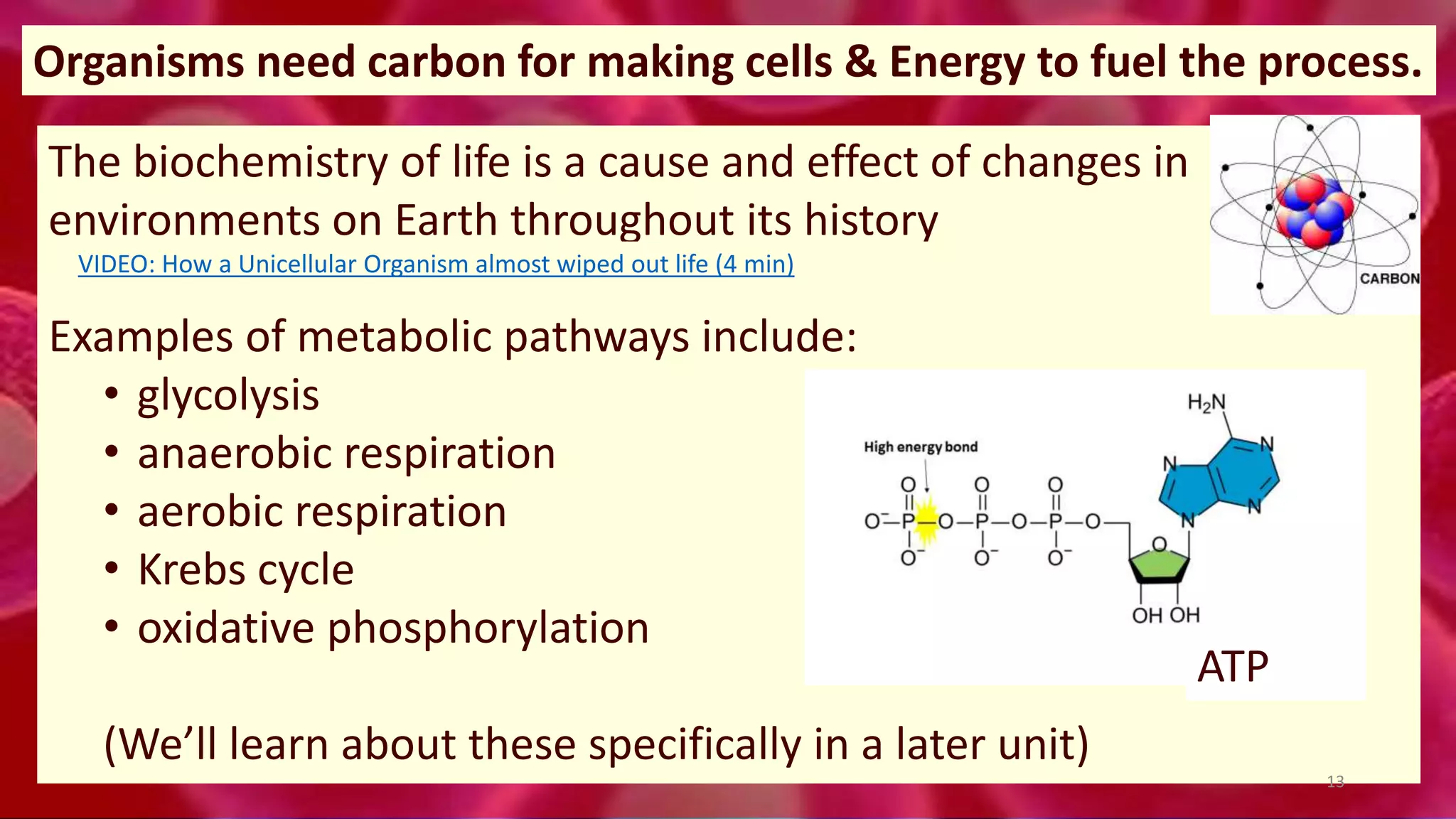
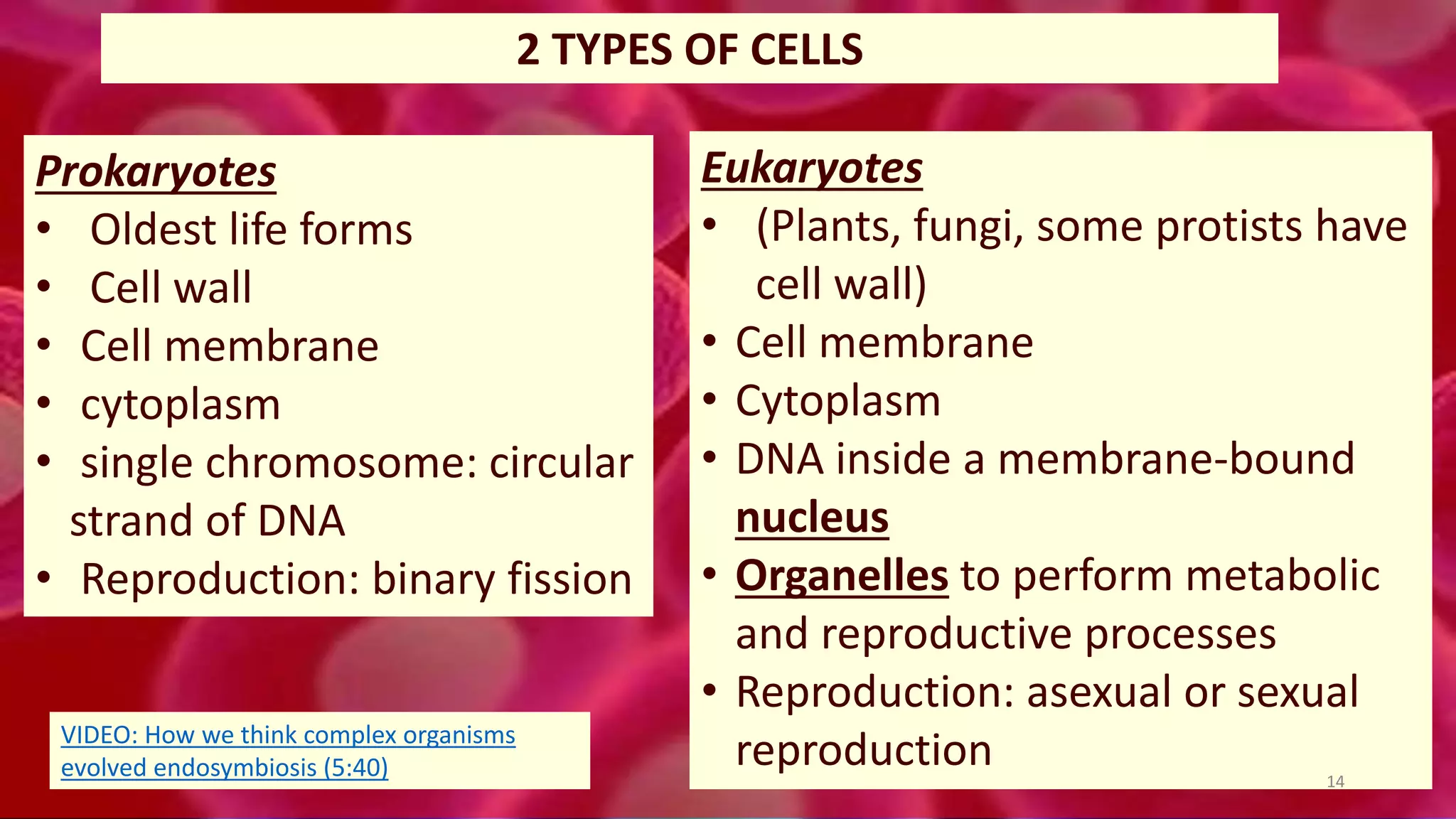
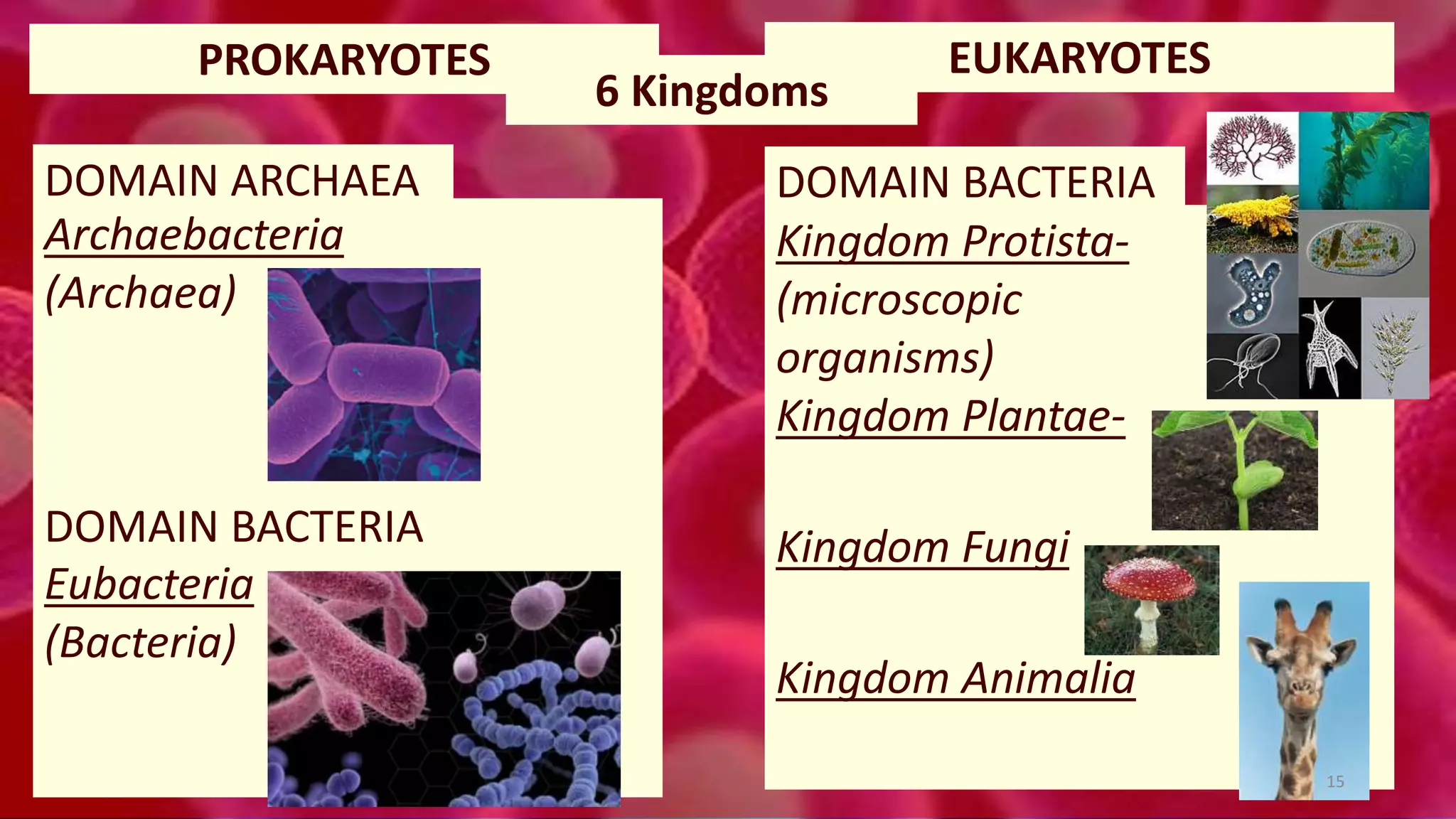
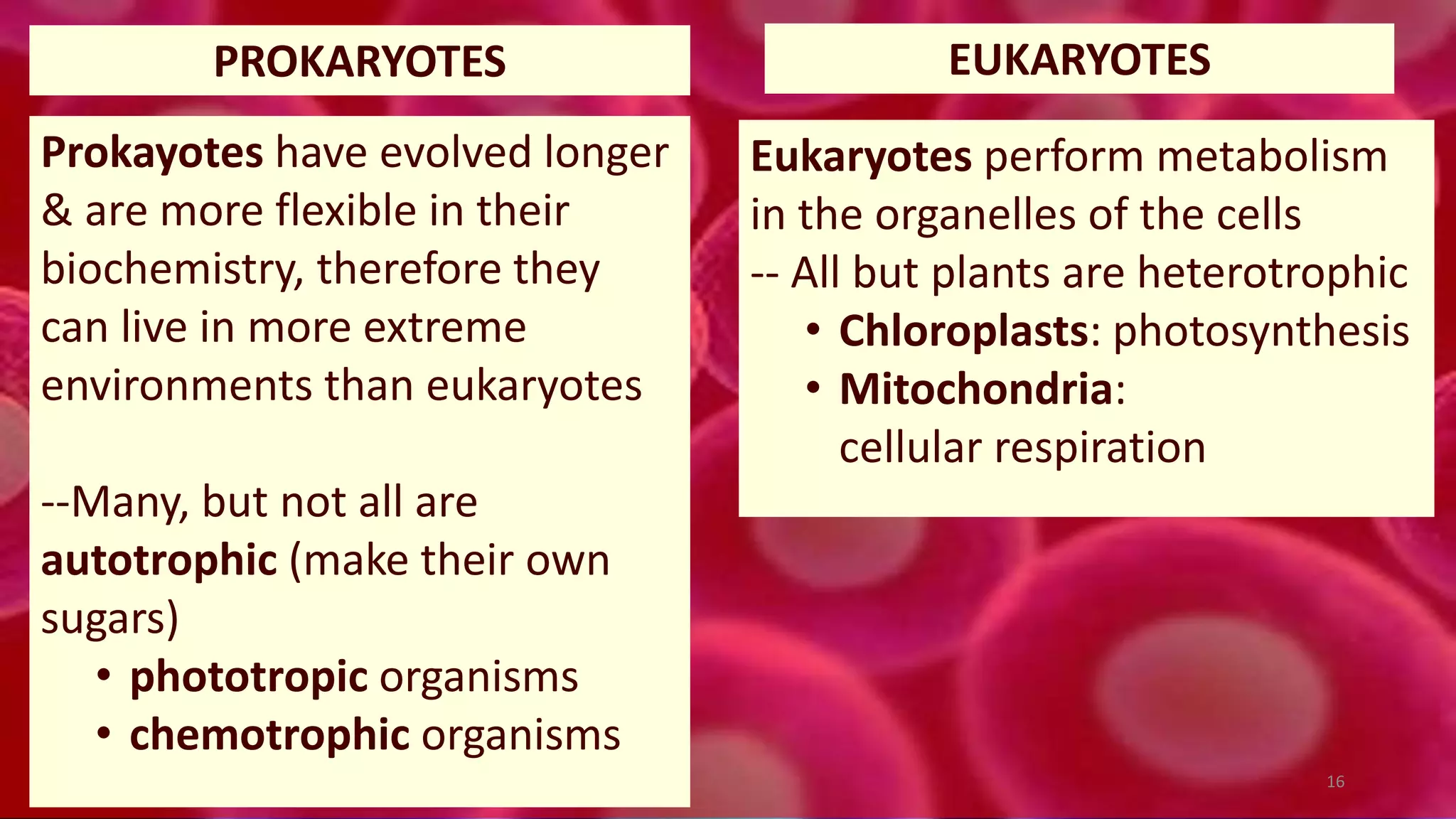
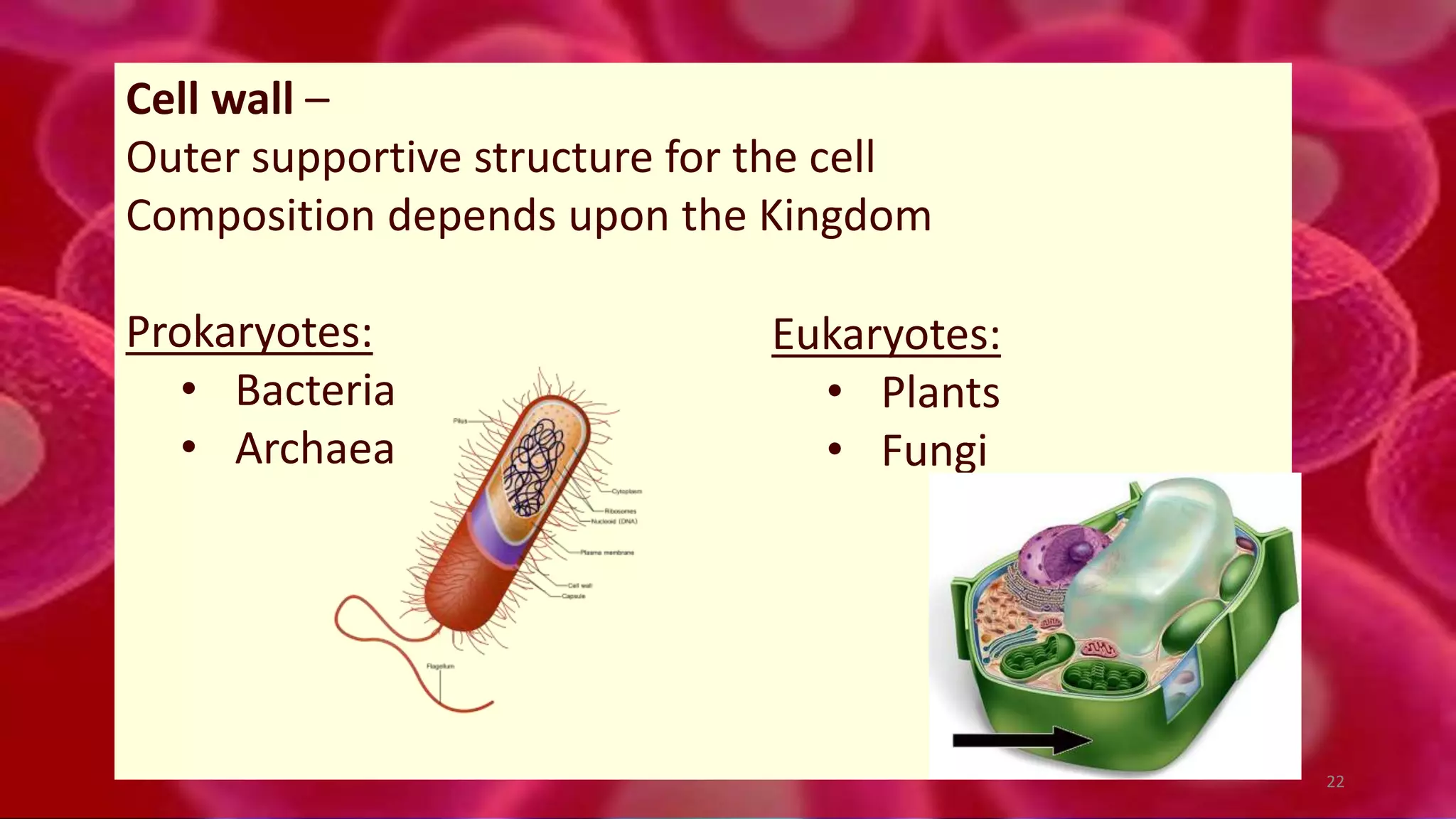
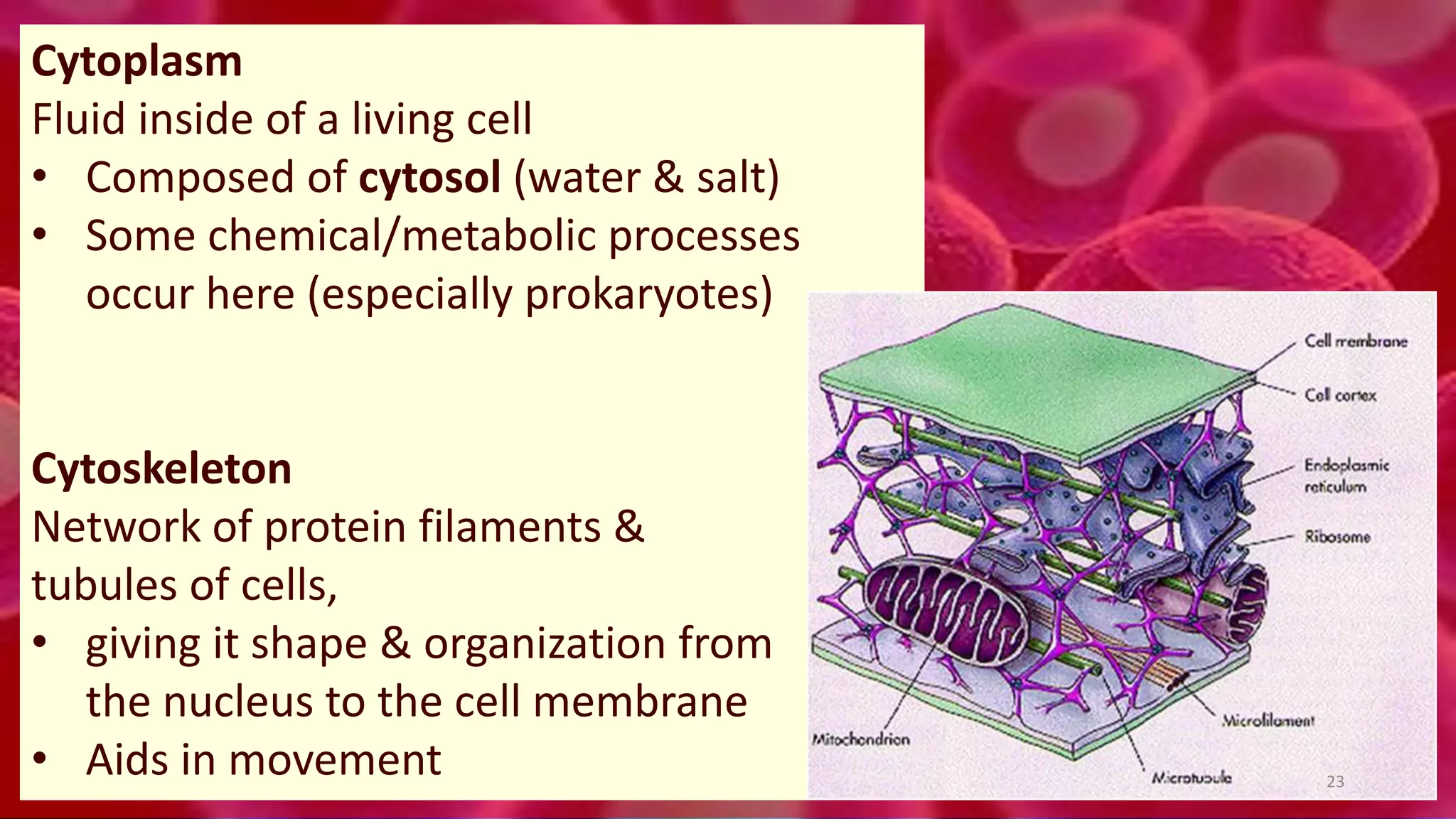
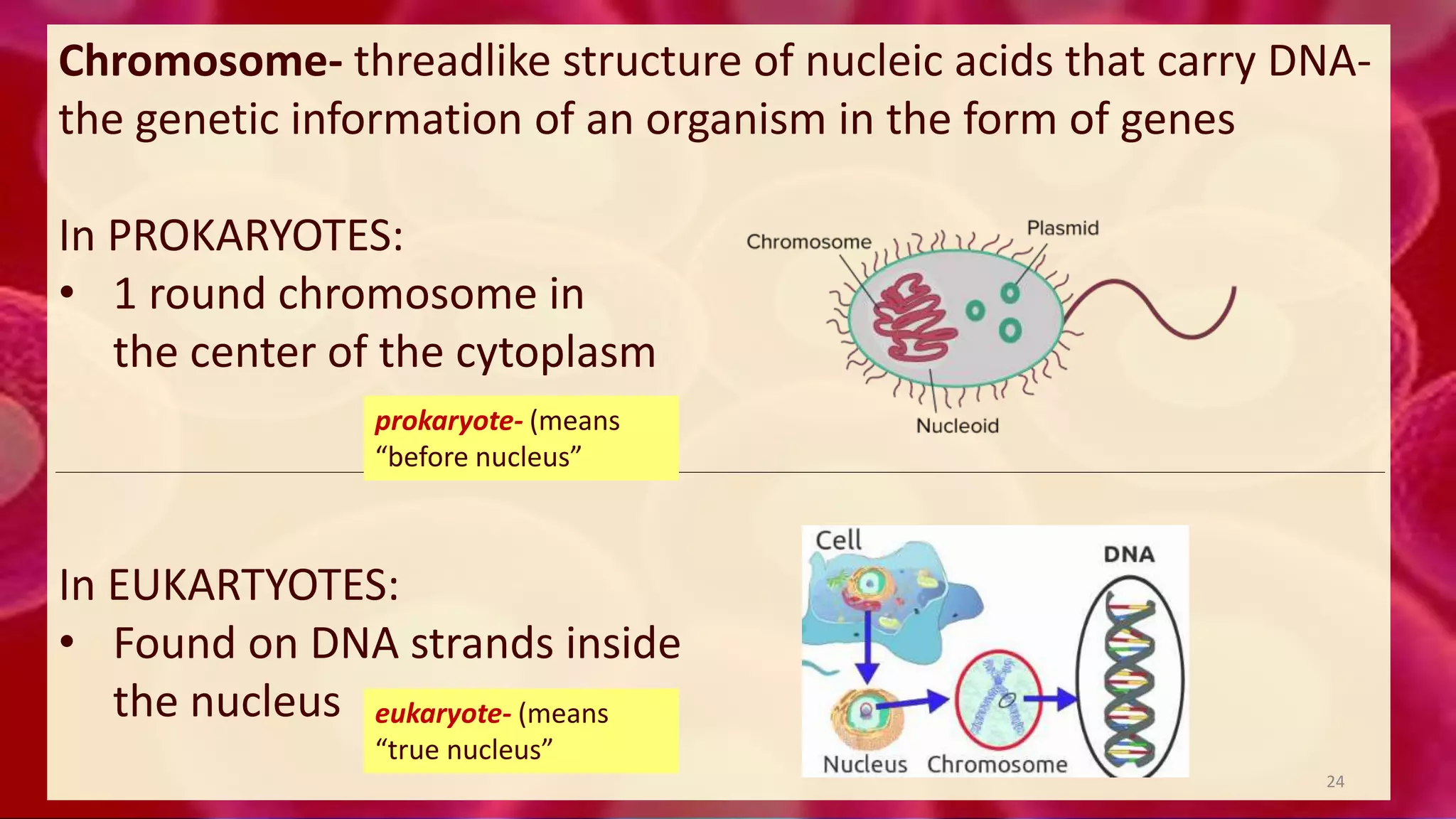
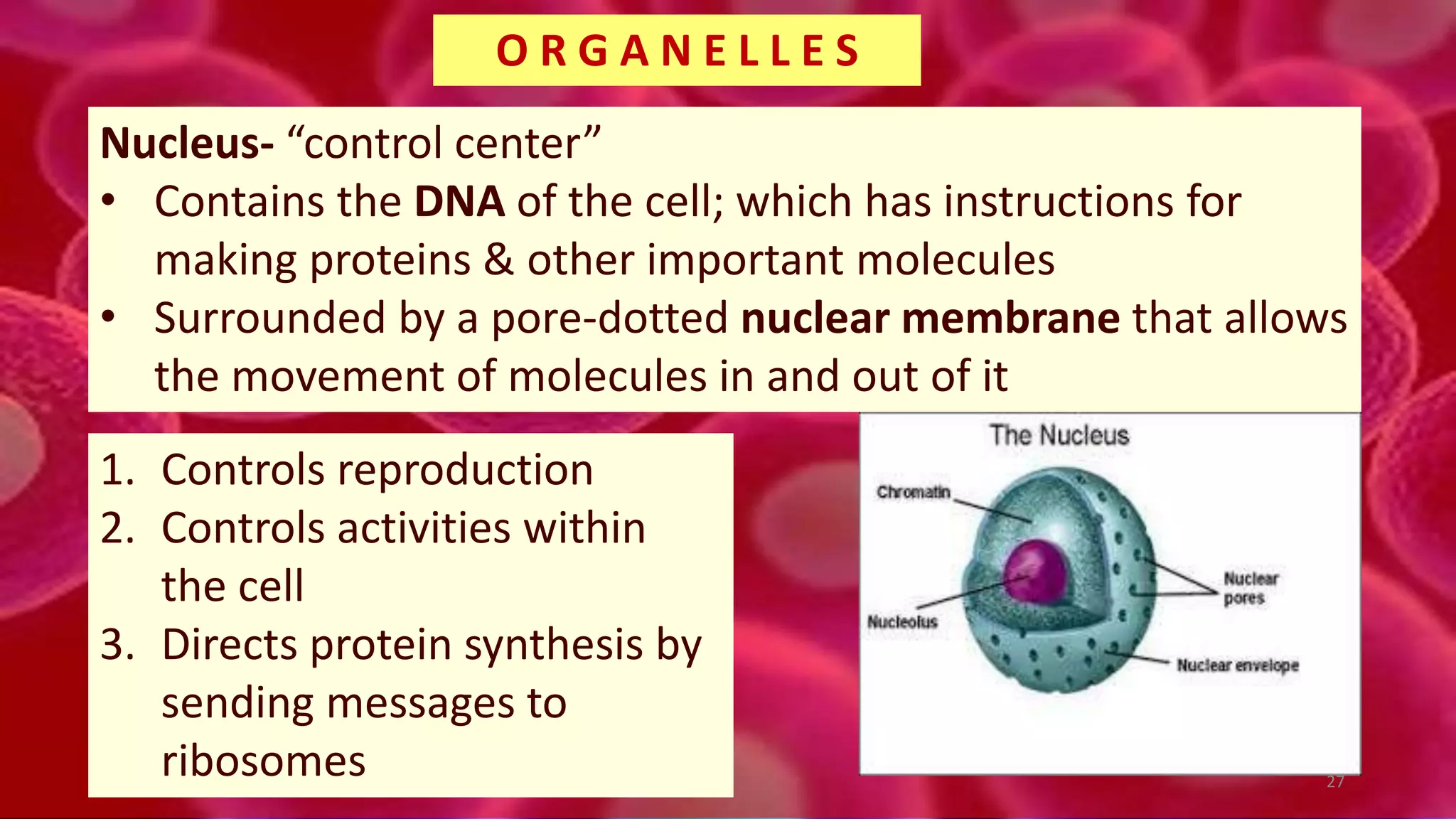
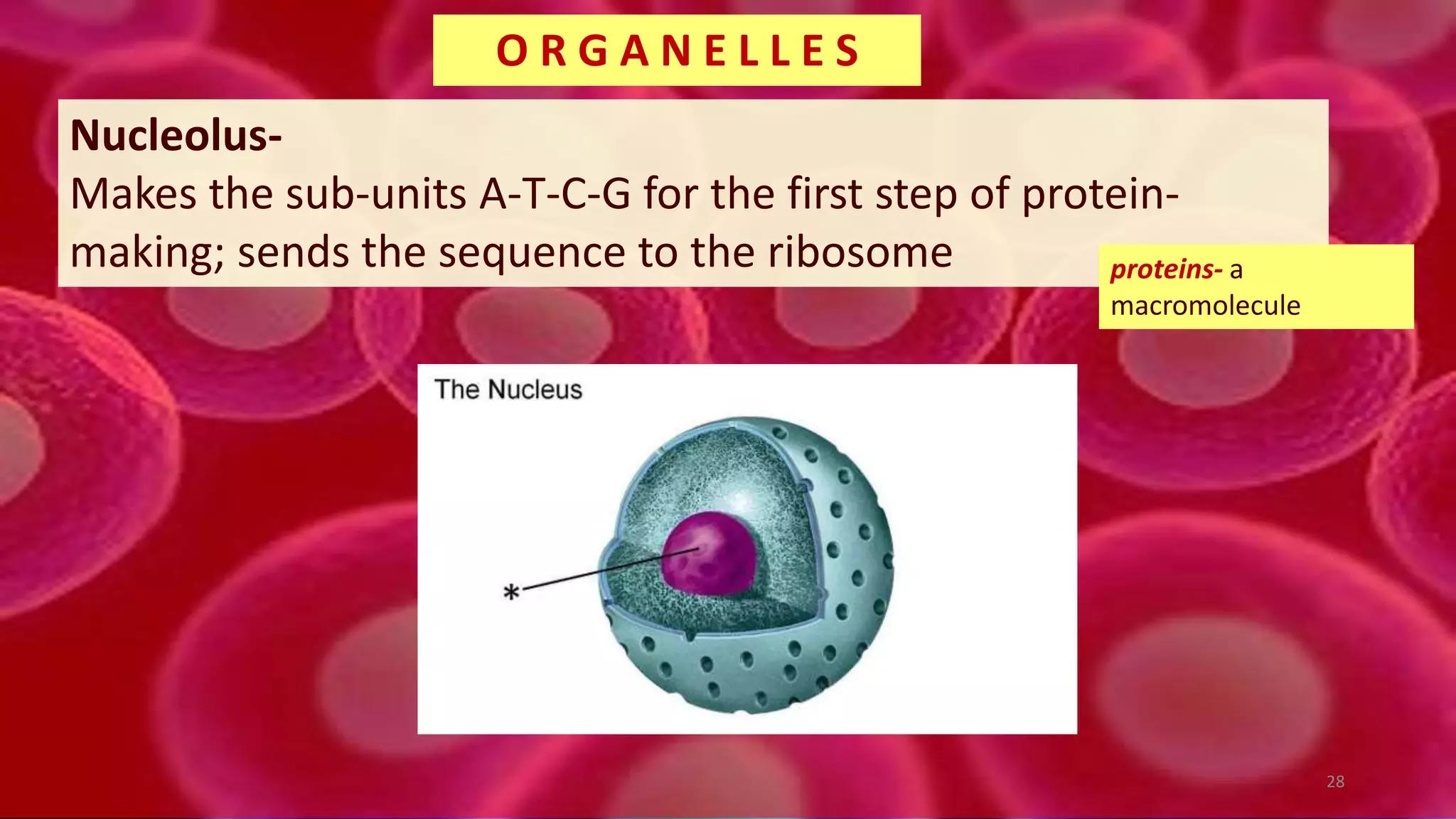
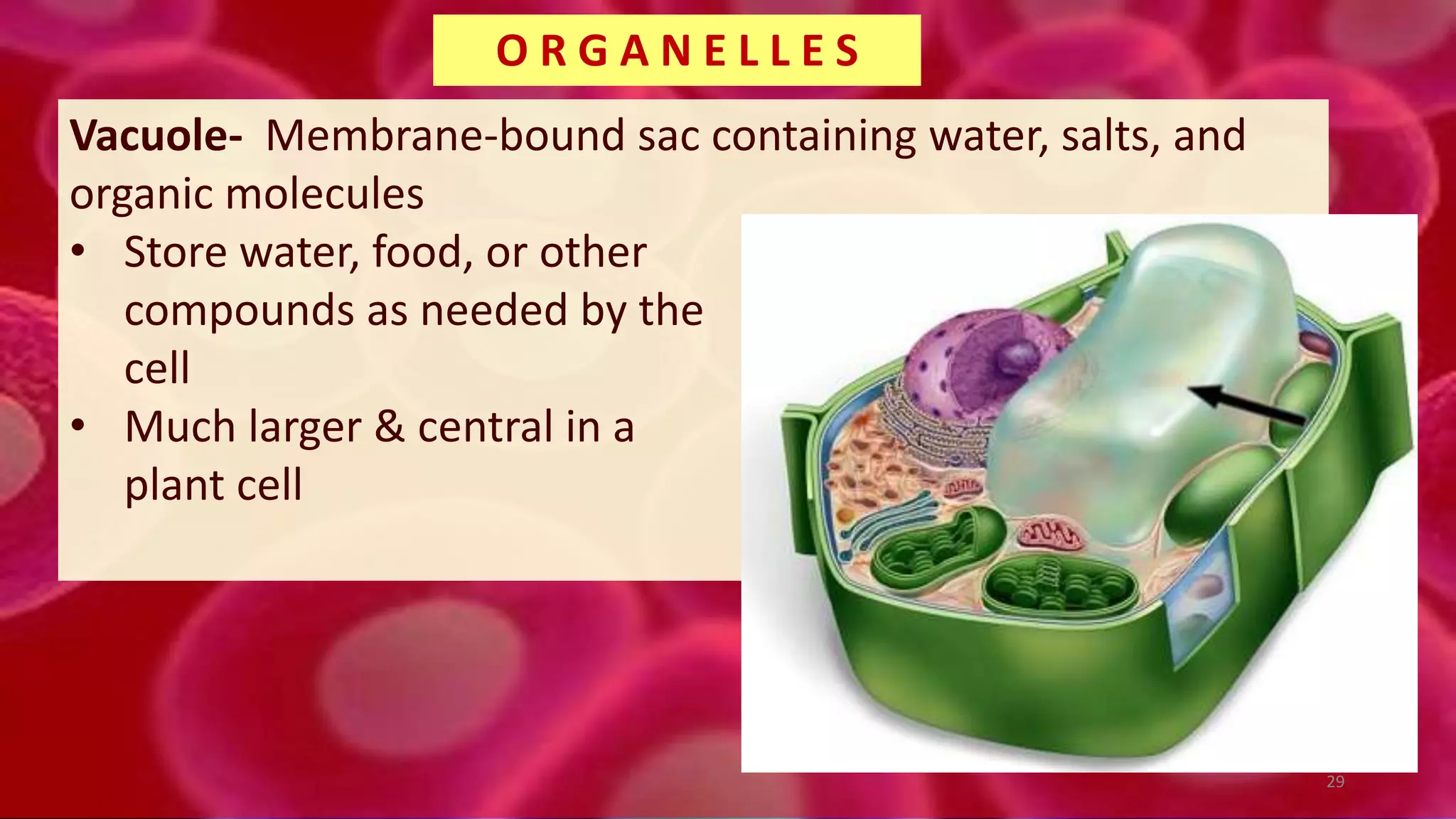
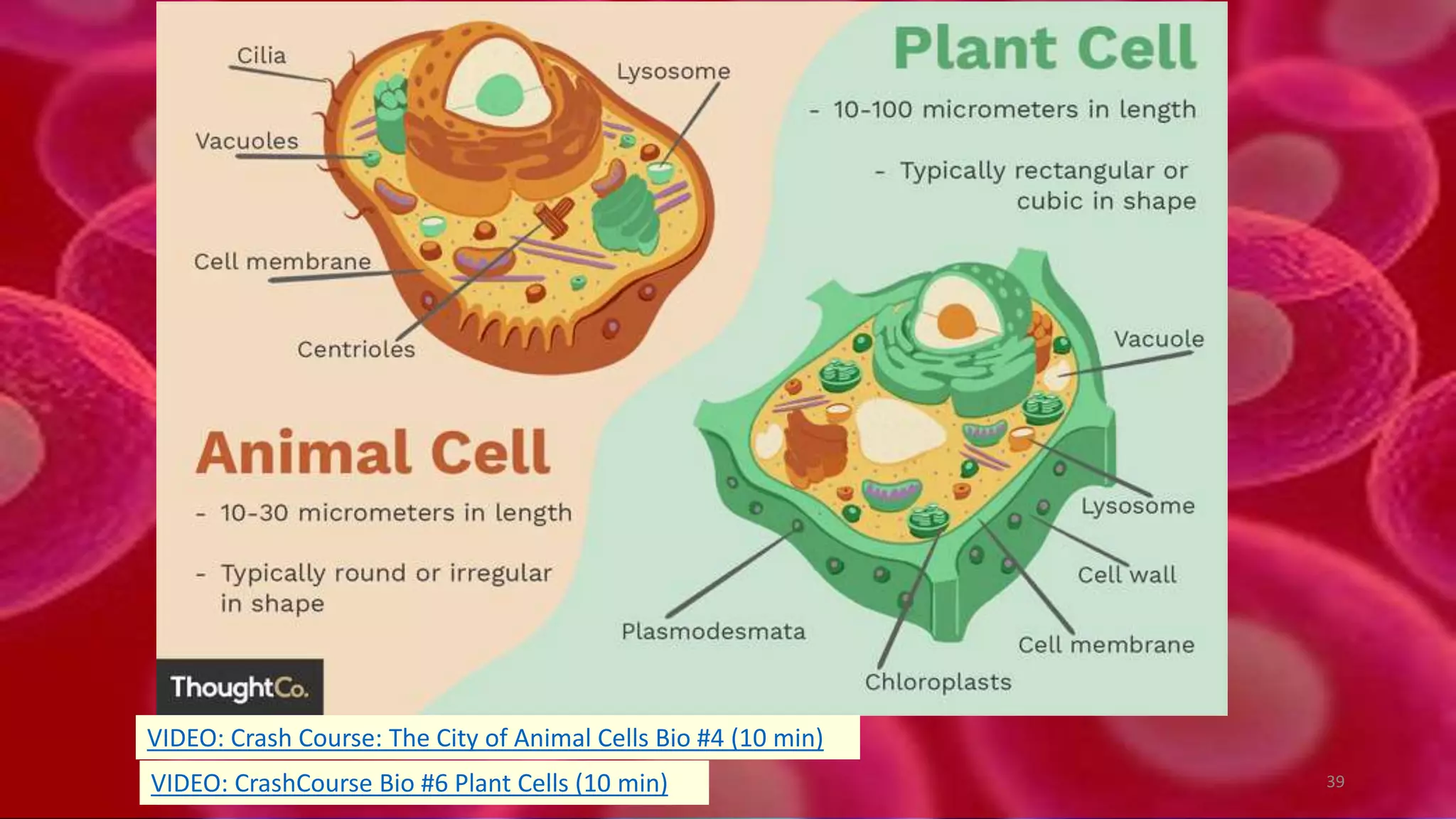
1. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells come in two main types - prokaryotic cells that lack a nucleus and eukaryotic cells that have a nucleus enclosed within membranes.
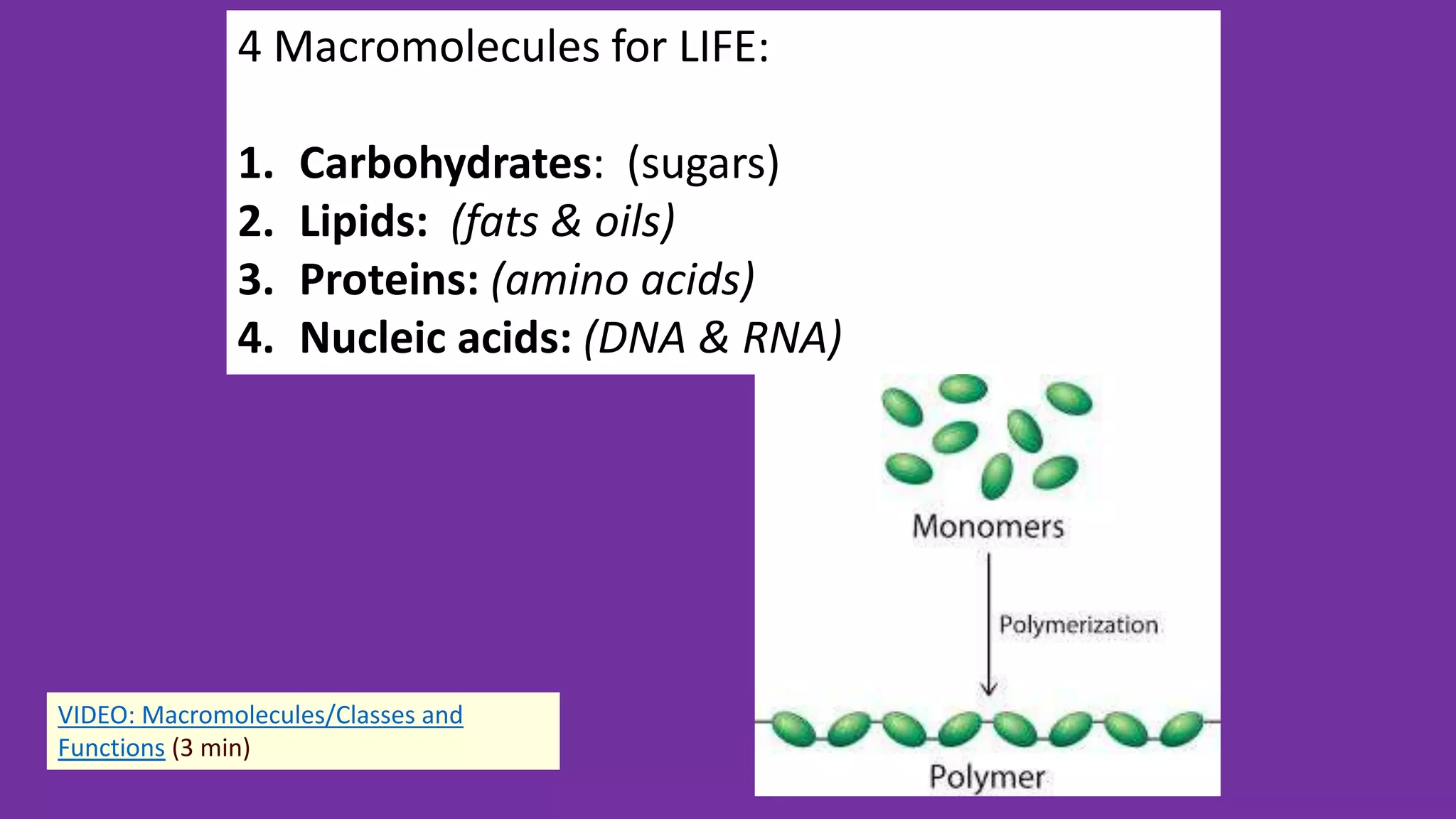
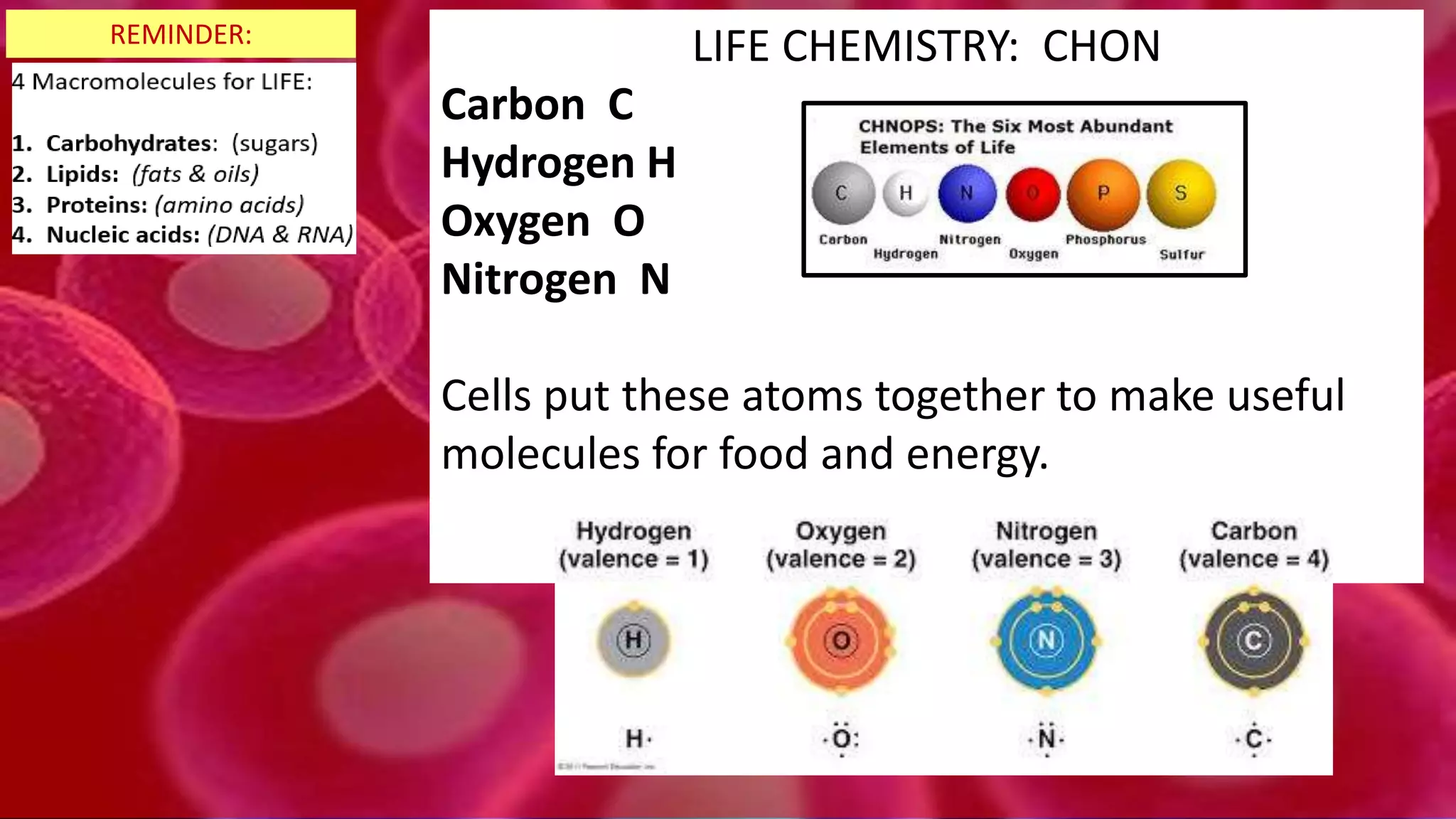
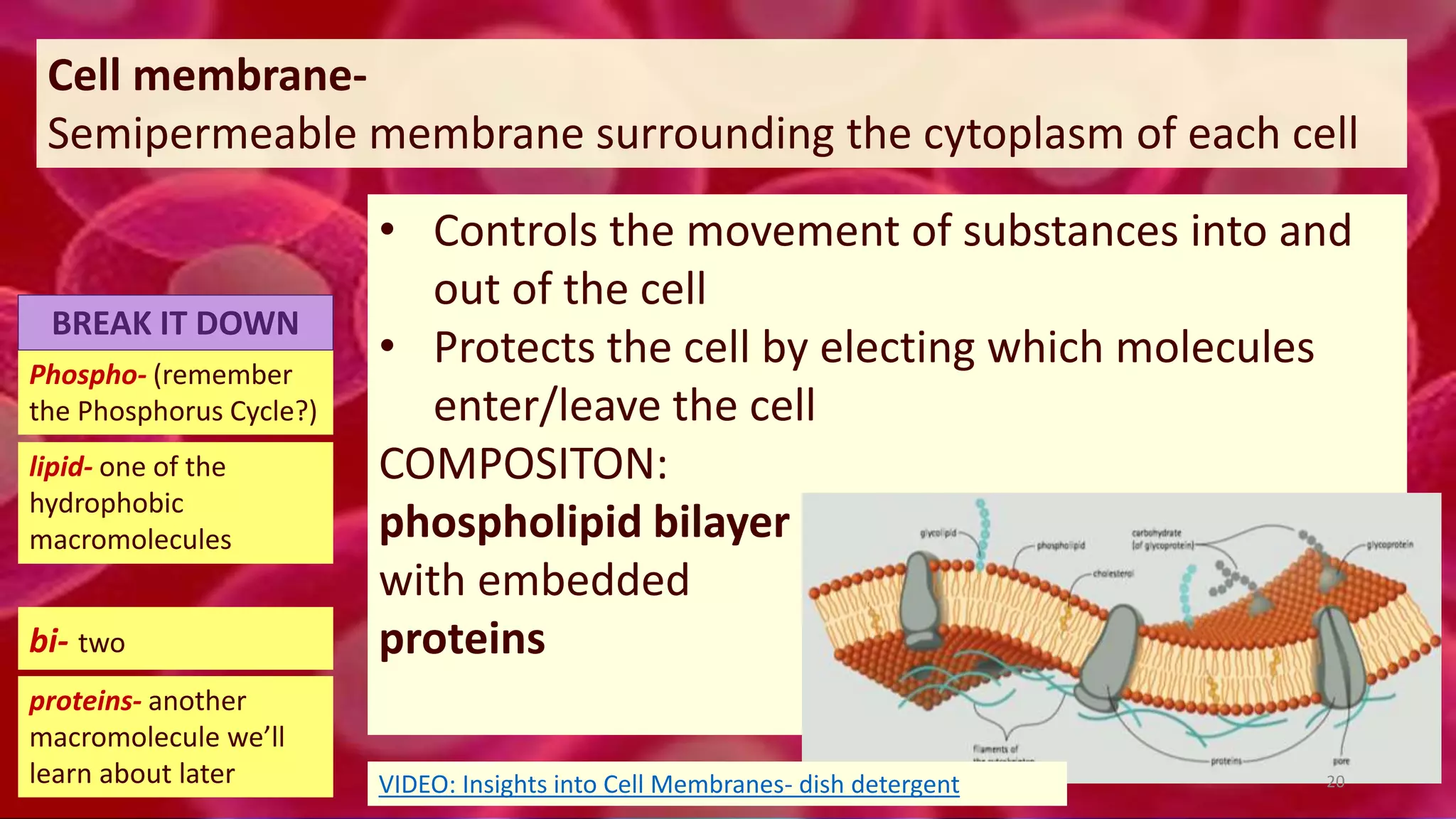
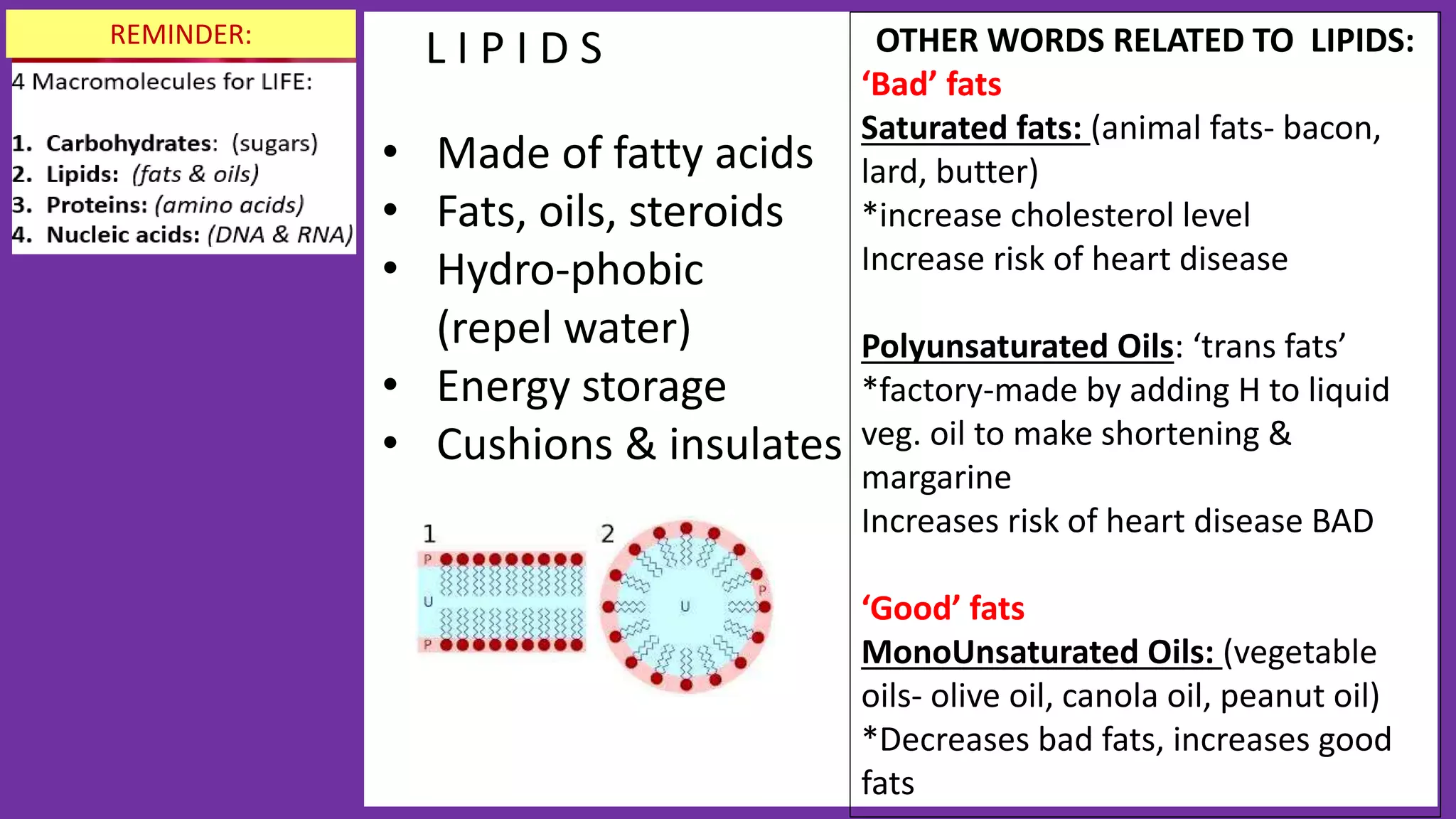
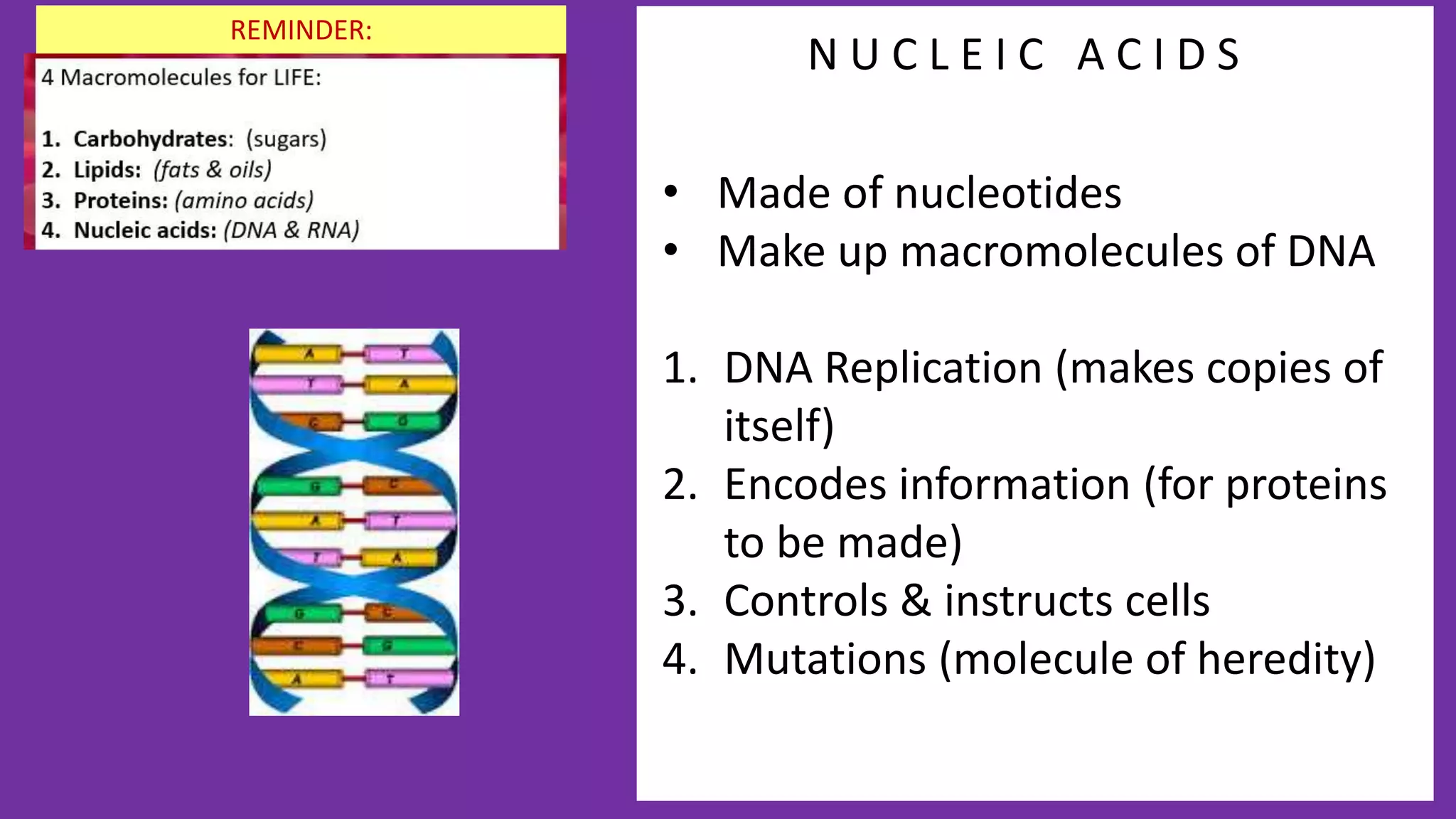
2. All cells contain macromolecules like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids and organelles that allow them to carry out functions necessary for life like metabolism, transport of molecules, and protein production.
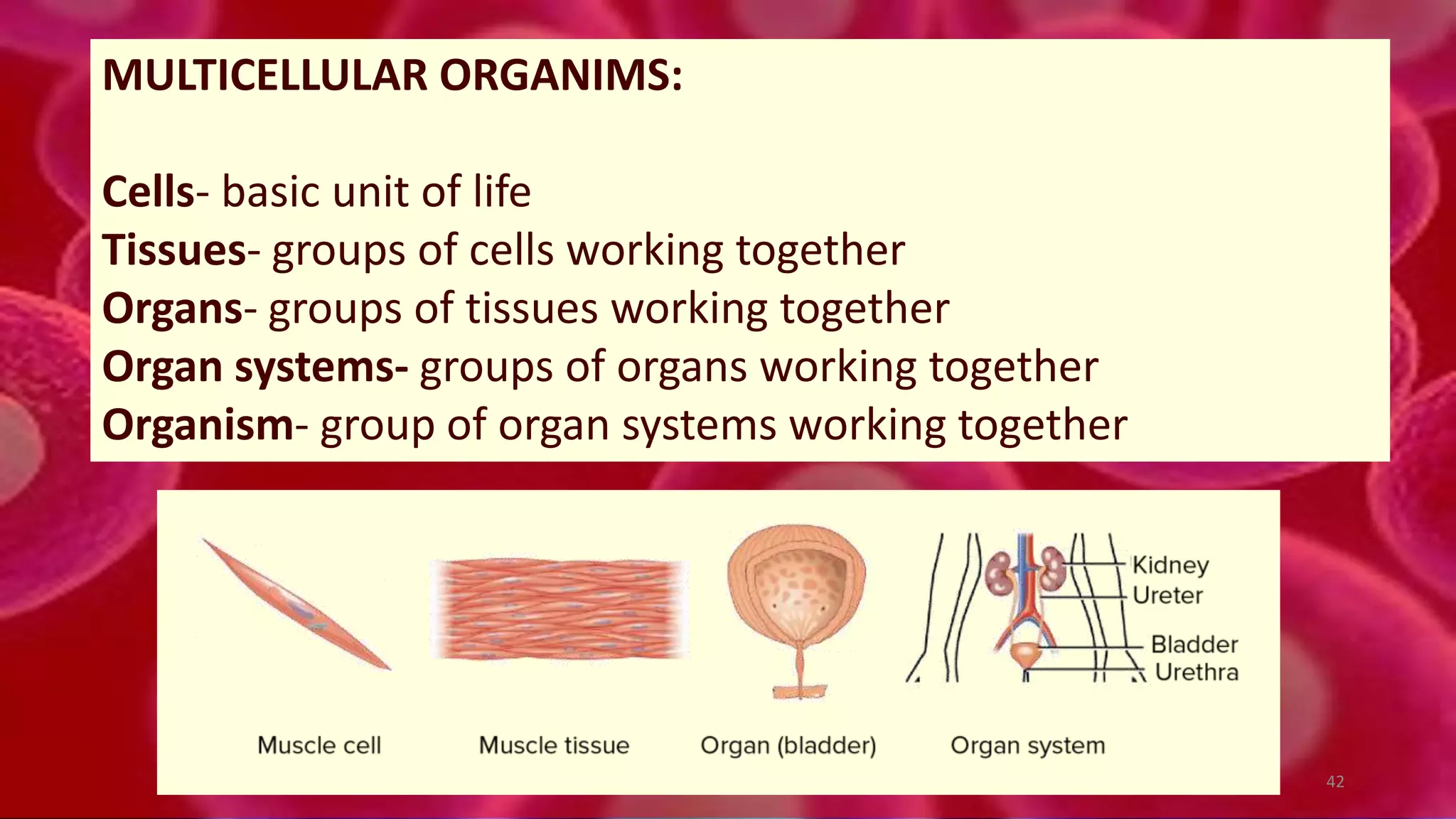
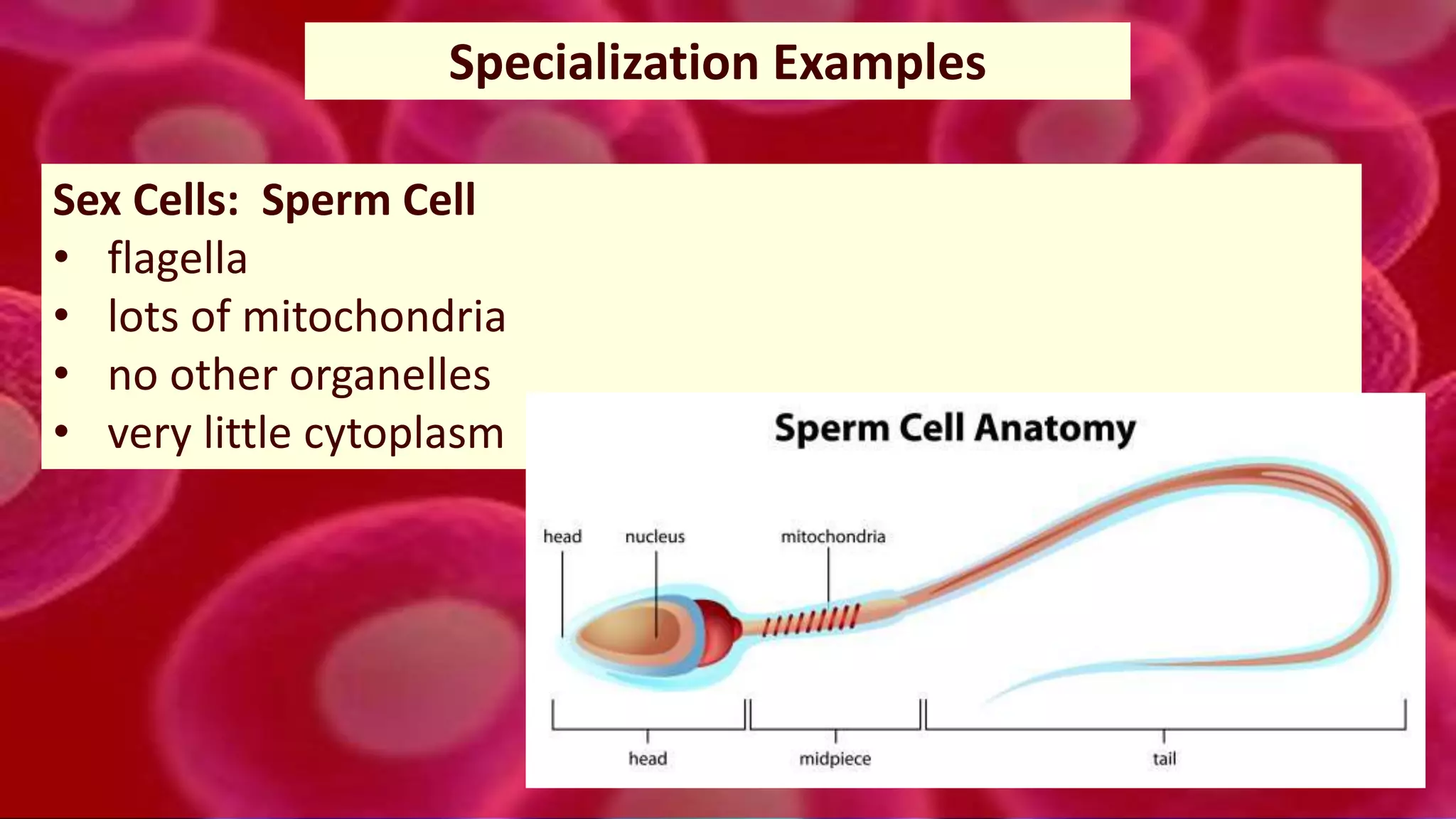
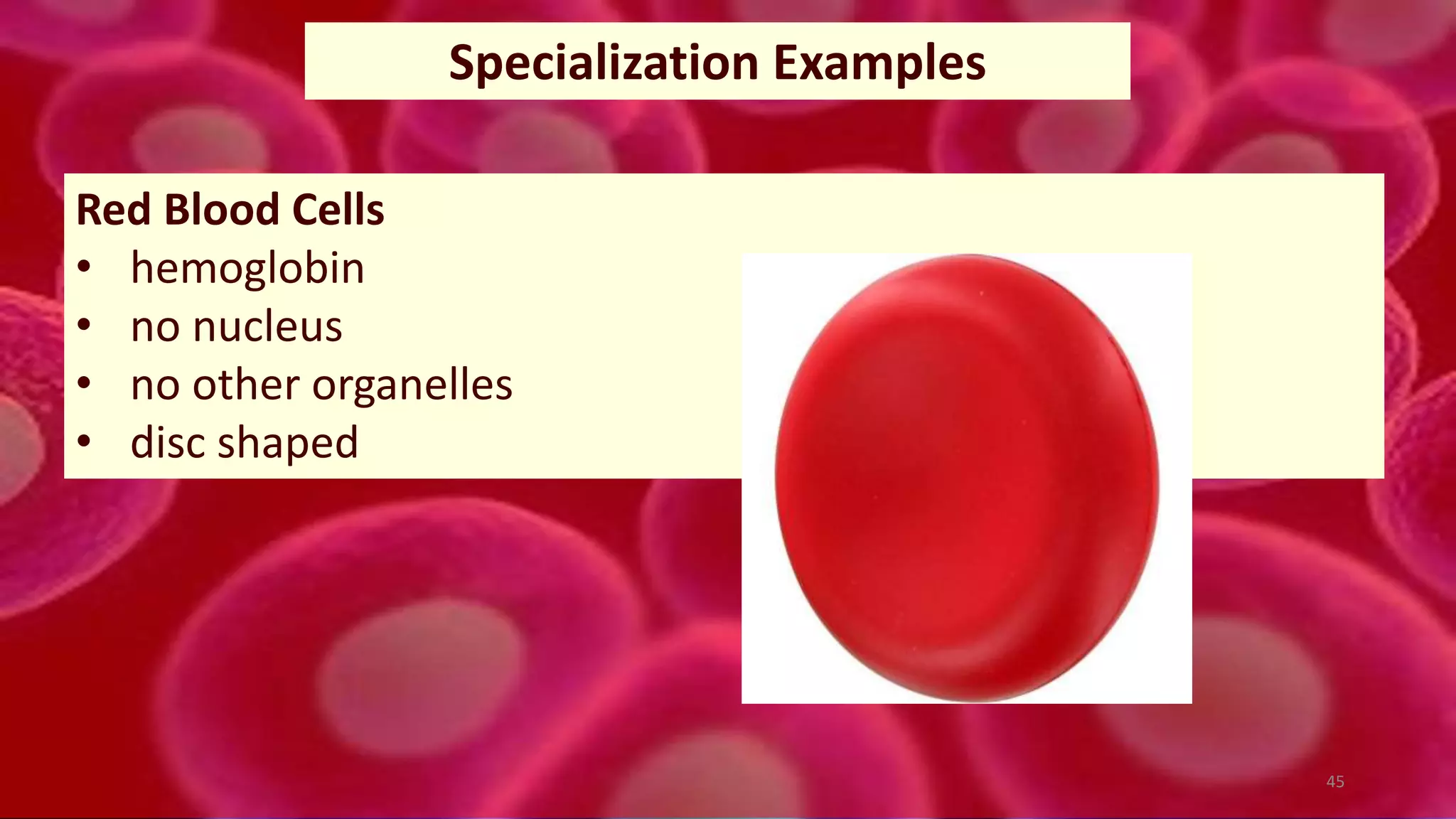
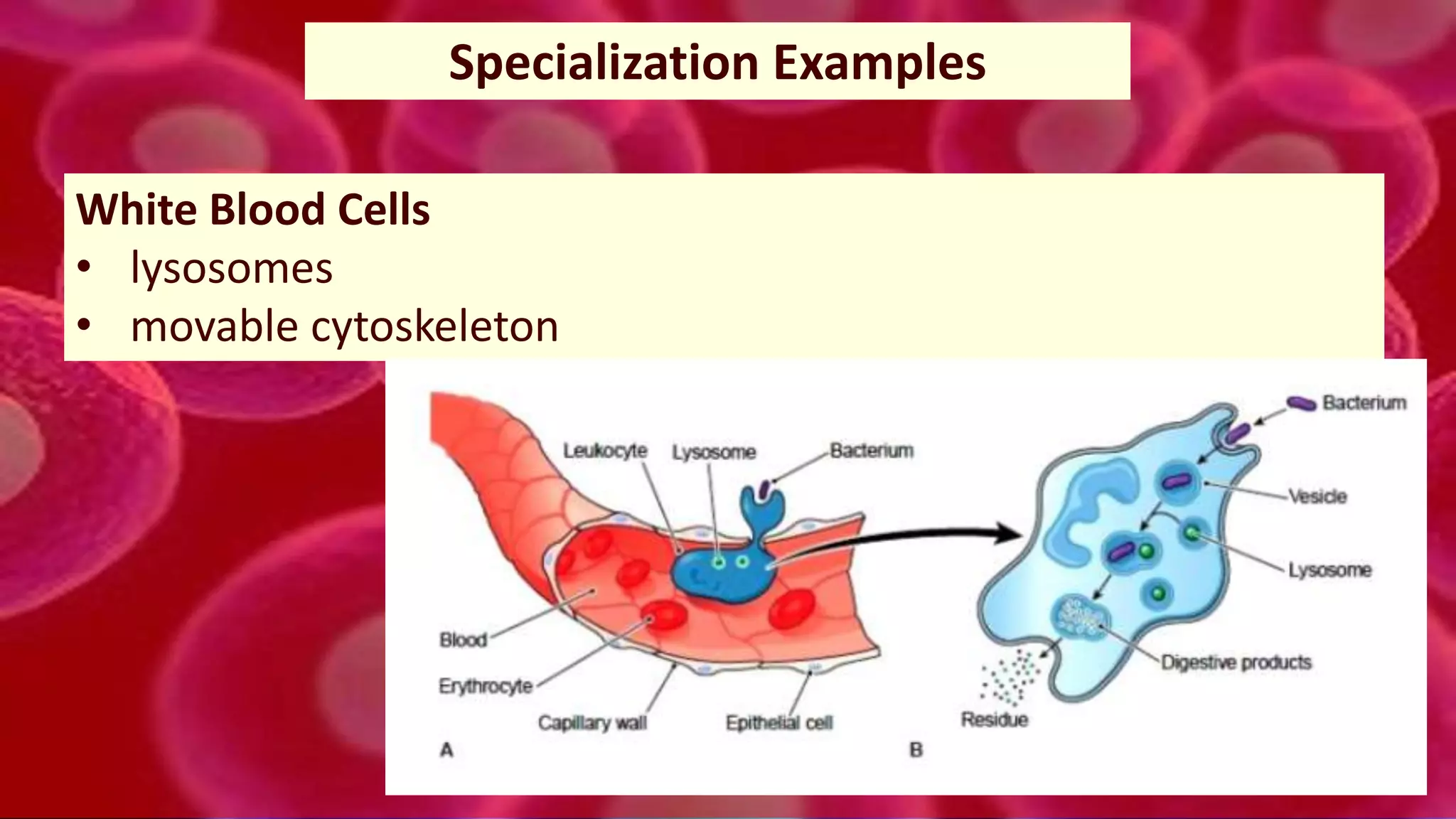
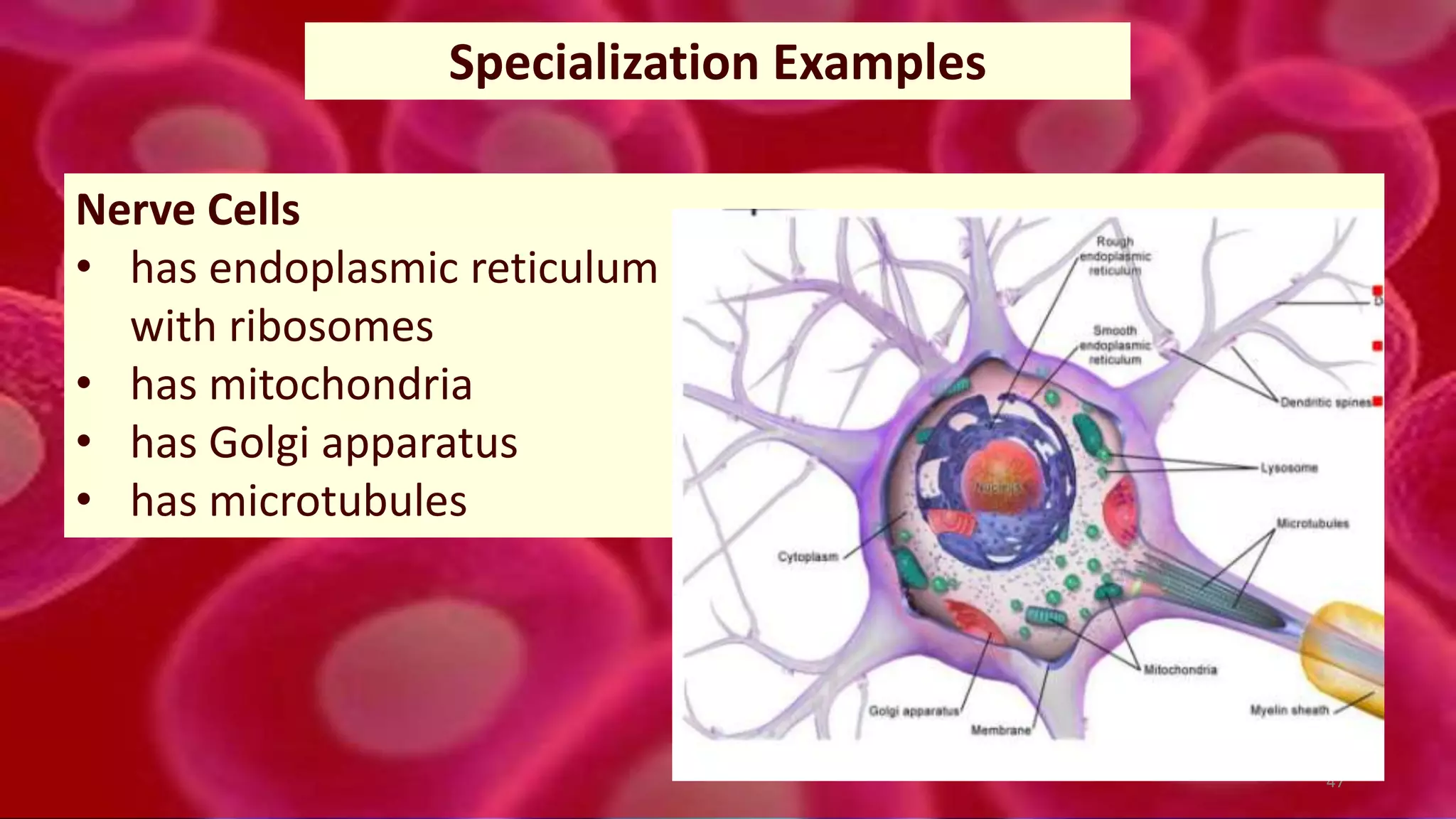
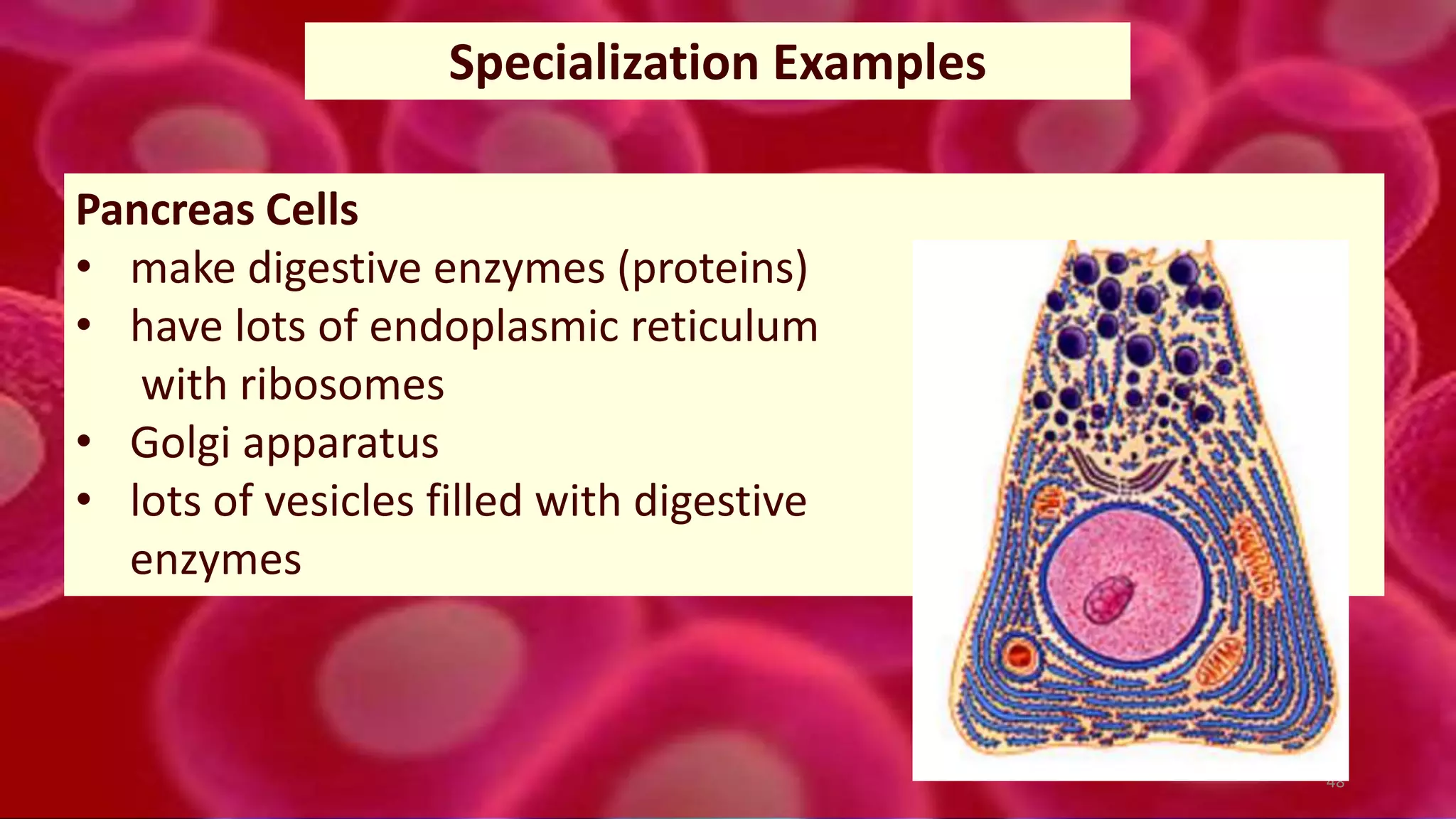
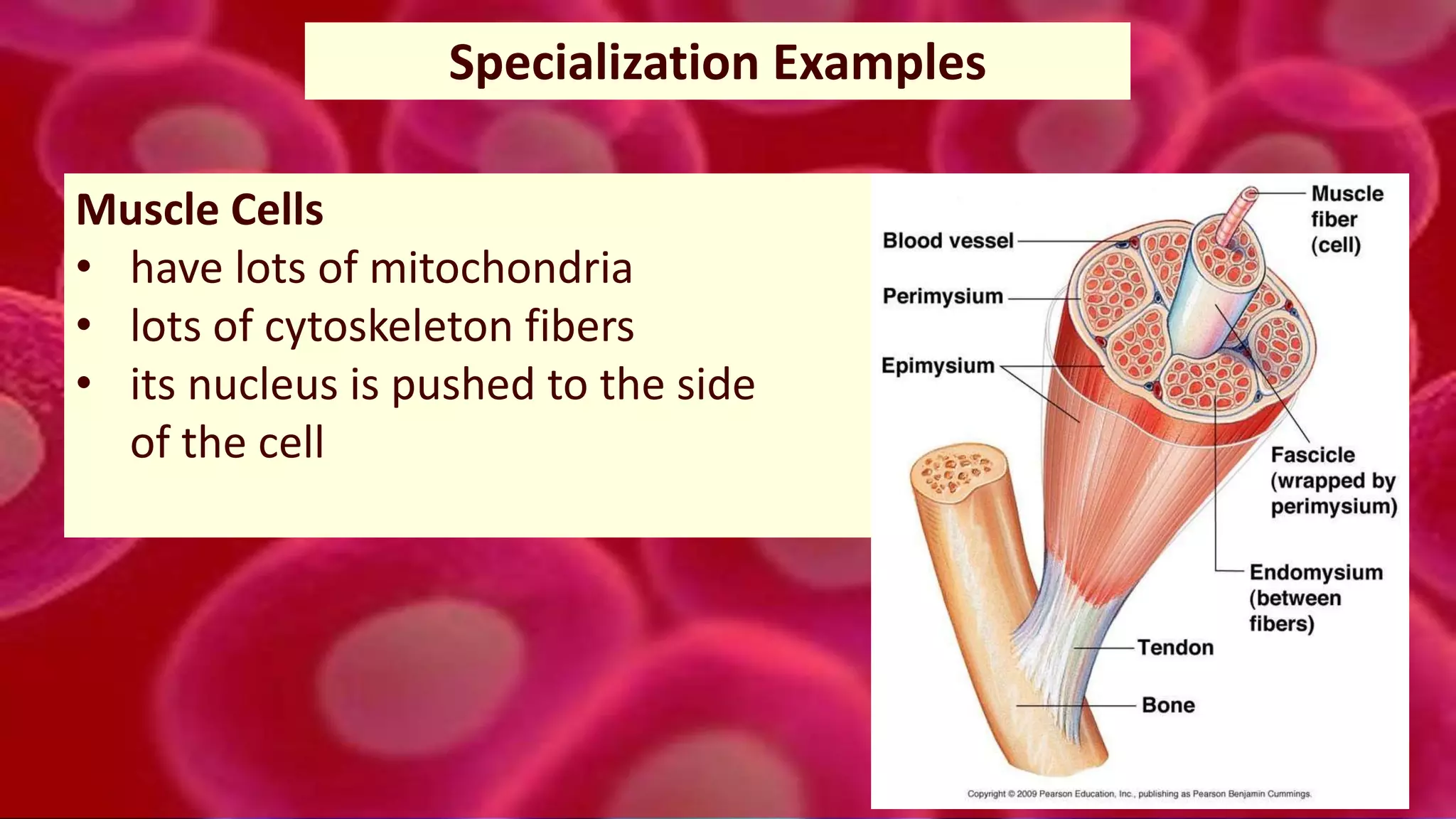
3. In multicellular organisms, cells become specialized through differentiation to perform specific functions like muscle contraction, nerve signaling, or production of enzymes. Specialized cells have unique structures tailored to their function.