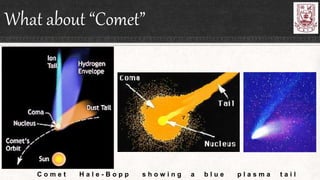
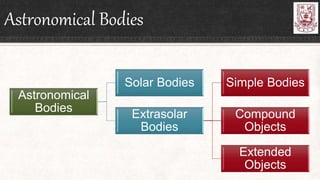
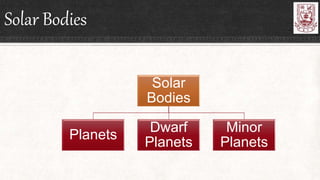
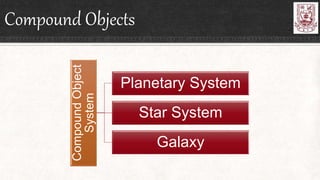
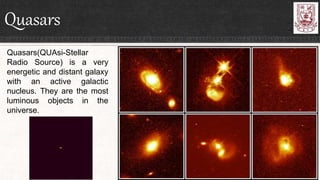
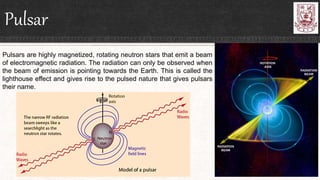
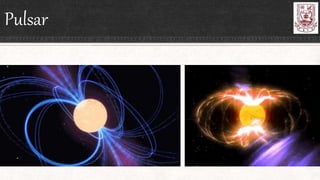
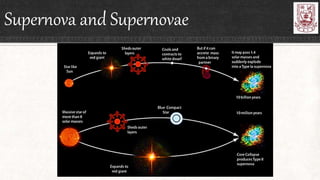
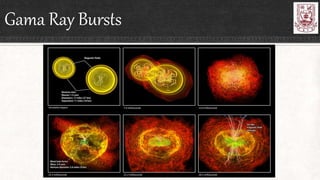
Celestial objects can be astronomical bodies or astronomical objects. Bodies refer to single, contiguous entities like asteroids or stars, while objects can consist of multiple bodies or structures like planetary systems or galaxies. Comets can be both bodies, referring to their frozen nuclei, or objects when including their diffuse comas and tails. Other celestial objects discussed include Kuiper belt objects, quasars, pulsars, supernovae, galaxies, meteors, and gamma ray bursts.