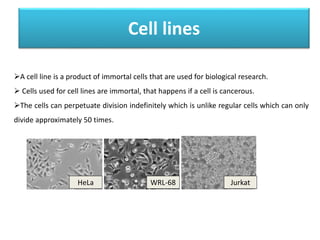
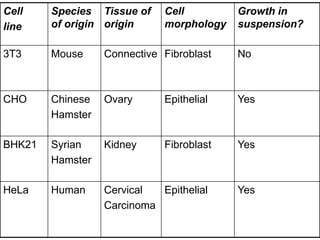
The document discusses the applications of cell cultures and cell lines in biotechnology, highlighting their importance in cancer research, drug testing, and vaccine production. It explains various types of cell cultures, including primary and continuous cell lines, along with the laboratory equipment and media used in cell culture processes. Emphasis is placed on the advancements in cell line technology for producing vaccines, antibodies, and recombinant proteins, as well as their role in therapeutic interventions and drug development.