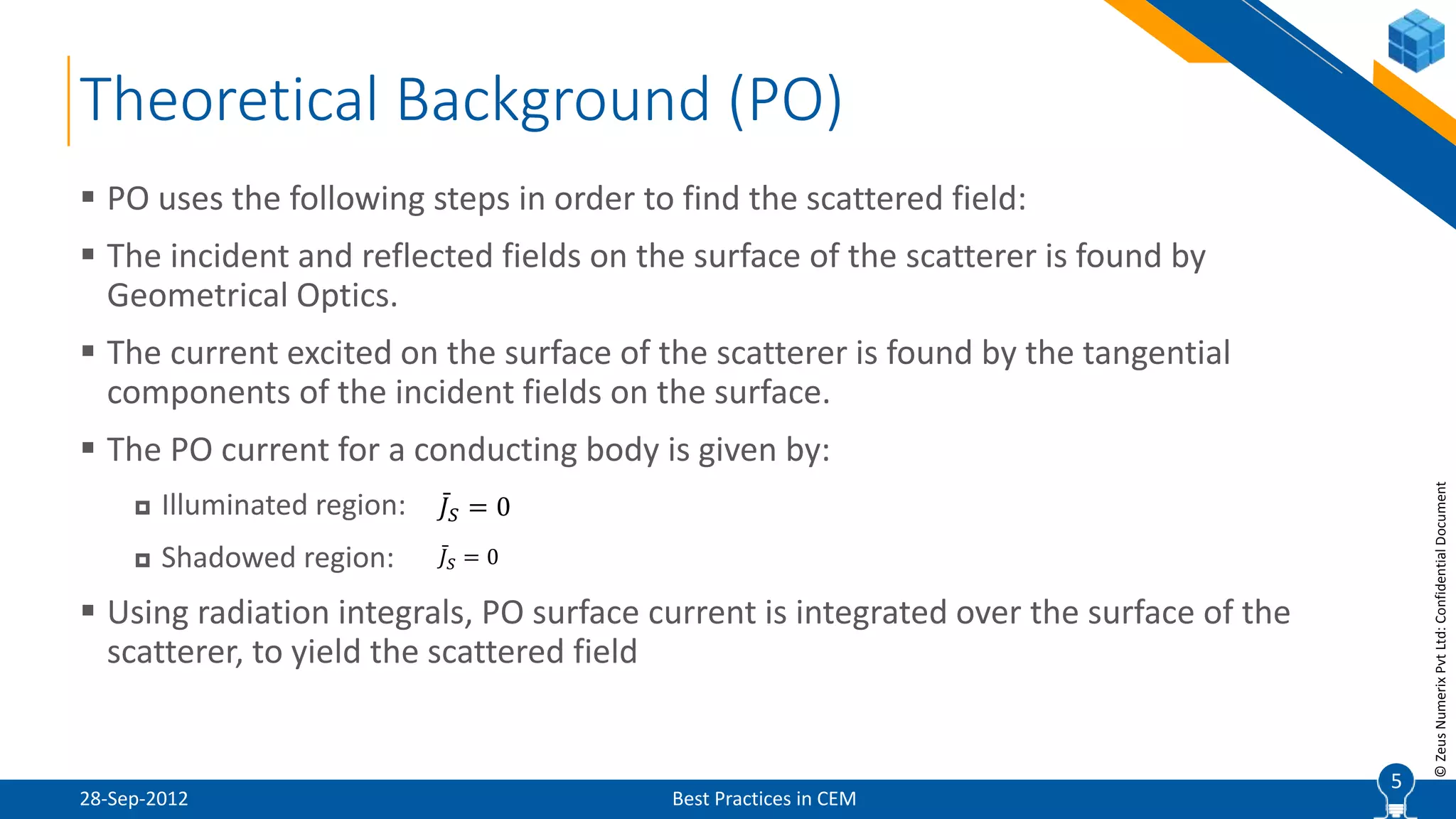
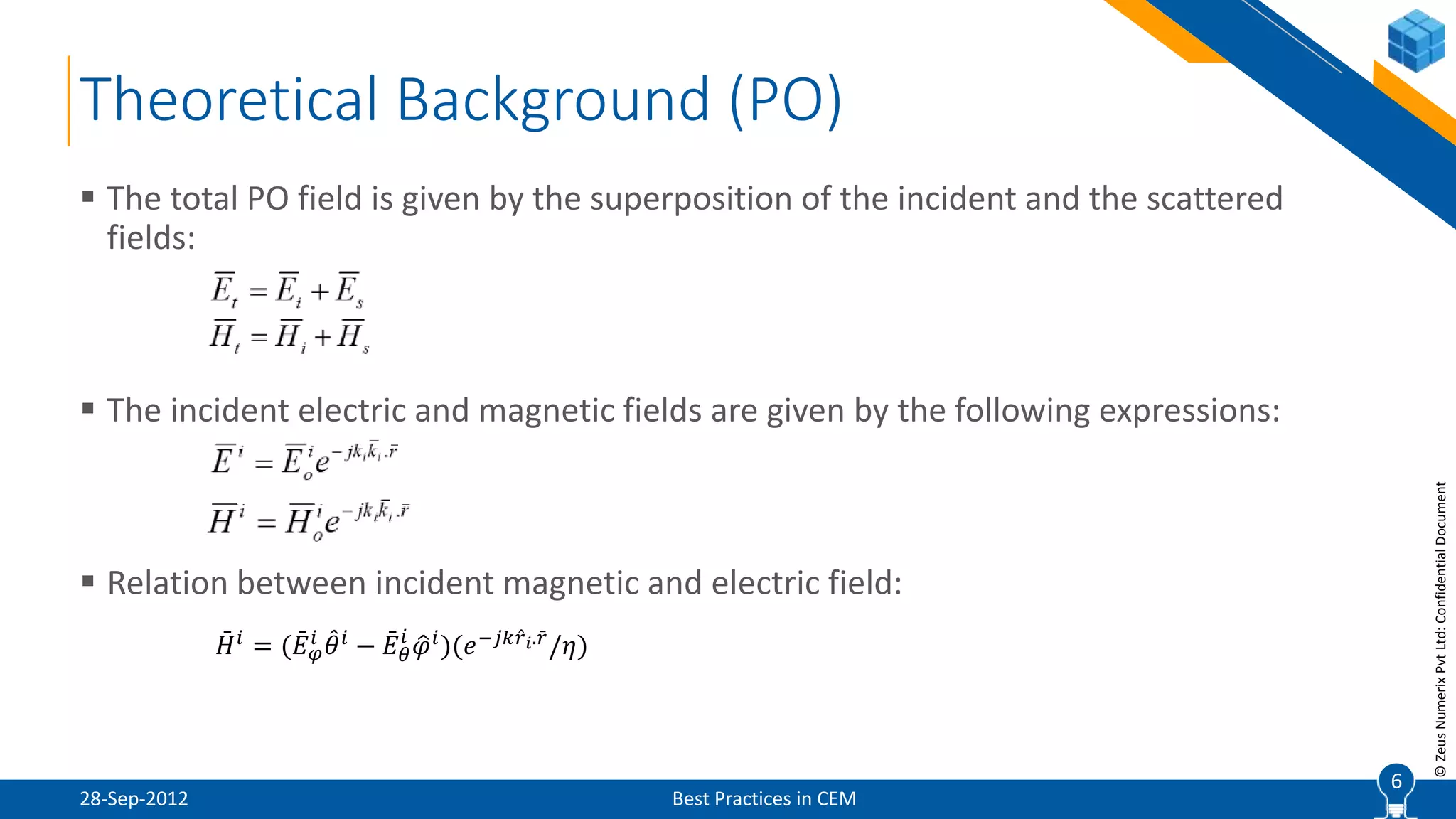
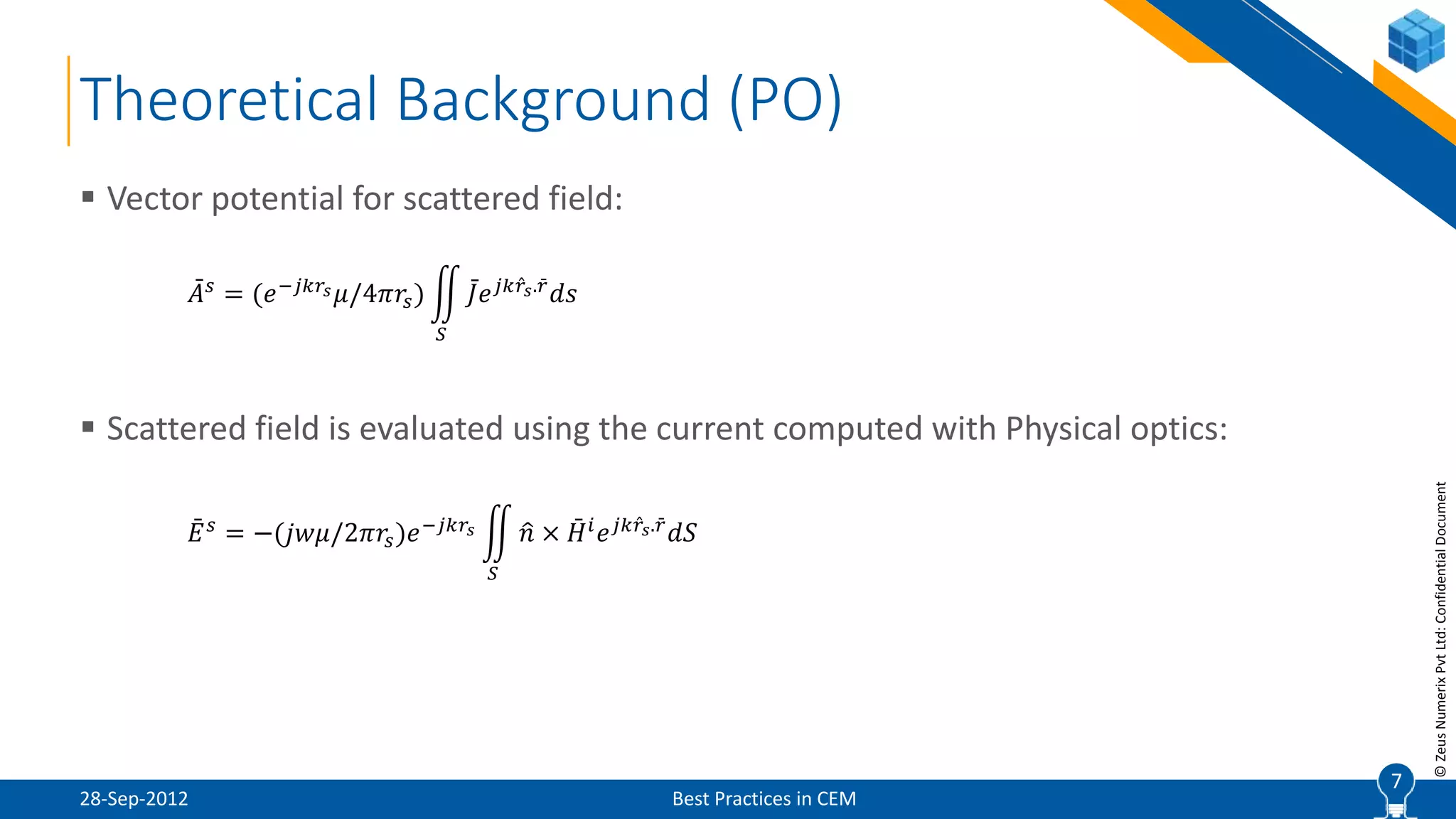
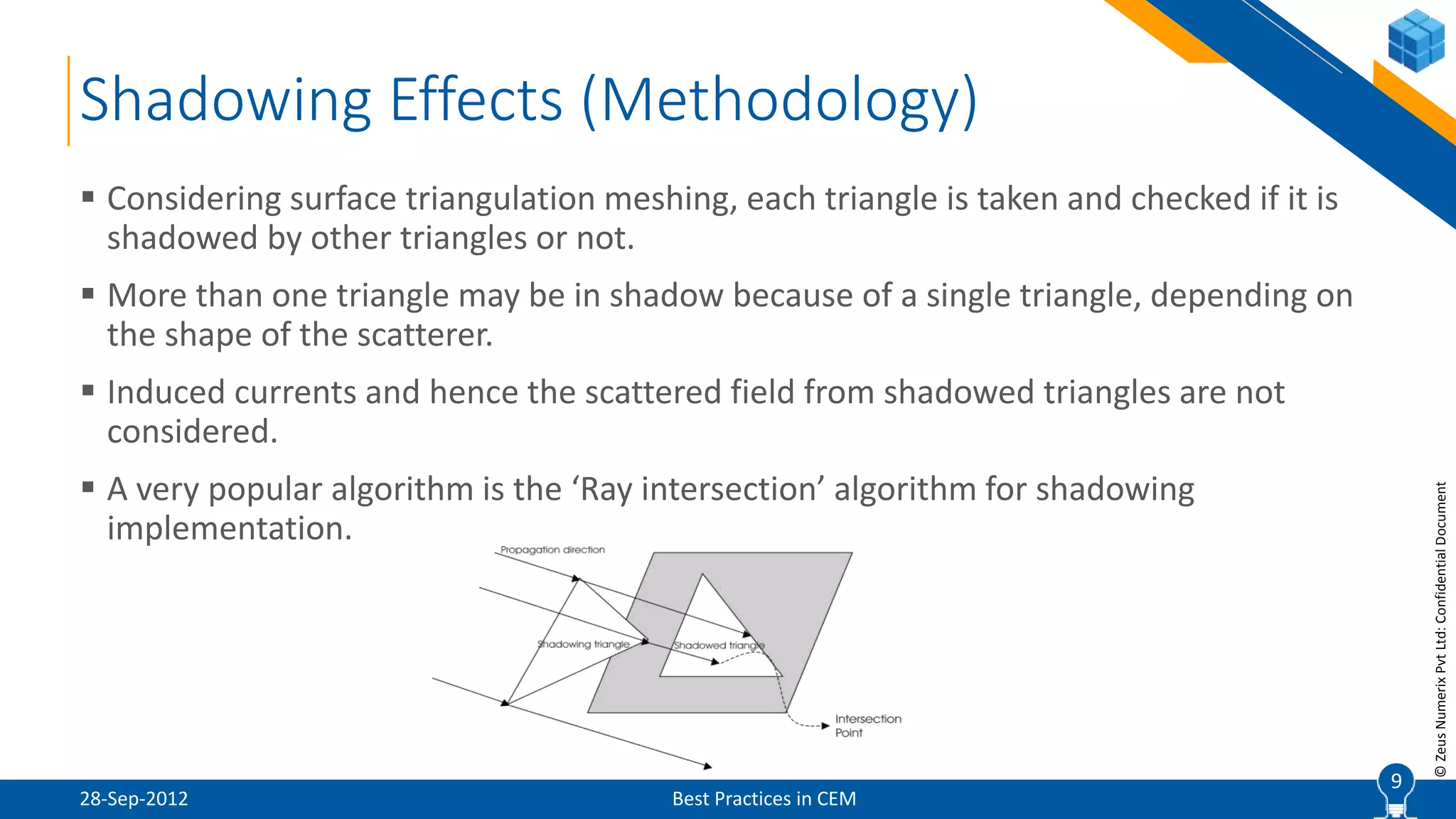
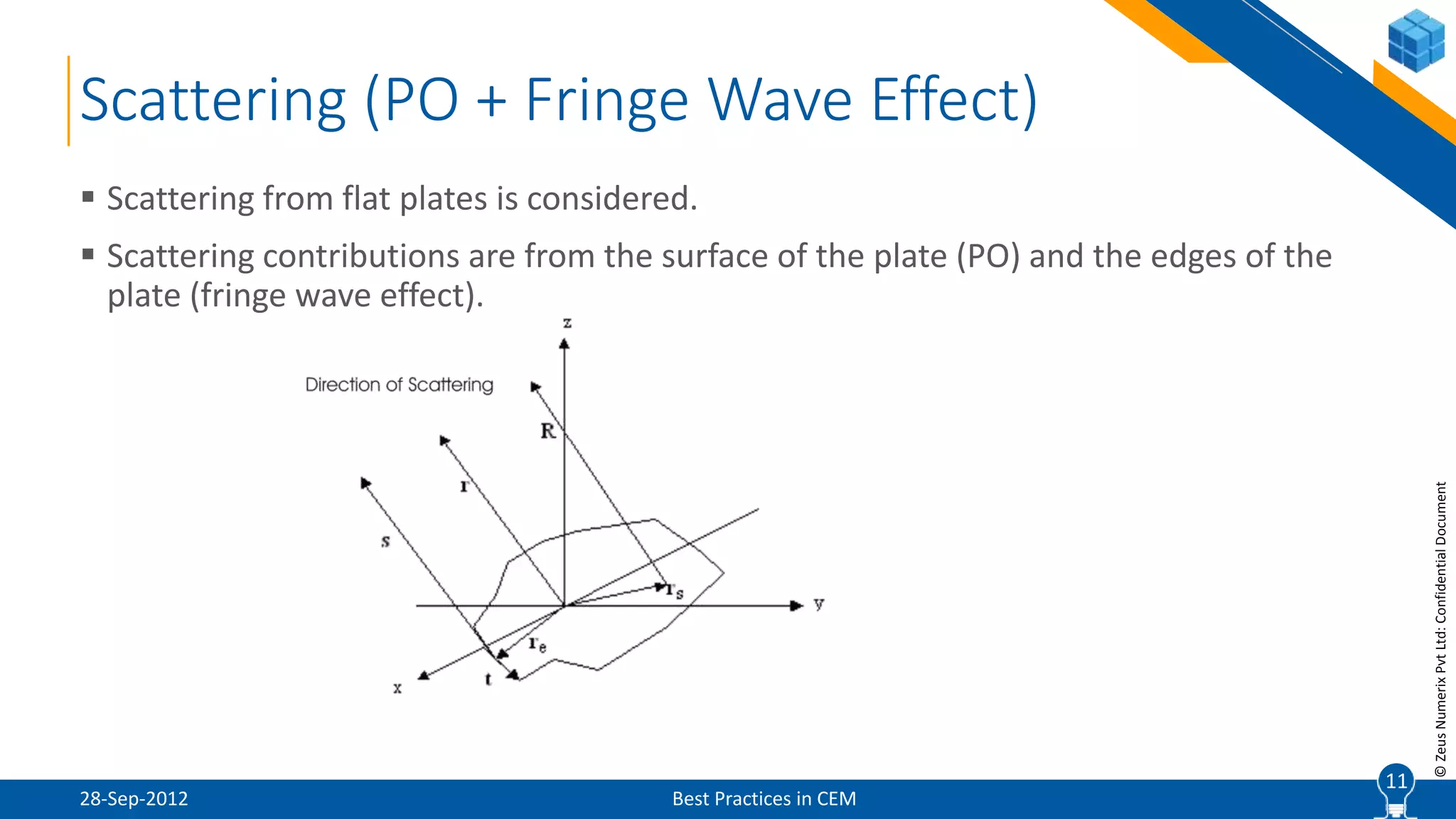
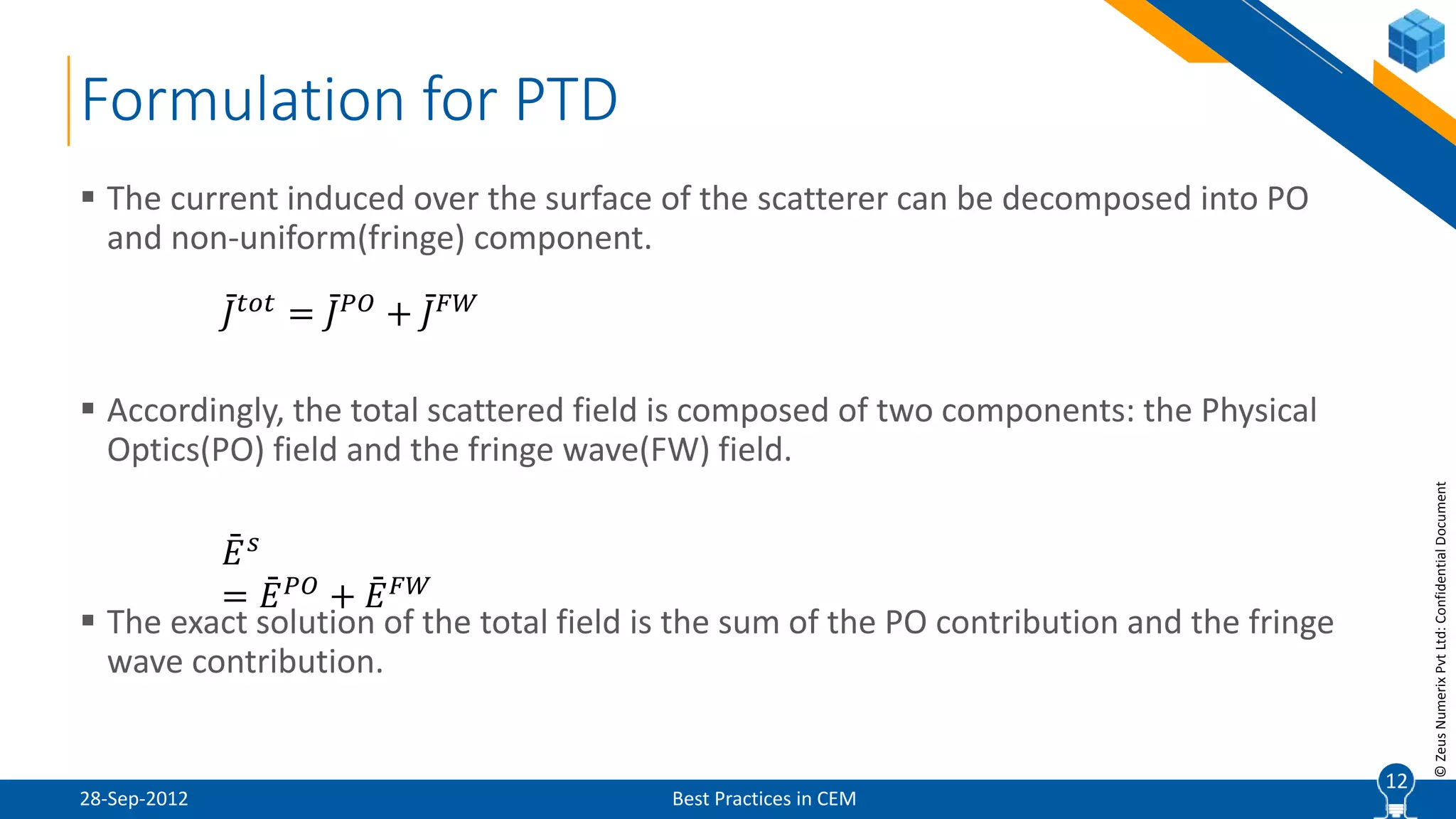
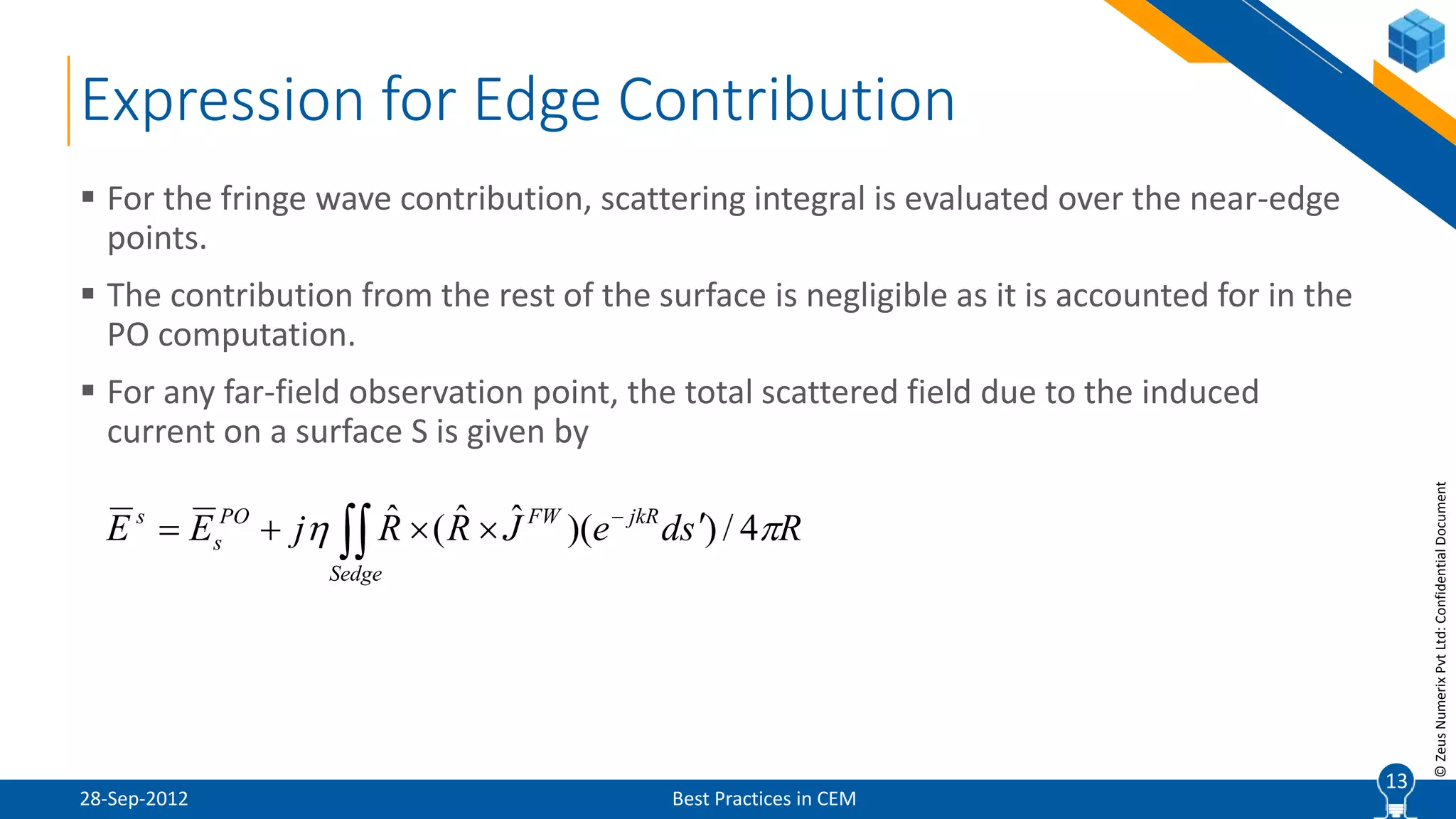
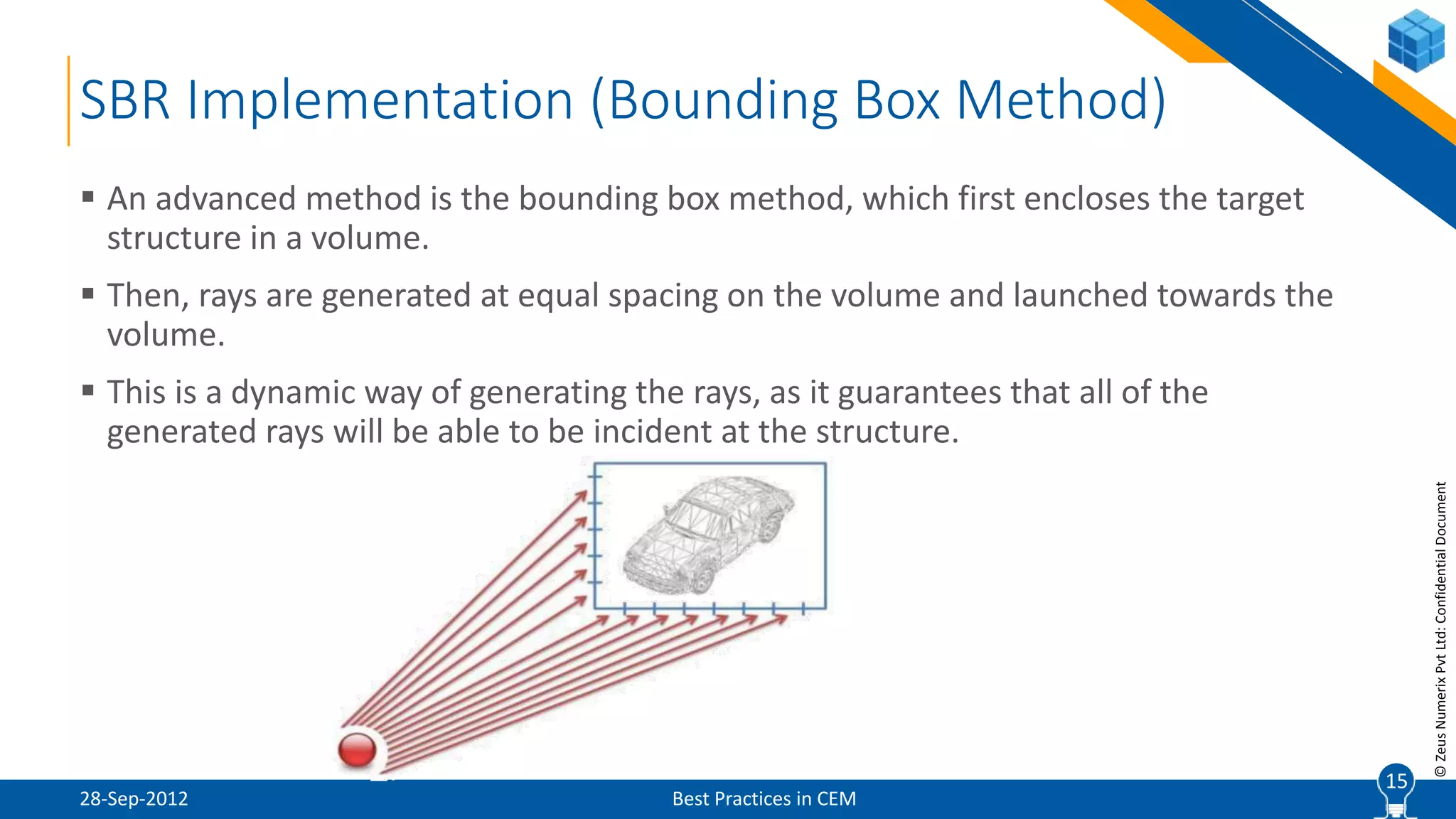
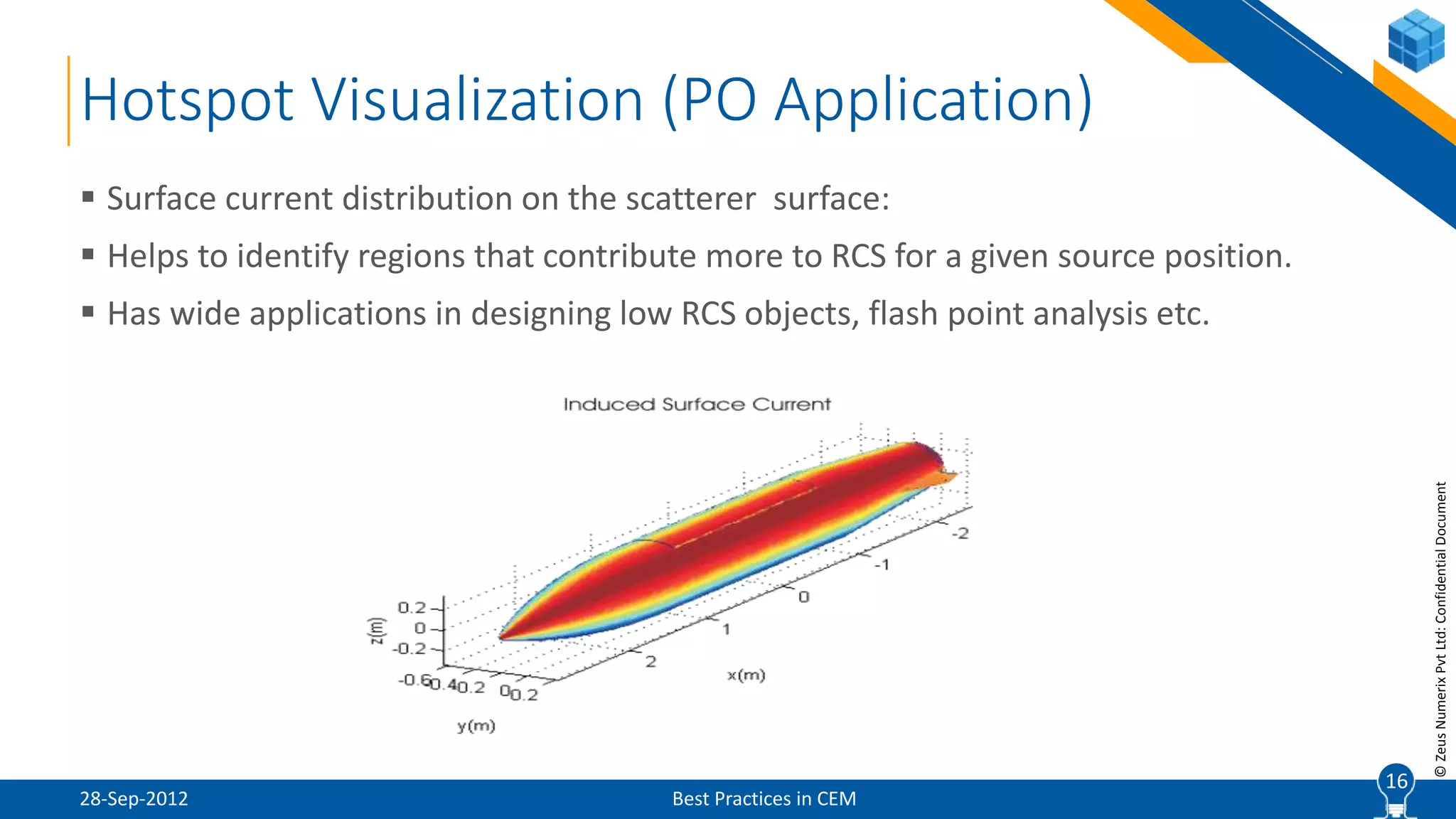
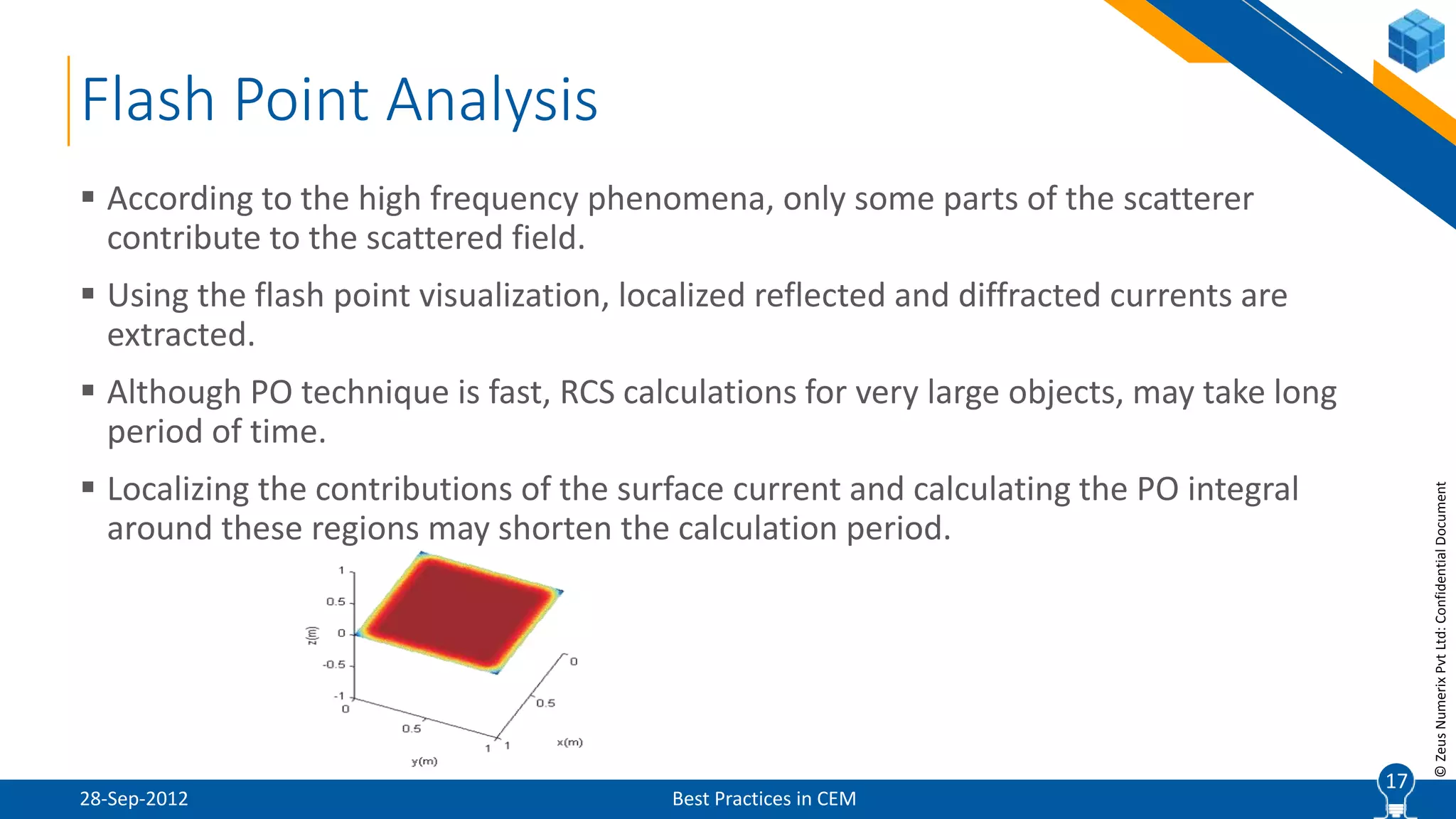
The document discusses best practices in computational electromagnetic (CEM) analysis, focusing on high-frequency methods such as physical optics (PO) and geometric optics (GO) for predicting scattered fields from conducting bodies. It covers methodologies, including the shooting and bouncing ray (SBR) technique, shadowing effects, and the use of equivalent edge currents to refine predictions. Additionally, it highlights applications like hot spot visualization and flash point analysis to improve radar cross-section (RCS) calculations.