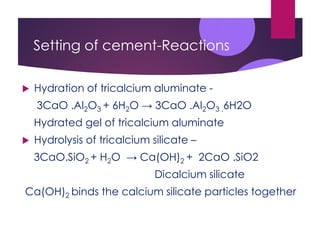
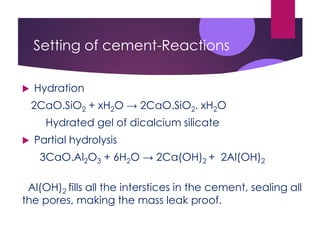
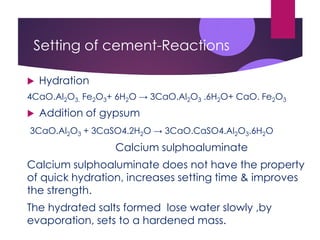
This document discusses cement, including its manufacture and composition. It notes that cement is made by heating limestone and clay at high temperatures which forms calcium silicates and other compounds. The raw materials are finely ground and mixed with water to form a slurry, then heated in a kiln at 1400-1500°C. This process forms cement clinker which is then cooled, ground into a powder, and mixed with gypsum. When cement is mixed with water, it undergoes hydration and hardening reactions that cause it to set and strengthen over time. The main uses of cement are in construction applications like buildings, bridges, and concrete.