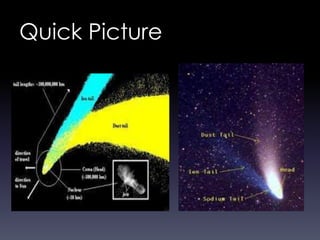
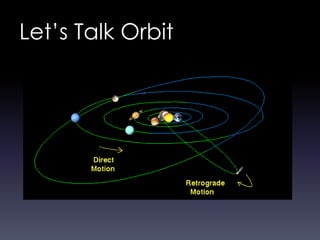
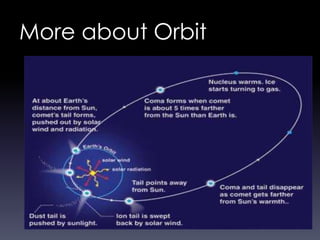
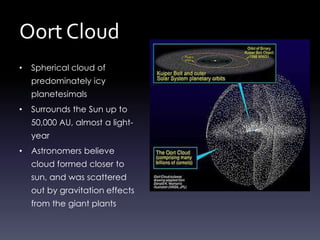
Comets are small icy bodies made up of dust and frozen gases like water, carbon dioxide and methane. As comets approach the sun, solar radiation causes their icy cores to heat up and release gases that form tails of dust and ions. The document focuses on Halley's Comet, one of the most famous comets that orbits the sun every 76 years. In 1986 it passed close to Earth and spacecraft were able to study its icy nucleus up close for the first time. The comet's periodic orbit was first determined in 1705 and it has been observed by many ancient civilizations throughout history.