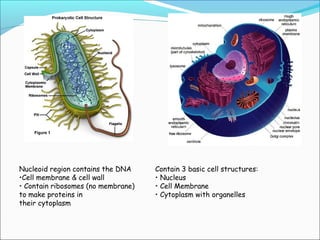
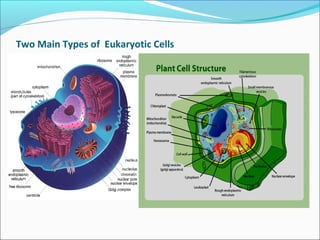
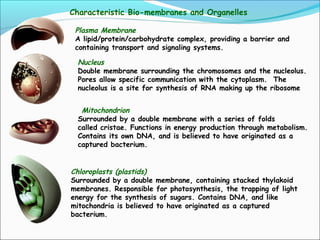
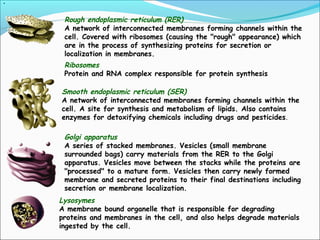
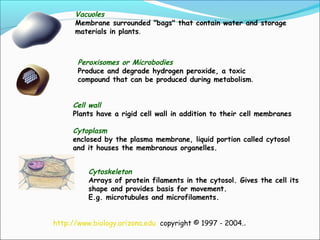
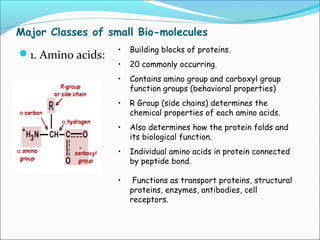
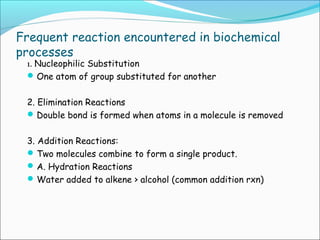
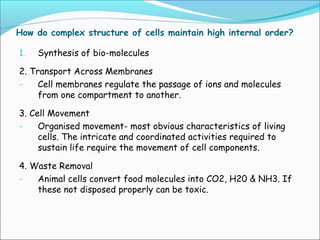
This document provides an introduction to biochemistry and cell structure and function. It begins with defining biochemistry as the application of chemistry to biological processes at the cellular and molecular levels. The main objectives are then outlined. Key points include that cells require a constant source of energy to maintain their highly organized state, and that biochemistry examines the complex molecules and chemical reactions in living systems. The major components of cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic, are then described in detail. The four main classes of biomolecules - proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids - are also introduced along with some of their functions. Common biochemical reactions and how cells generate and maintain energy to prevent disorganization are then discussed