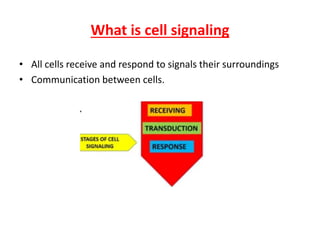
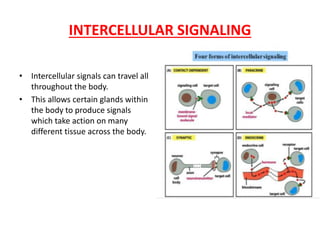
This document discusses different types of intercellular signaling pathways:
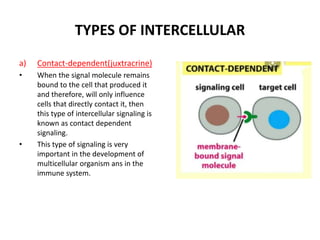
- Contact-dependent signaling occurs when signal molecules remain bound to the producing cell and only influence directly contacting cells. This is important in development and the immune system.
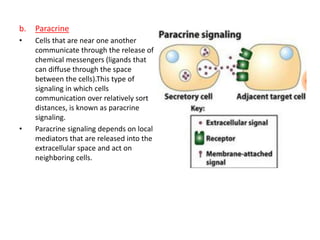
- Paracrine signaling involves diffusion of chemical messengers between nearby cells over short distances.
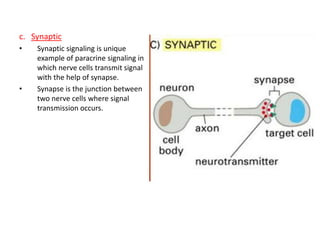
- Synaptic signaling is a form of paracrine signaling where nerve cells transmit signals at synapses.
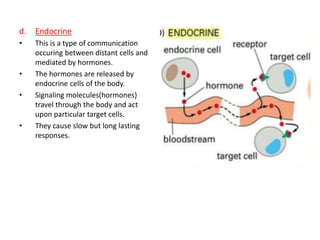
- Endocrine signaling involves hormones released by endocrine glands that travel through the body and act on distant target cells, causing slow but long-lasting responses.
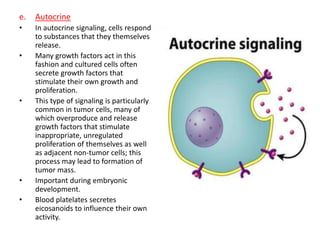
- Autocrine signaling occurs when cells respond to substances they secrete themselves, which is common in tumor cell growth and embryonic