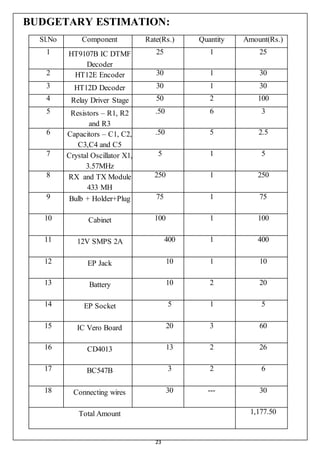
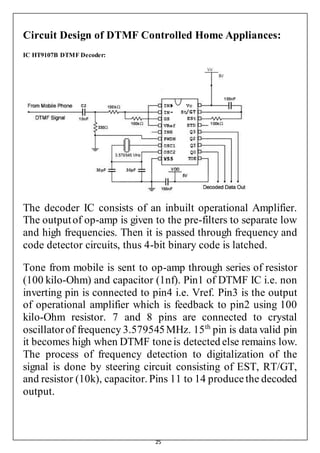
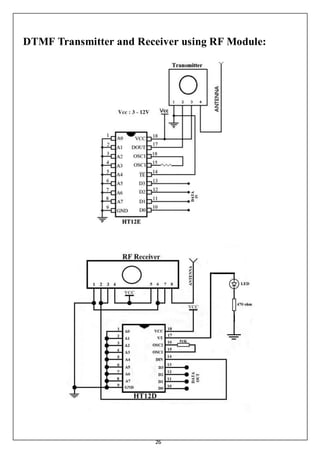
This document details a thesis on a cell phone-controlled home automation system using DTMF technology, aimed at controlling household appliances through a mobile phone interface. The project utilizes various electronic components, including DTMF decoders and RF modules, for circuit design and operation, allowing for remote management of appliances. The thesis also addresses theoretical foundations, circuit principles, budget estimation, results, advantages, limitations, and concludes with potential future developments in home automation technology.















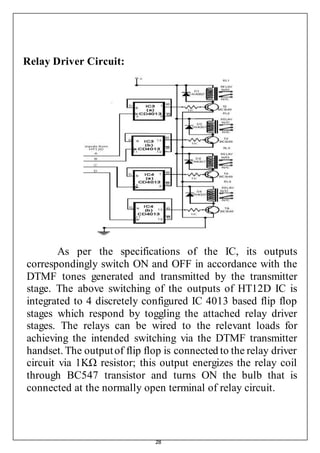











![40
REFERENCES:
[1] GSM SYSTEM SURVEY ,Student text, EN/LZT 1233321,
R5B revised upgrade edition. p. 192.
[2] Dual-tone multi-frequency, Available:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dual-tone_multi-frequency
[3] Schenker, L., “Pushbutton Calling with a Two-Group
Voice-Frequency Code” - The Bell system technical journal
(ISSN 0005-8580) vol:39 iss:1 pp:235-255, 1960
[4] DTMF decoding, Available:
http://www.dattalo.com/technical/theory/dtmf.html
[5] “Microcontroller Technology:16F84A”, prentice hall , 7th
edition, page32, 2002
[6] I. Coskun and H. Ardam, “A Remote Controller for Home
and Office Appliances by Telephone”, IEEE Trans. Consumer
Electron. , vol. 44, no. 4, pp. 1291- 1297, November 1998
[7] PIC16F84A microcontroller data sheet, Available:
http://ww1.microchip.com/downloads/en/devicedoc/35007b.pd
f
[8] Daldal Nihat, “GSM Based Security and Control System”
(In Turkish), M.Sc. Term Project, Gazi University, Ankara,
2003.
[9] E. Wong, “A Phone-Based Remote Controller For Home
And Office Automation”, IEEE Trans.Consumer Electron. ,
vol. 40, no. 1, pp. 28-33, February 1995.
[10] Relay Information, Available:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/4th-mainpart-160601150306/85/Cell-Phone-Controlled-Home-Automation-System-using-DTMF-Technology-40-320.jpg)
