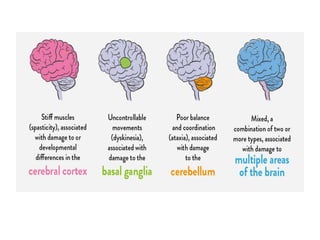
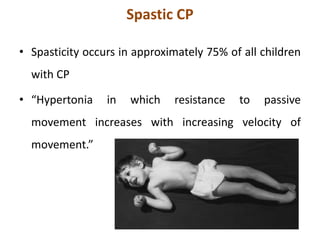
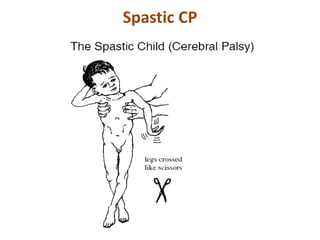
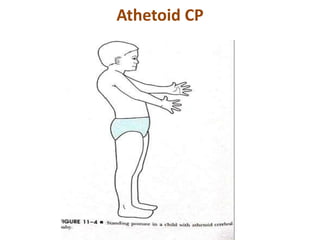
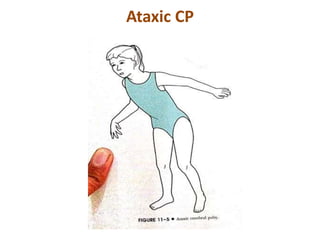
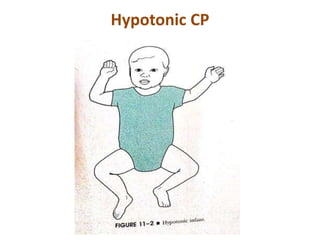
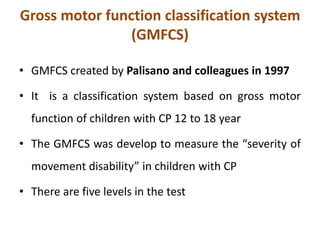
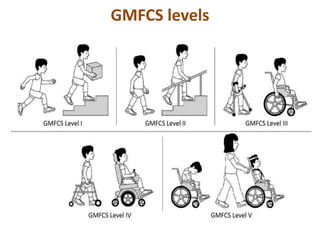
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of permanent movement and posture disorders caused by non-progressive disturbances in the developing brain, often leading to cognitive, sensory, and musculoskeletal issues. CP manifests in various forms such as spastic, athetoid, and ataxic types, with symptoms including motor delays and abnormal reflexes. The prevalence is approximately 2-2.5 per 1000 live births, and its causes can be prenatal, perinatal, or postnatal, affecting children's mobility and motor skills.