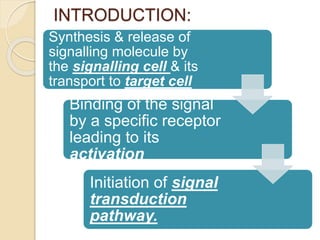
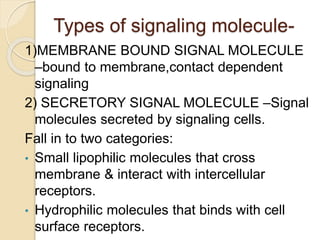
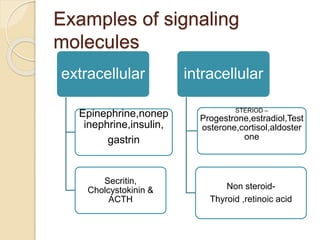
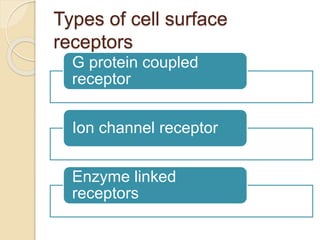
This document provides an overview of cell signalling and the key components involved. It discusses the main types of signalling molecules, including membrane-bound and secretory signals. Examples are given such as epinephrine, insulin, and steroid hormones. The document also describes the role of receptors in cell signalling, noting that receptors undergo a conformational change upon ligand binding to initiate downstream signalling pathways. The main types of receptors are described as intracellular receptors, cell surface receptors, and receptor types including G protein coupled receptors and ion channel receptors.