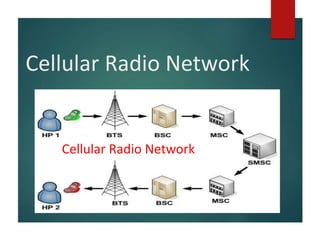
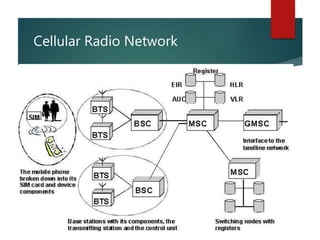
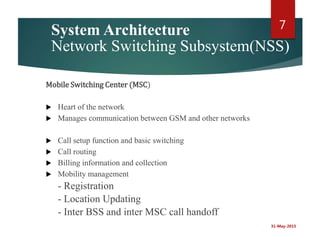
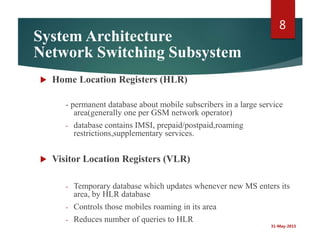
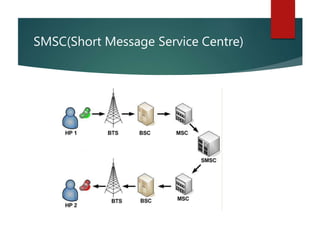
A cellular radio network consists of cells served by base stations that communicate with mobile stations (MS), which include mobile equipment and SIM cards. The network architecture is divided into three main components: the Base Station Subsystem (BSS), which manages communication between the mobile stations and base stations, and the Network Switching Subsystem (NSS), which oversees call management and routing. Key elements include the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), Home Location Register (HLR), Visitor Location Register (VLR), and authentication for security.