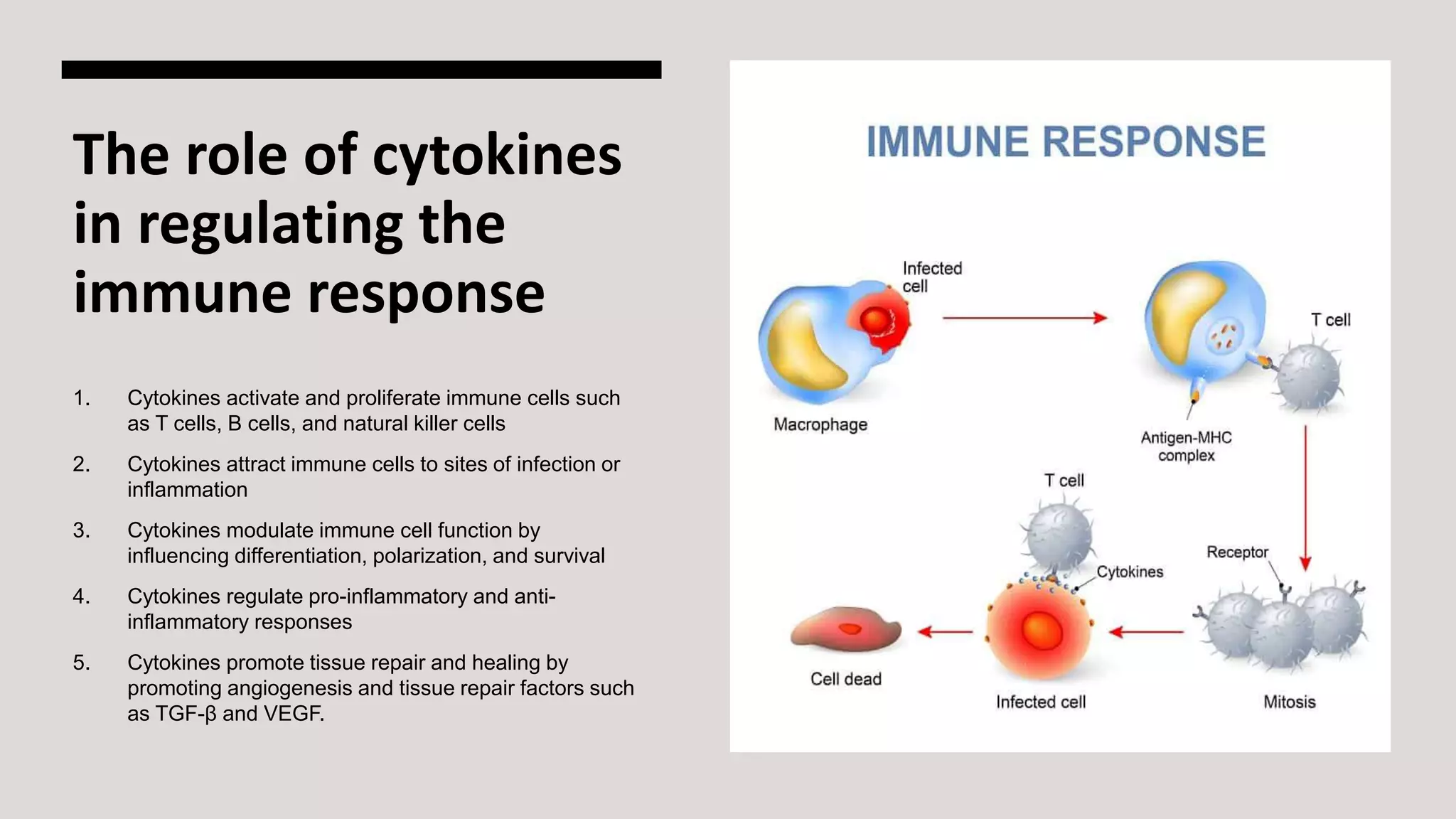
Cell-mediated immunity is an immune response involving T cells, natural killer cells, and macrophages that target infected or abnormal cells, distinct from humoral immunity which produces antibodies. The activation of T cells by antigen-presenting cells is crucial for immune response, leading to differentiation and clonal expansion for effective pathogen elimination. Current research focuses on therapies to enhance cell-mediated immunity in cancer treatment and vaccines, as well as approaches to manage autoimmune diseases and transplant rejection.