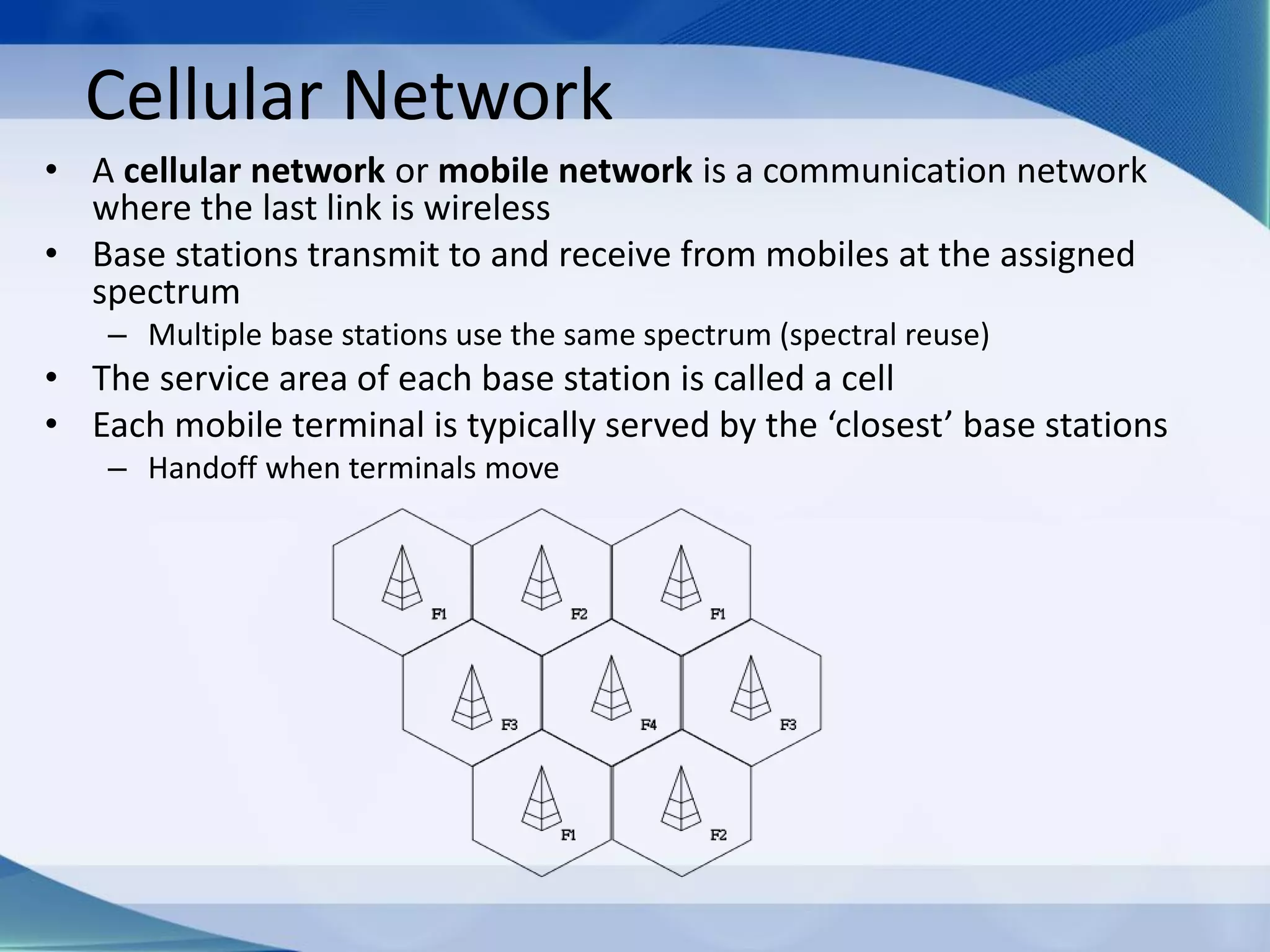
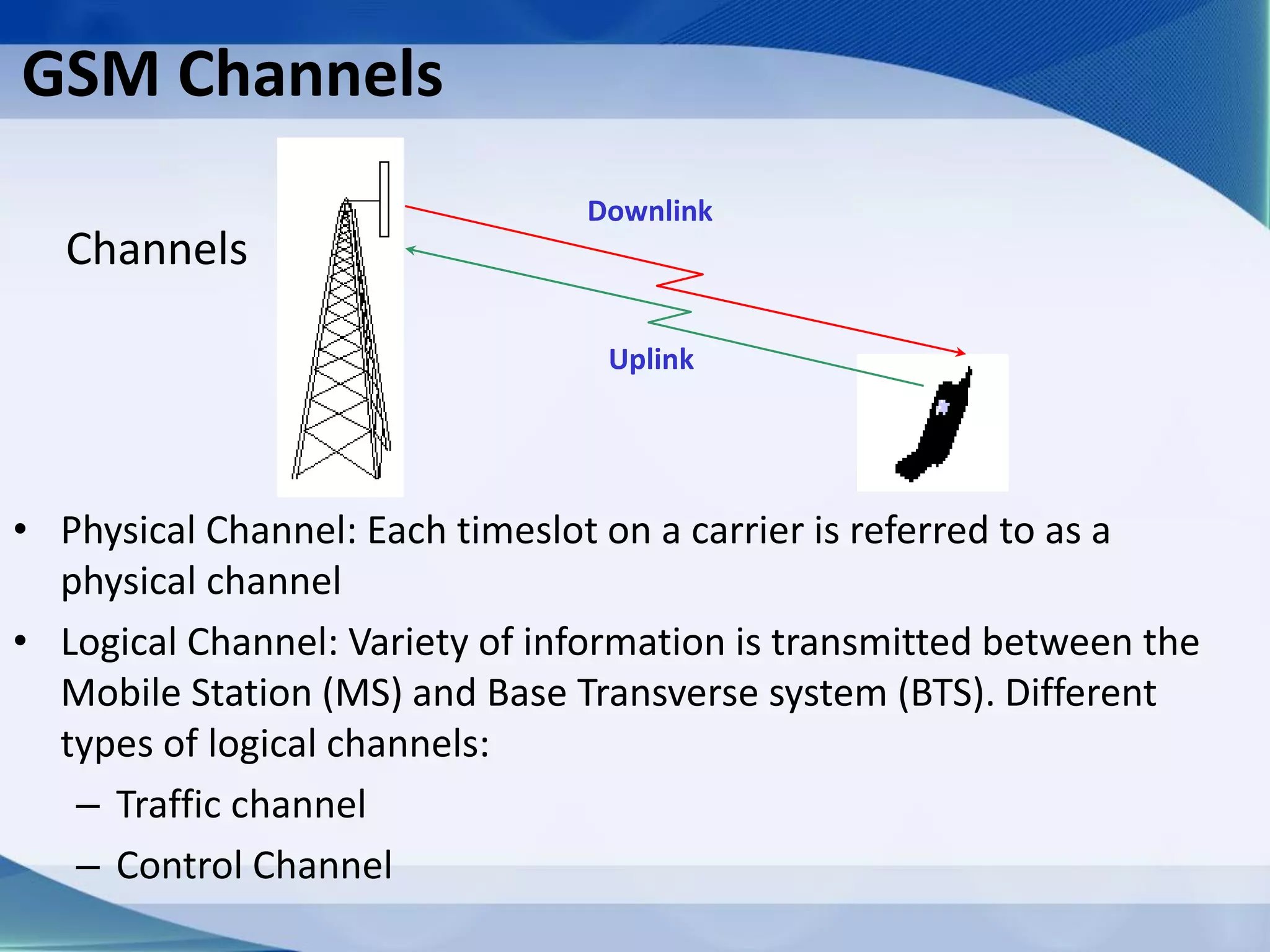
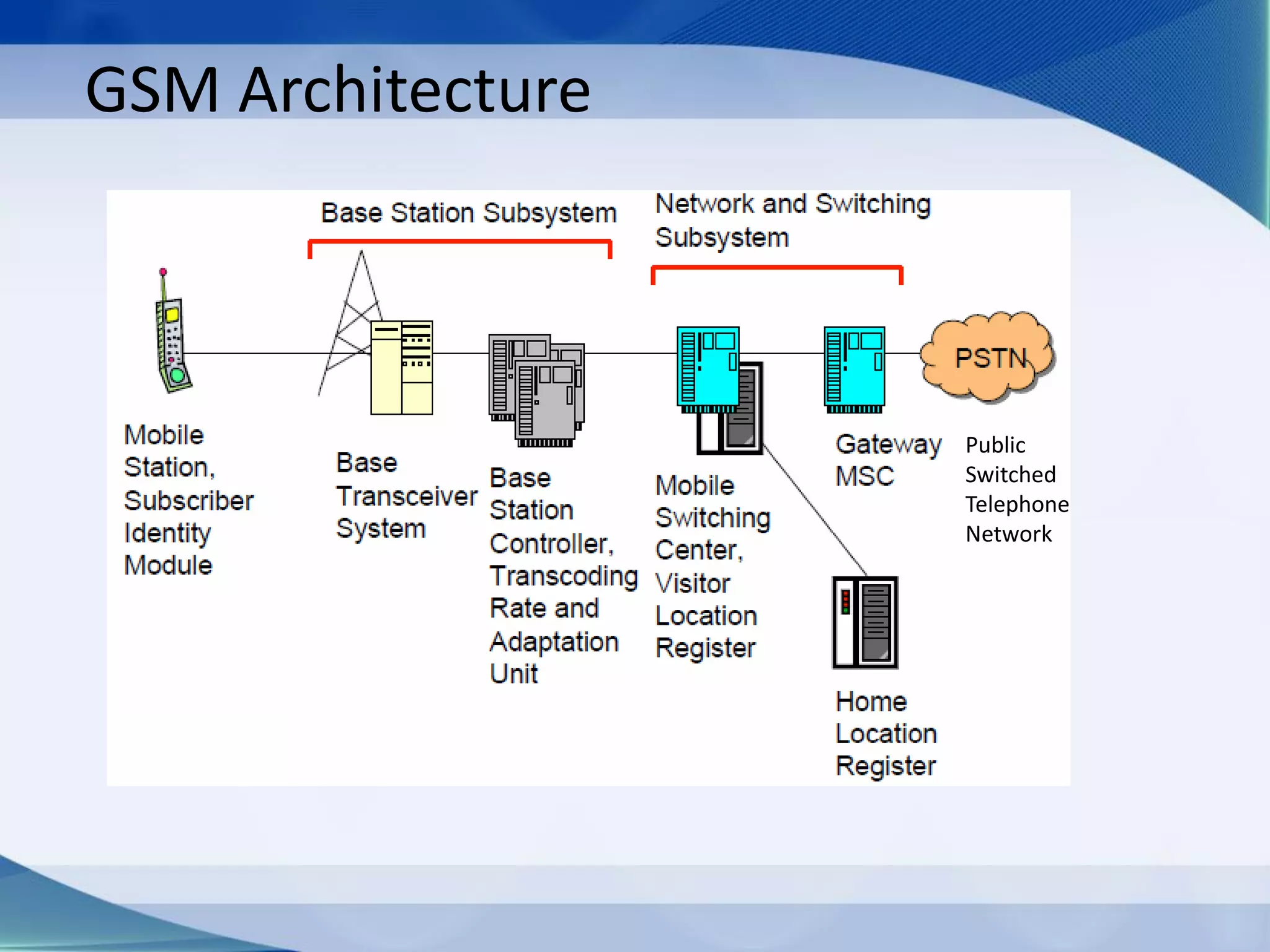
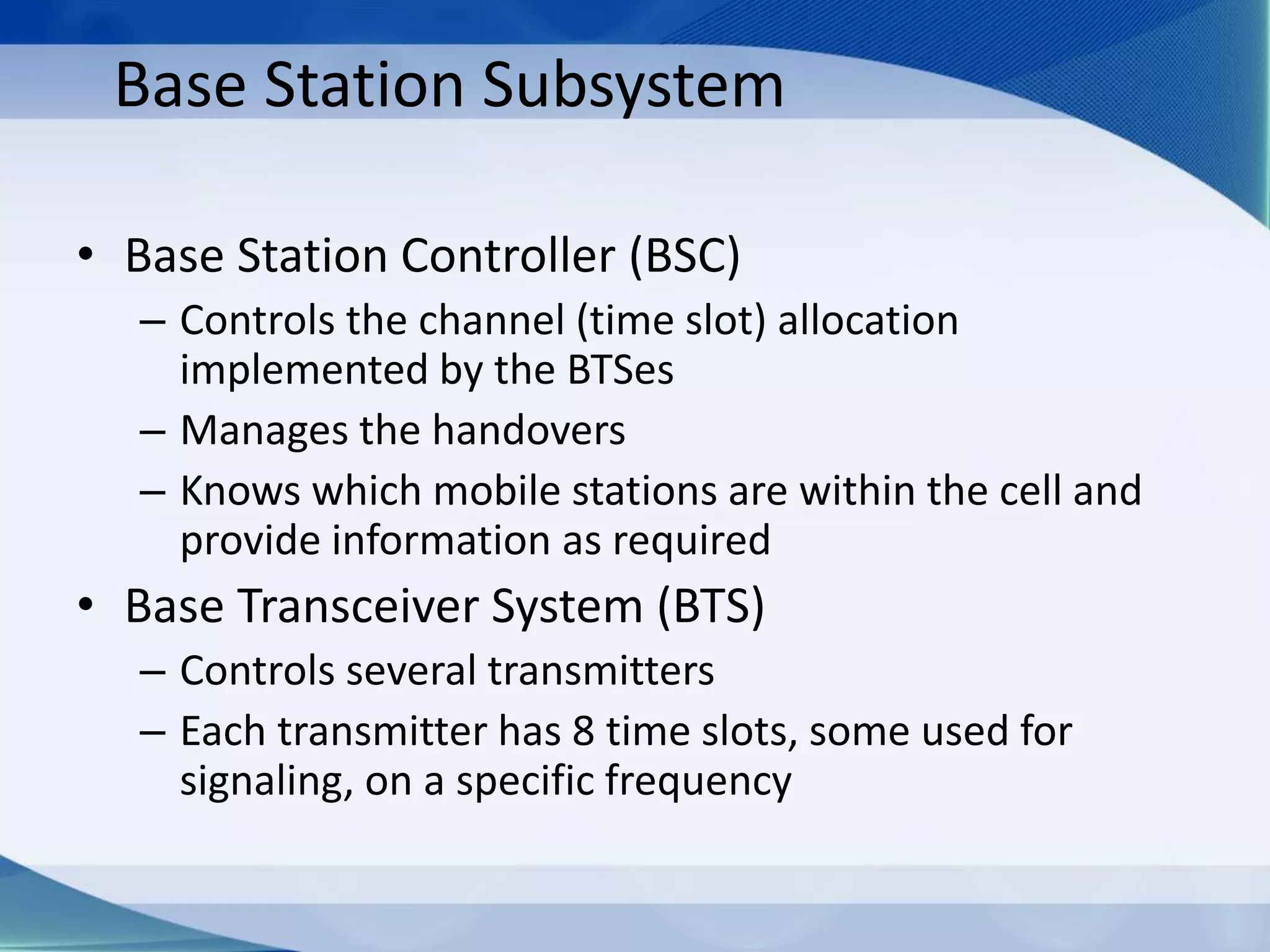
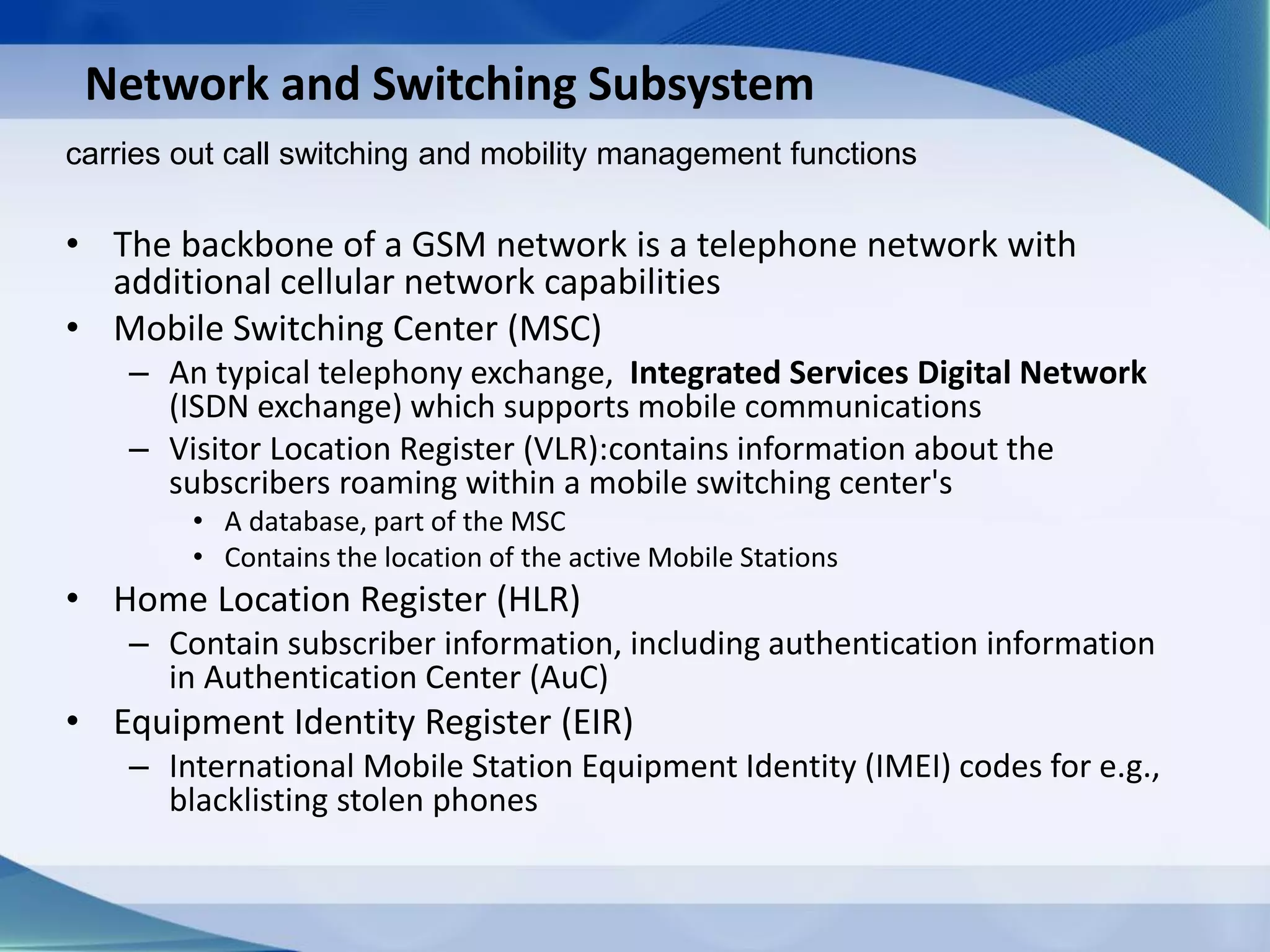
1. Cellular networks use multiple base stations that transmit and receive from mobile devices using assigned frequencies to allow frequency reuse and increase both coverage and capacity.
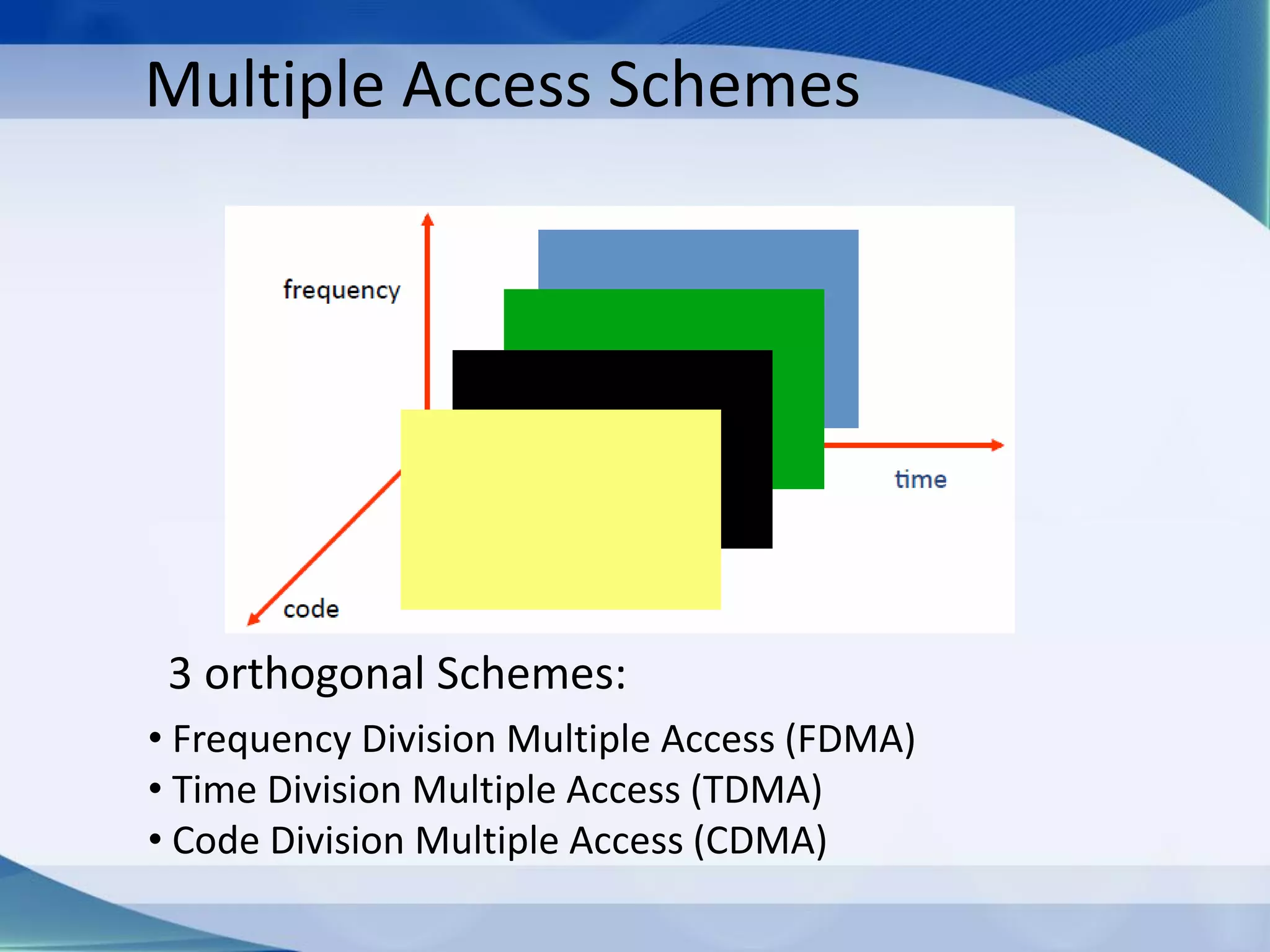
2. Multiple access schemes like FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA allow multiple users to access the network simultaneously by dividing the available bandwidth.
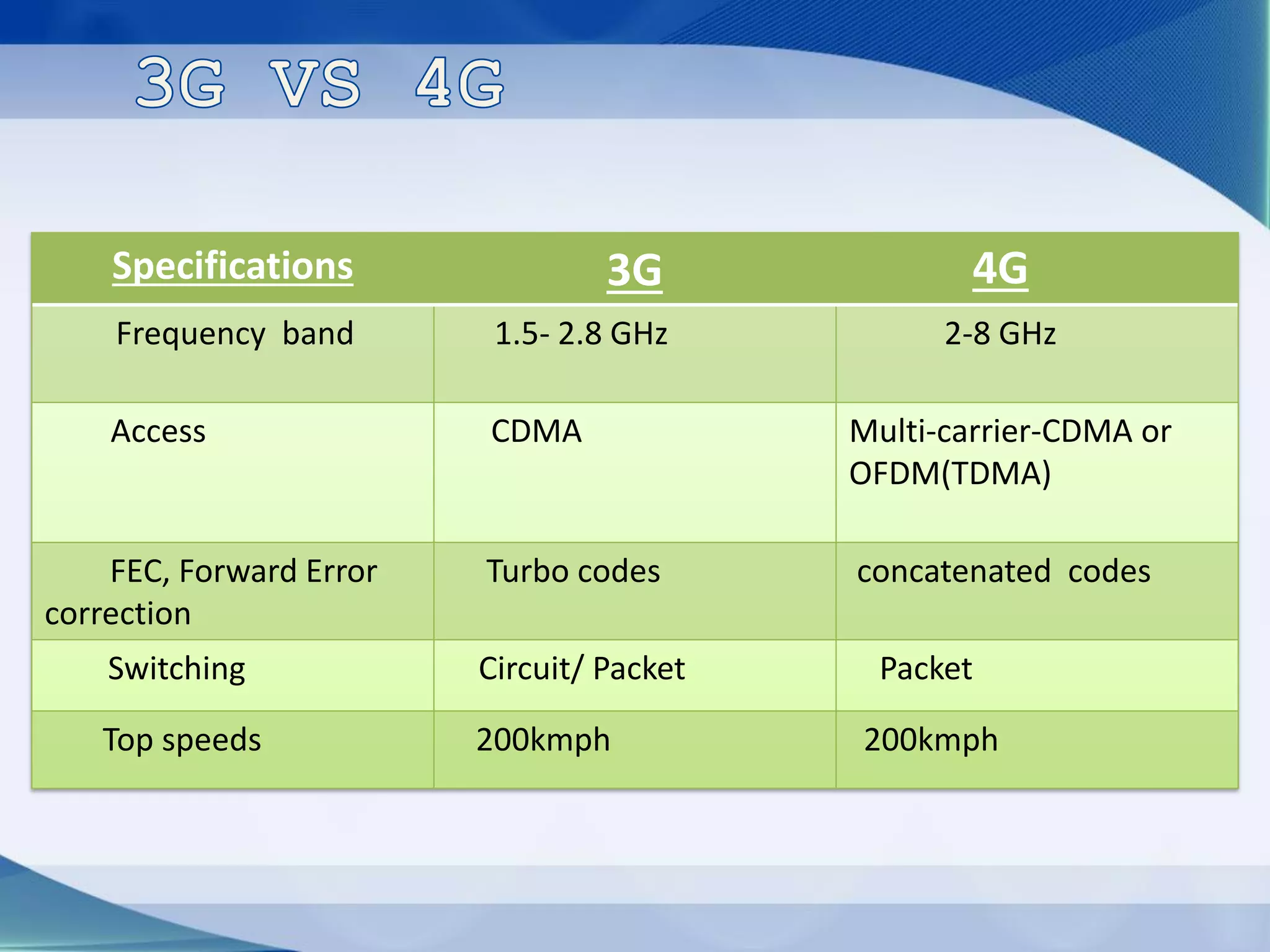
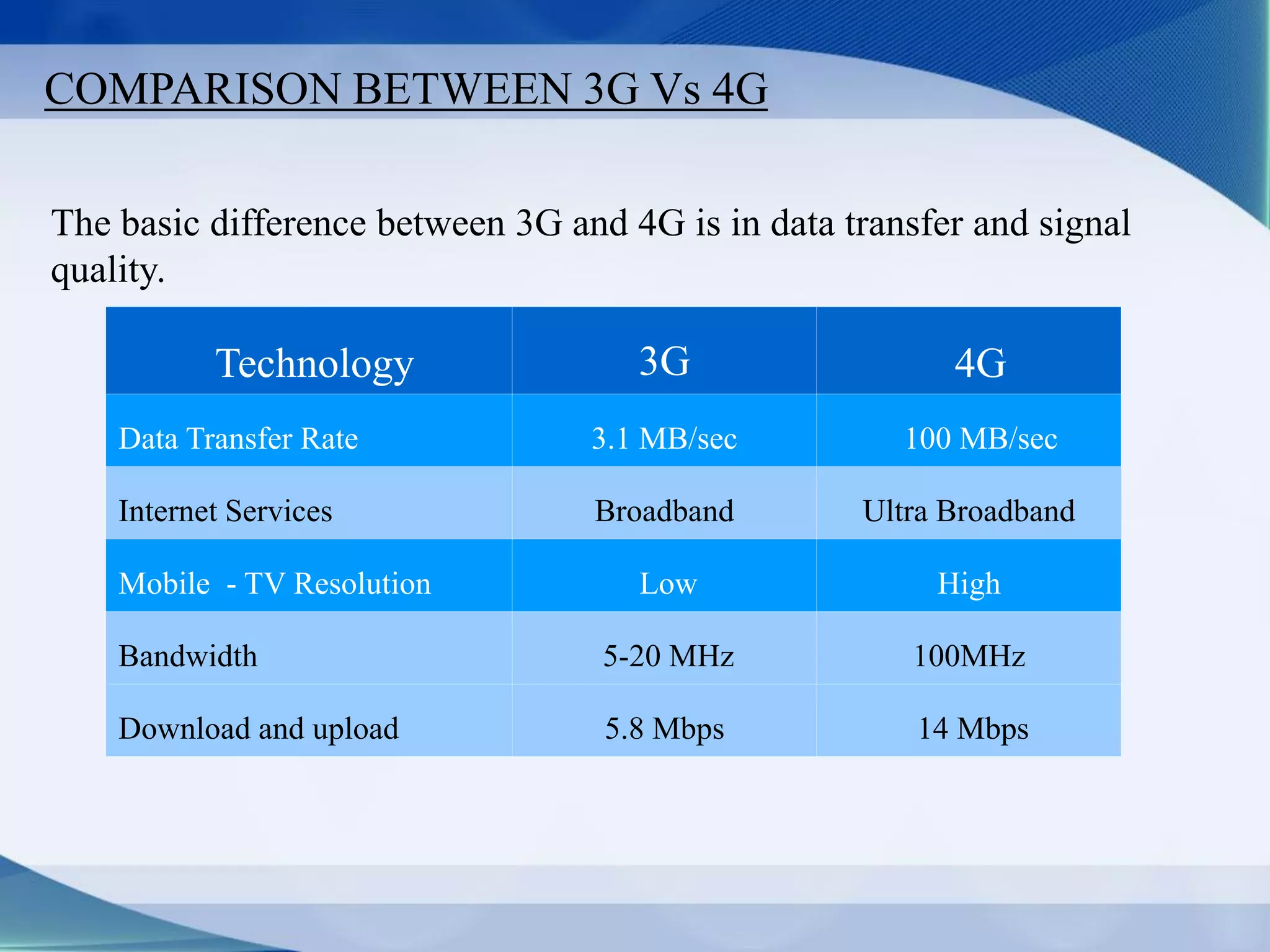
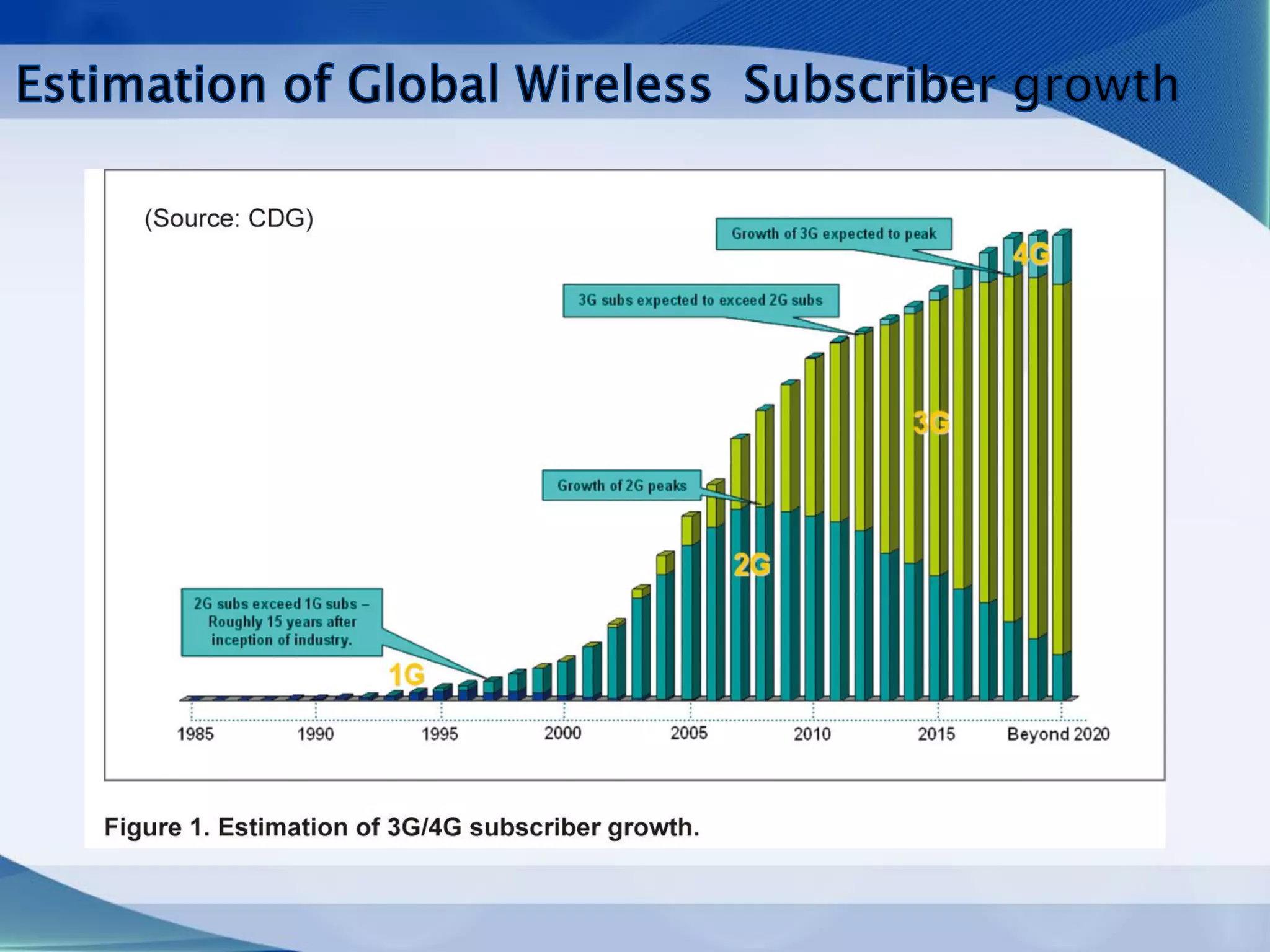
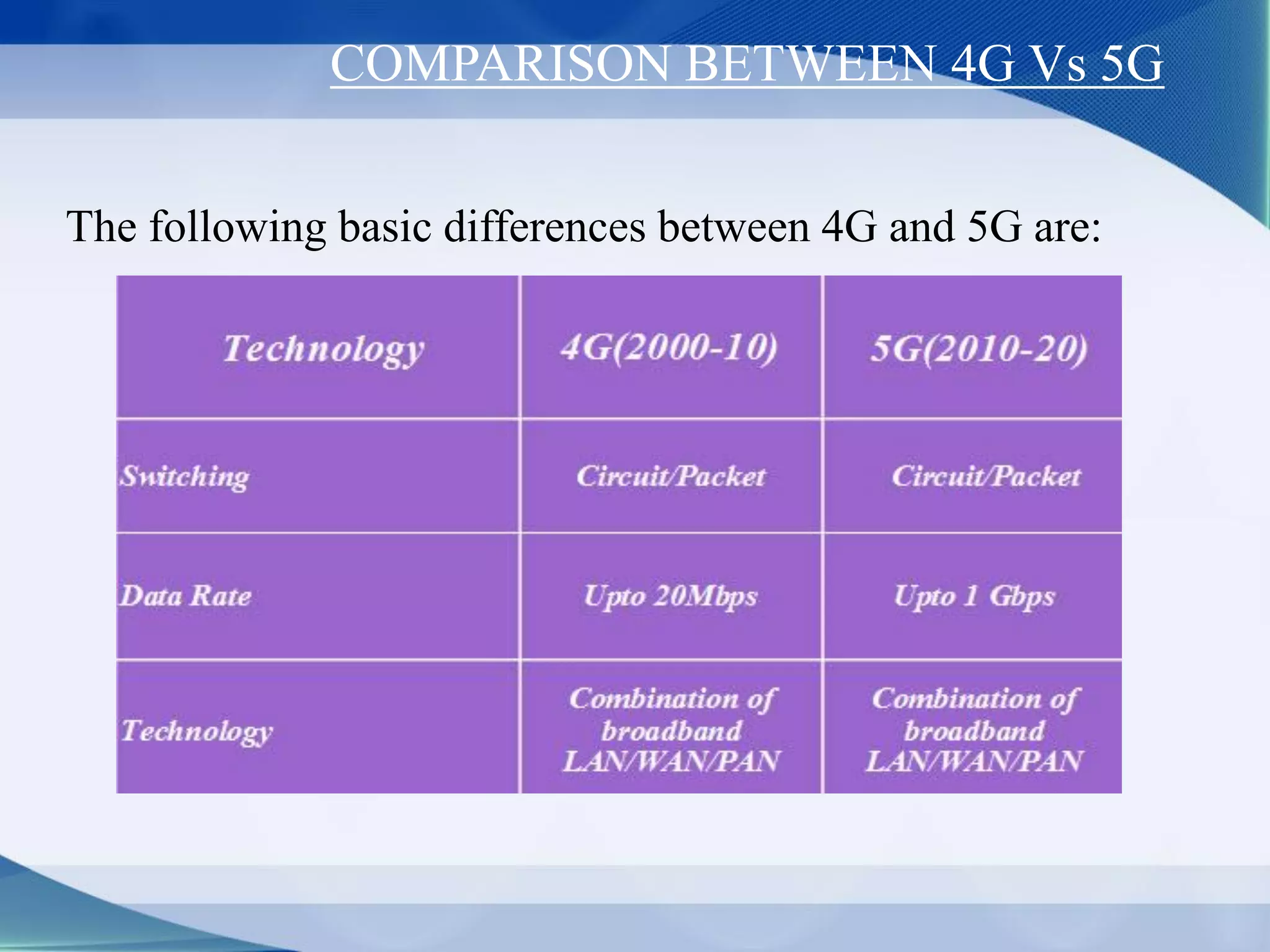
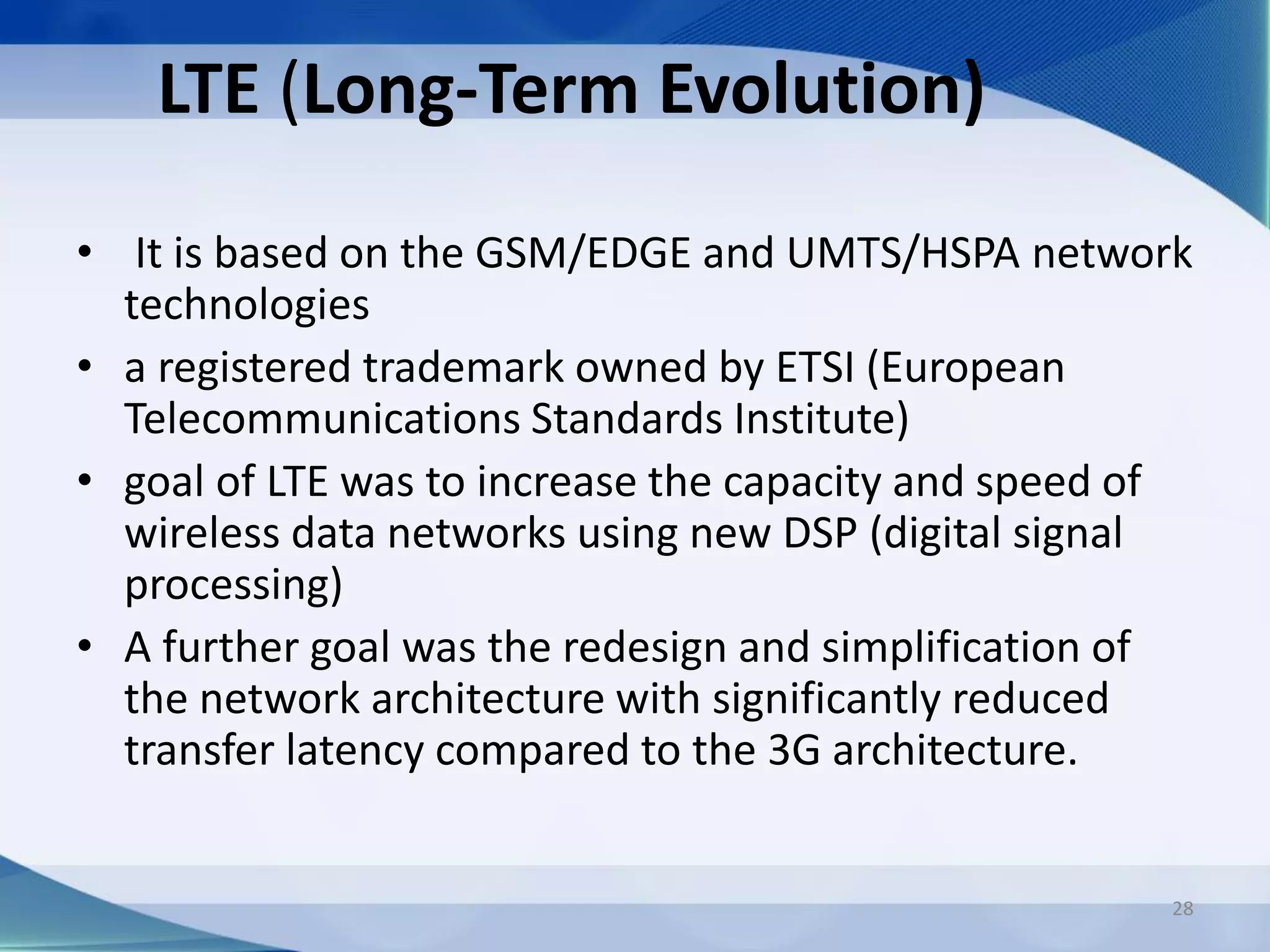
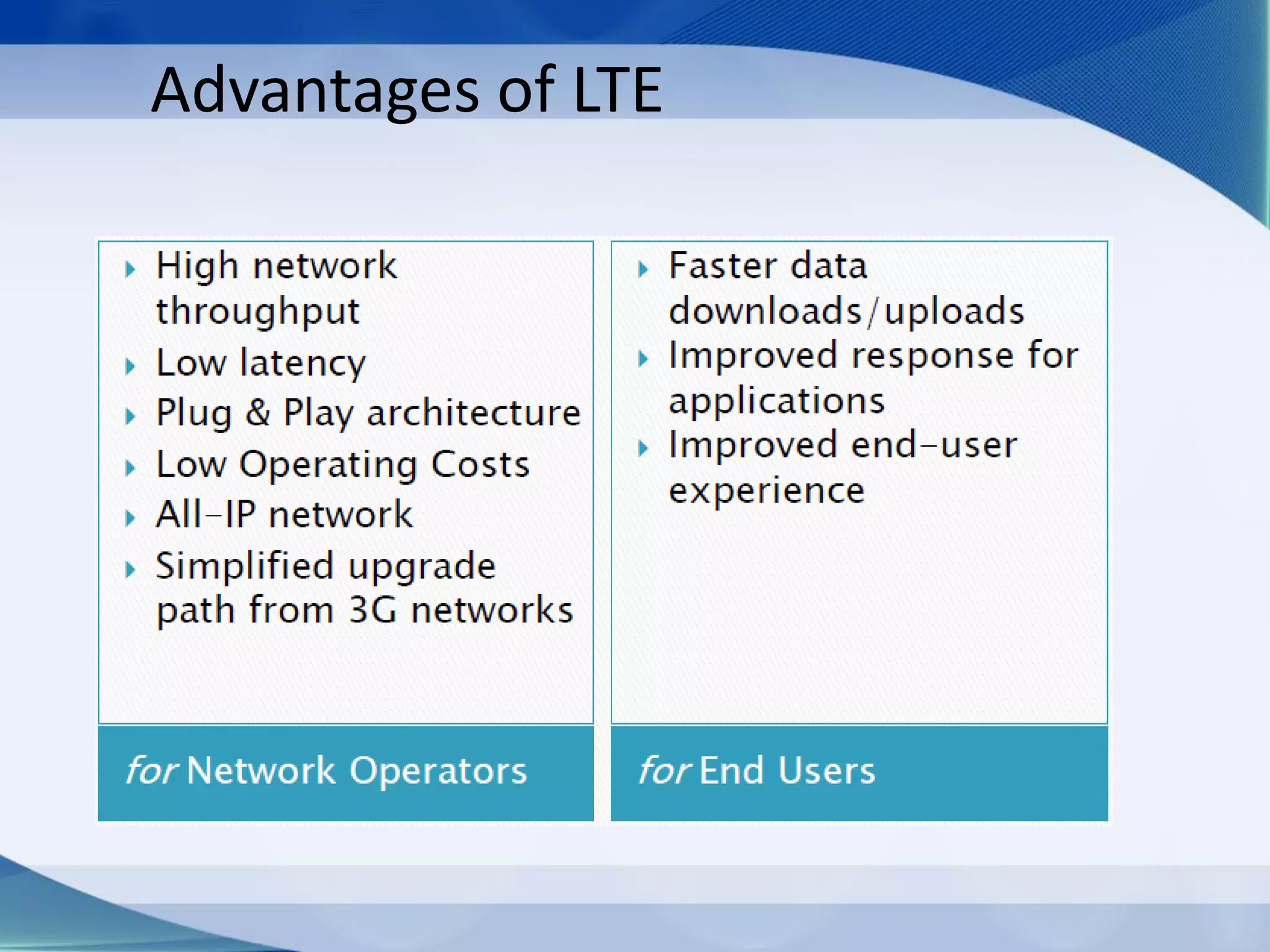
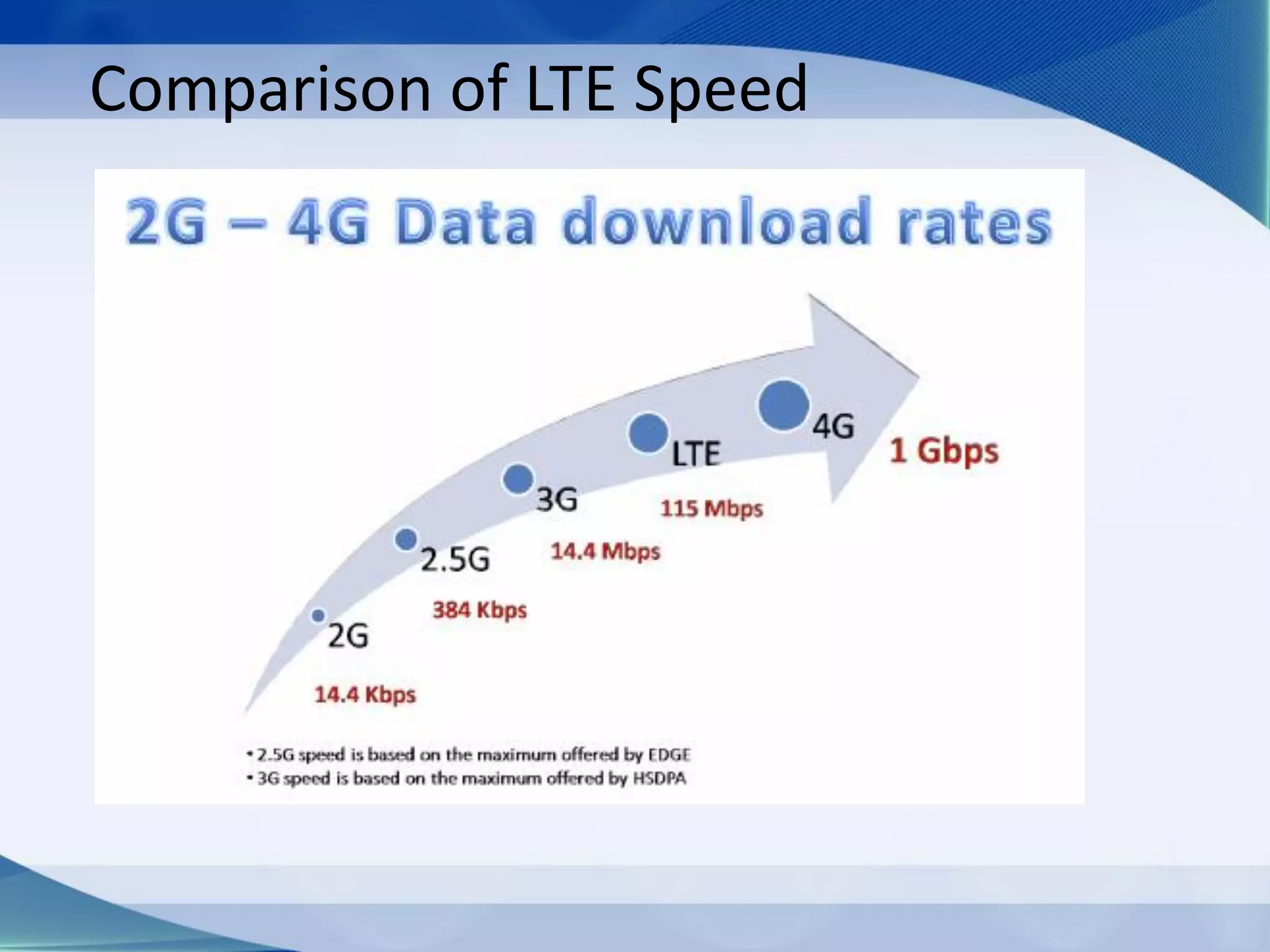
3. Generations of cellular networks have increased capabilities with 2G supporting digital signals and data, 3G allowing faster data rates including video calls, and 4G providing high-speed multimedia access.