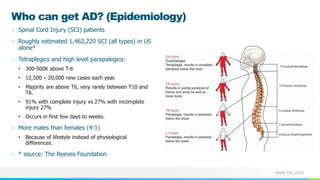
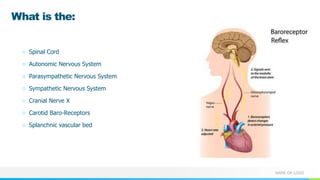
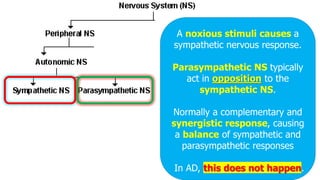
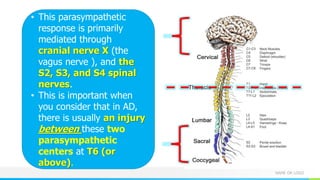
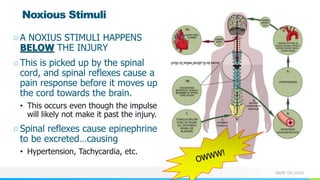
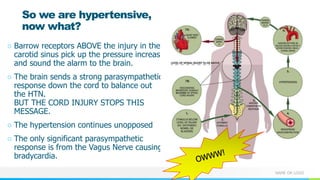
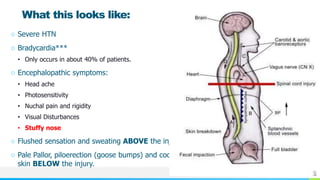
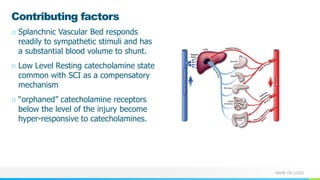
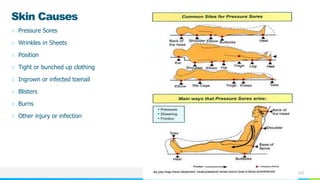
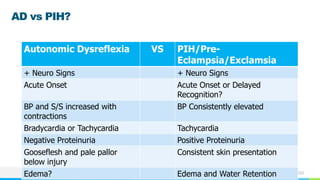
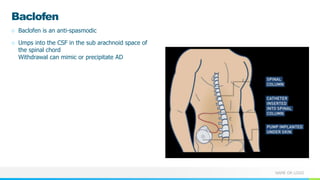
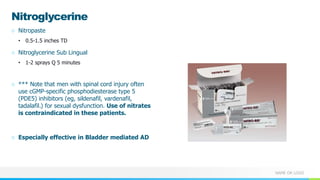
This document provides information about autonomic dysreflexia (AD), a potentially life-threatening condition that affects individuals with spinal cord injuries above T6. It defines AD as an abnormal sympathetic response to a noxious stimulus below the level of injury, causing a surge in blood pressure that is not counteracted by the parasympathetic nervous system due to the spinal cord injury. The document discusses the pathophysiology, causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of AD, emphasizing the importance of promptly relieving noxious stimuli and using short-acting antihypertensives like nitroglycerin to rapidly lower blood pressure in cases of AD.