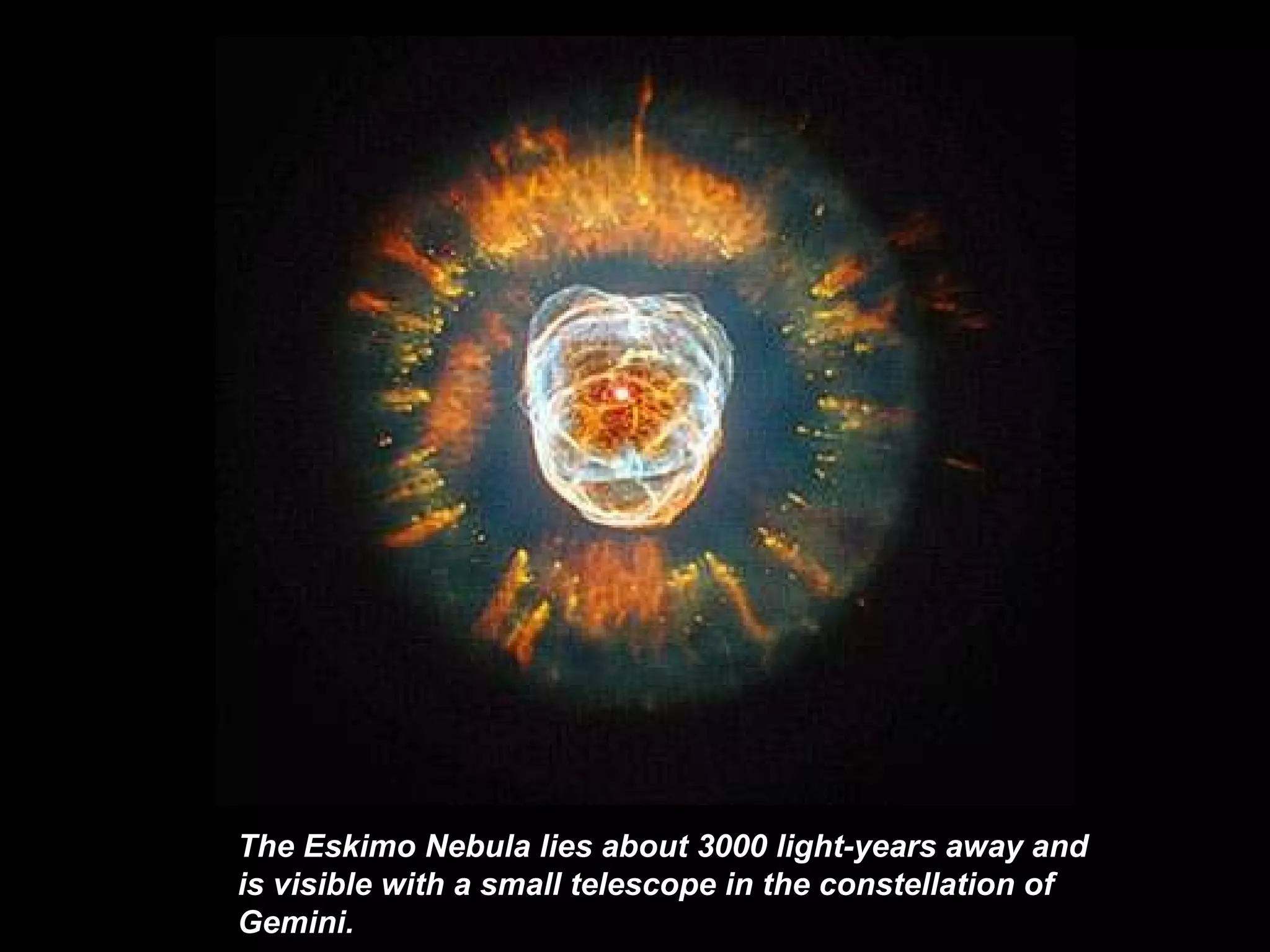
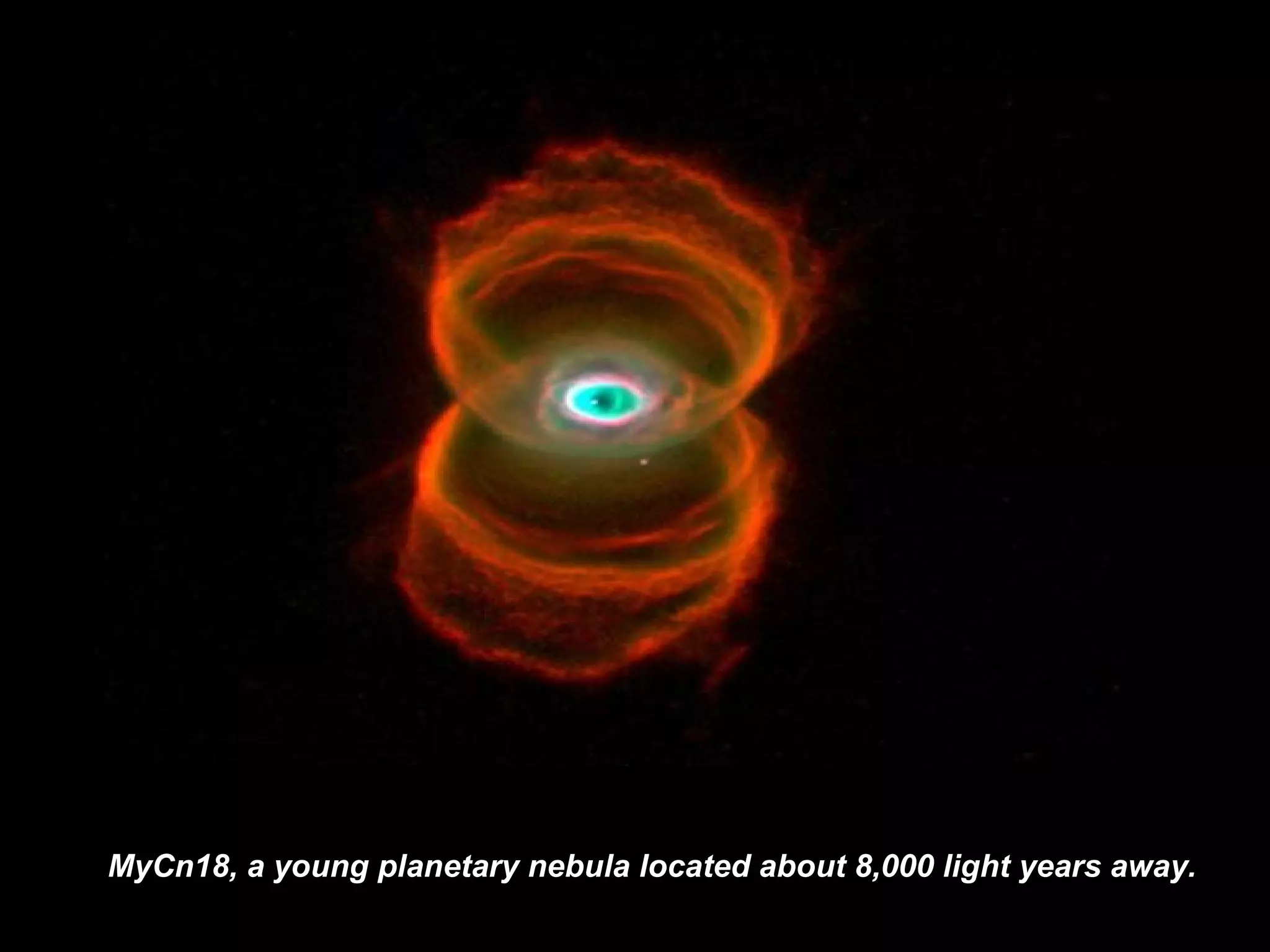
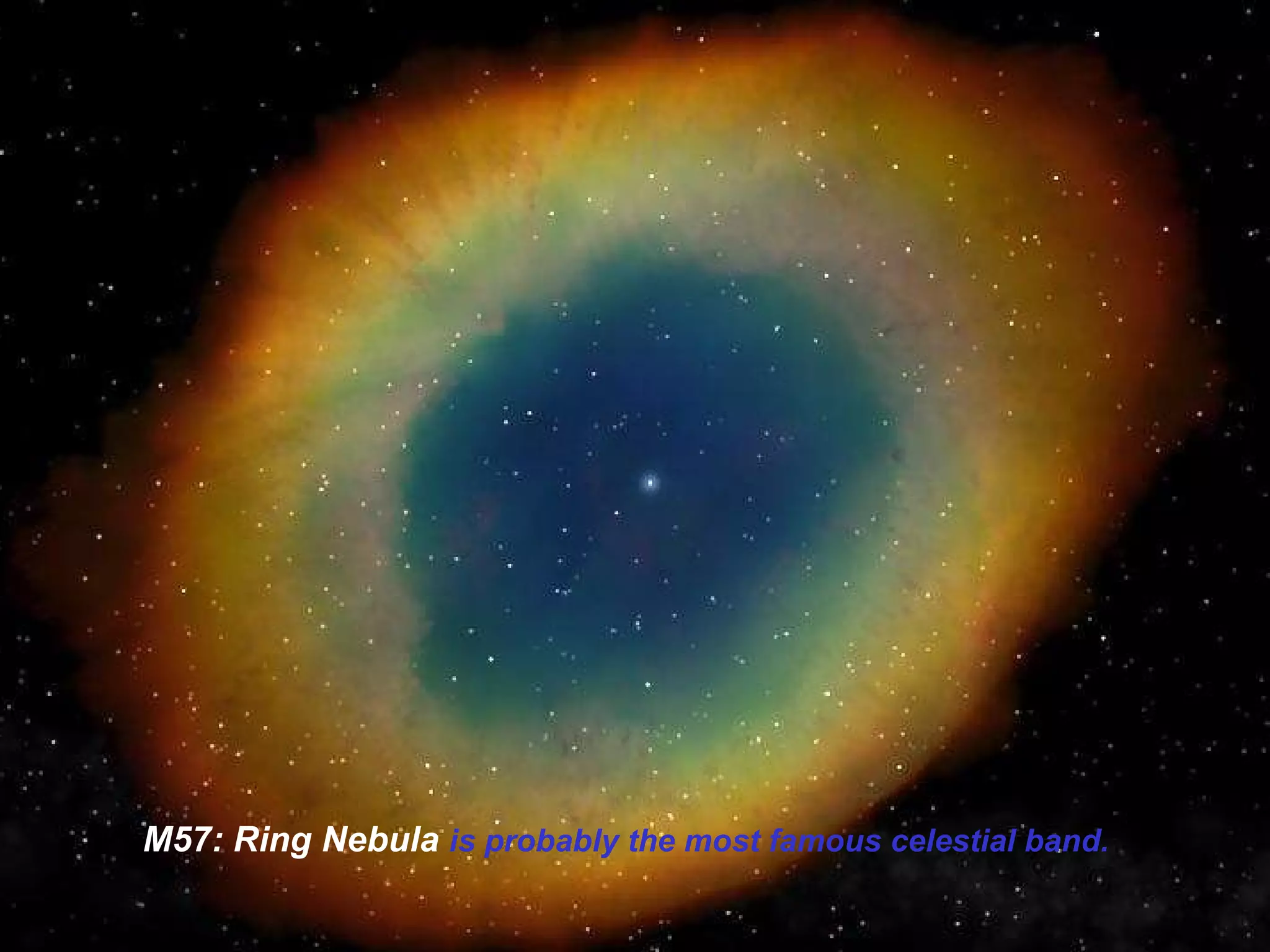
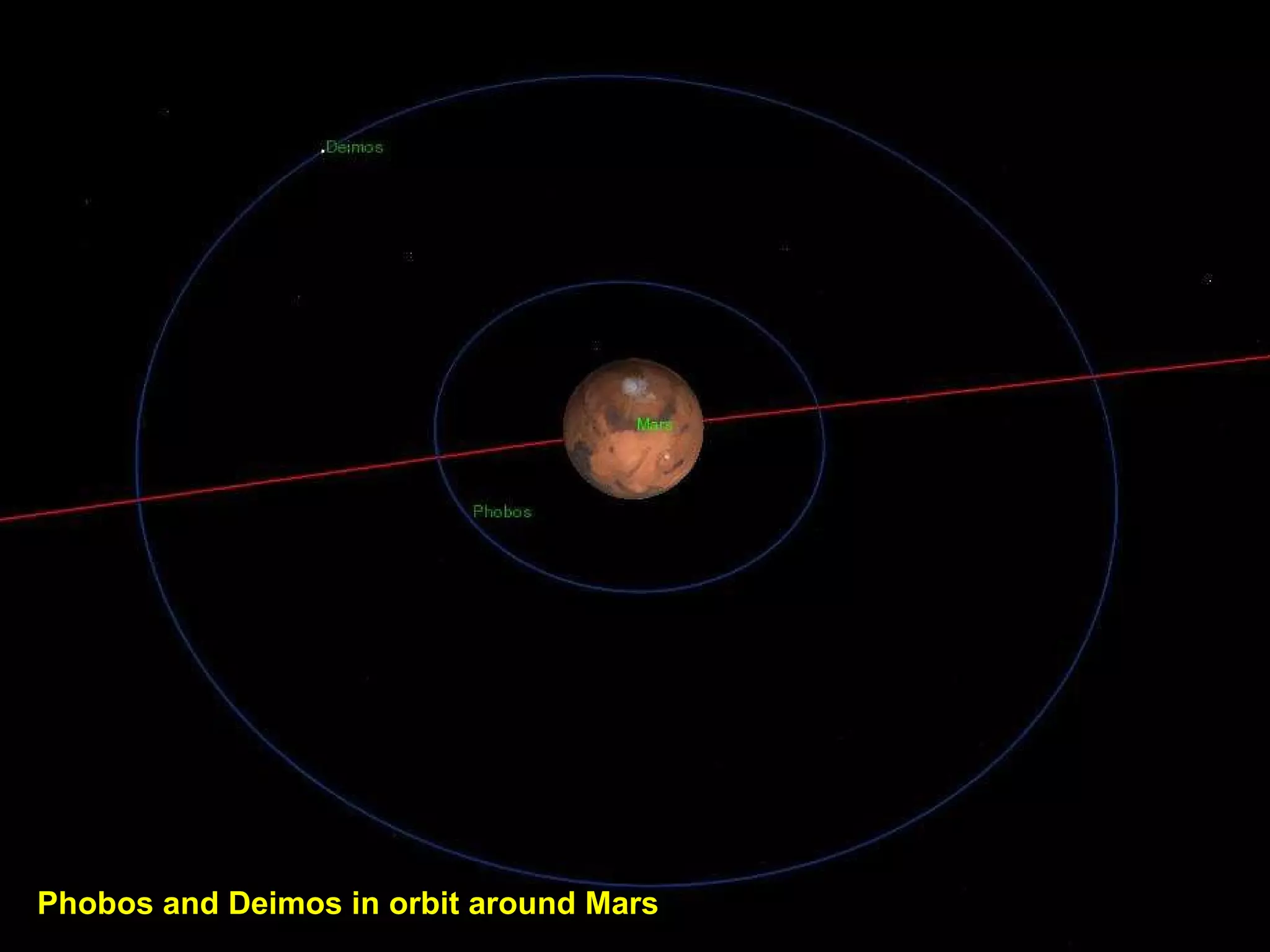
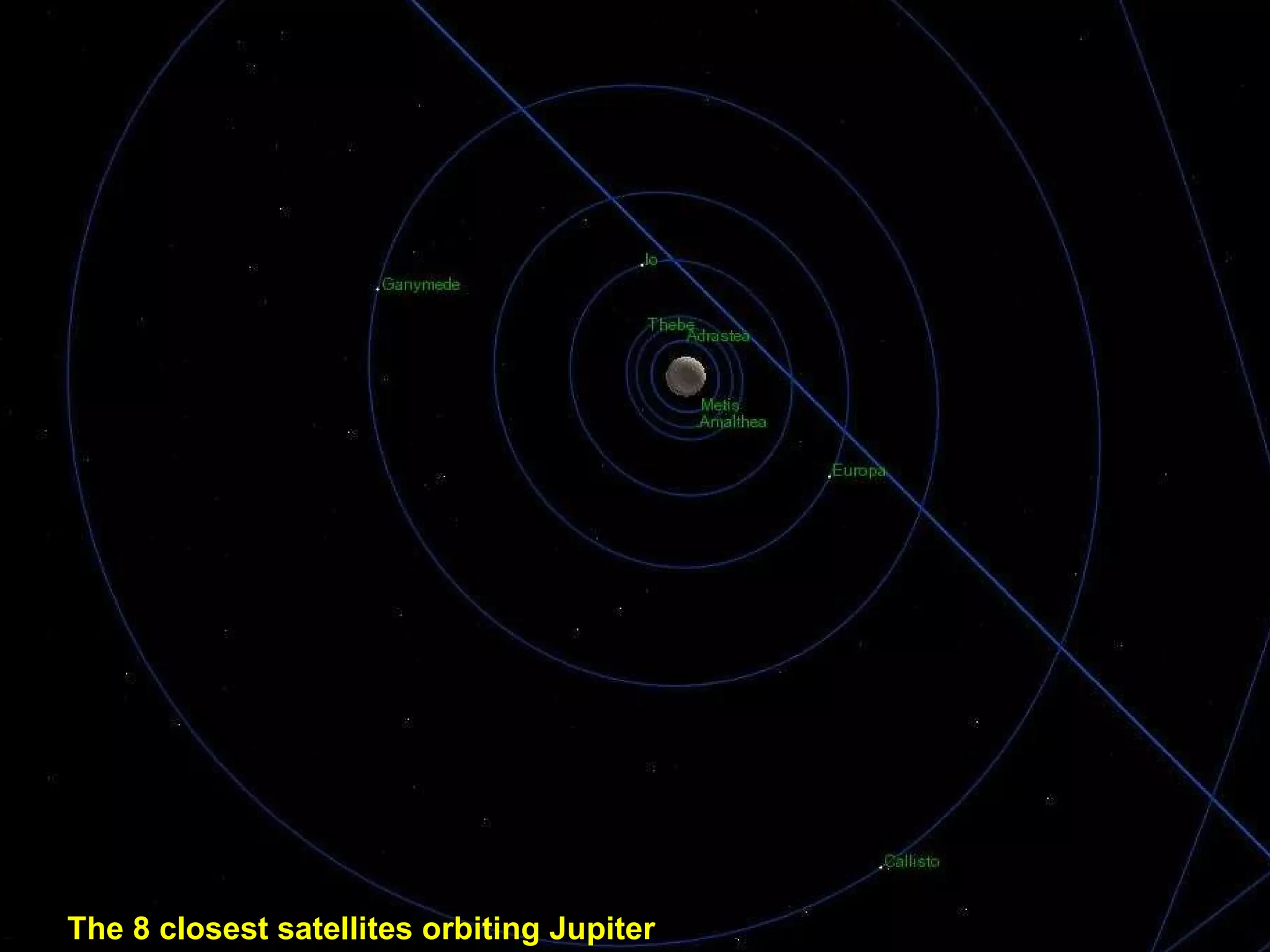
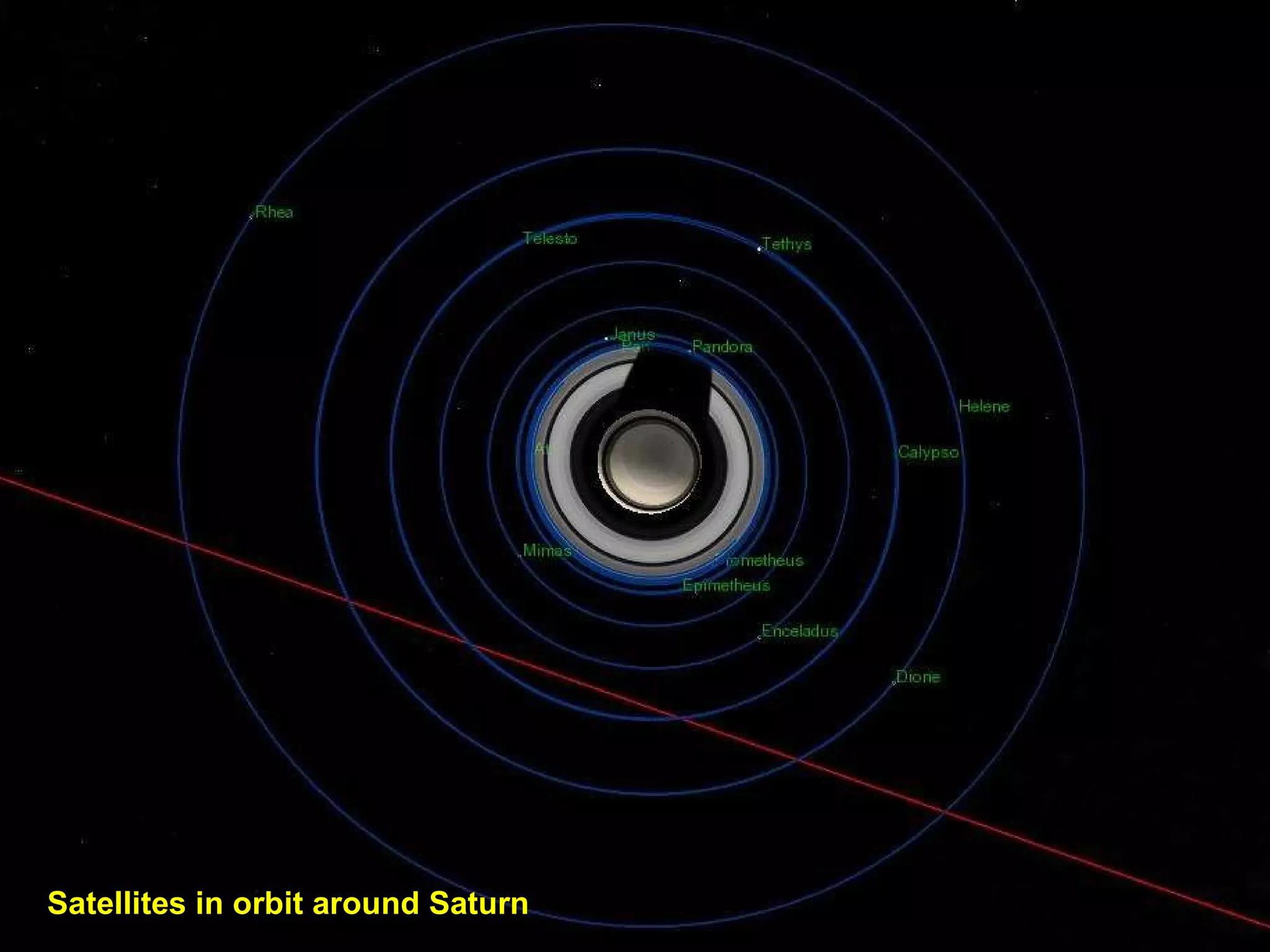
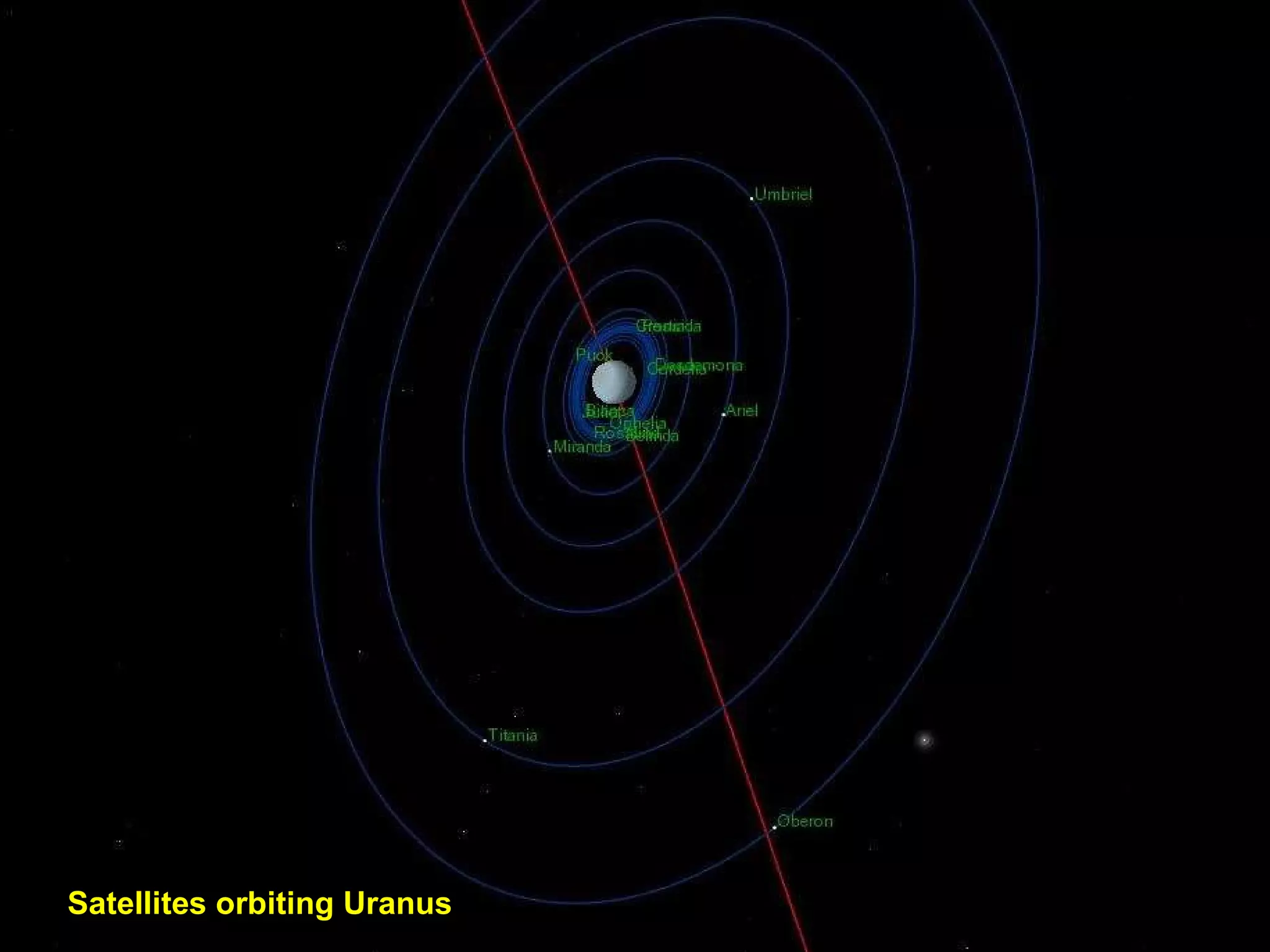
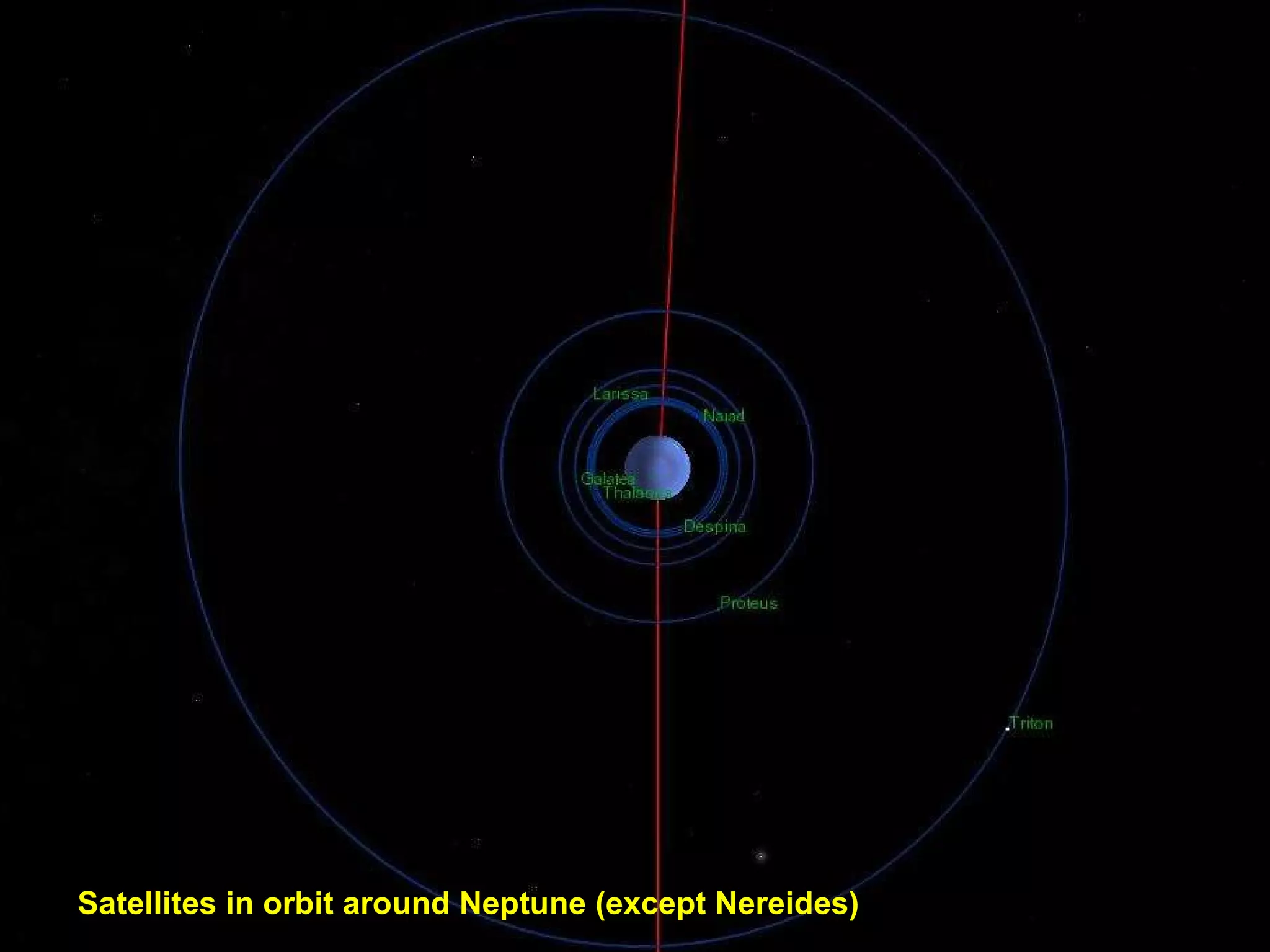
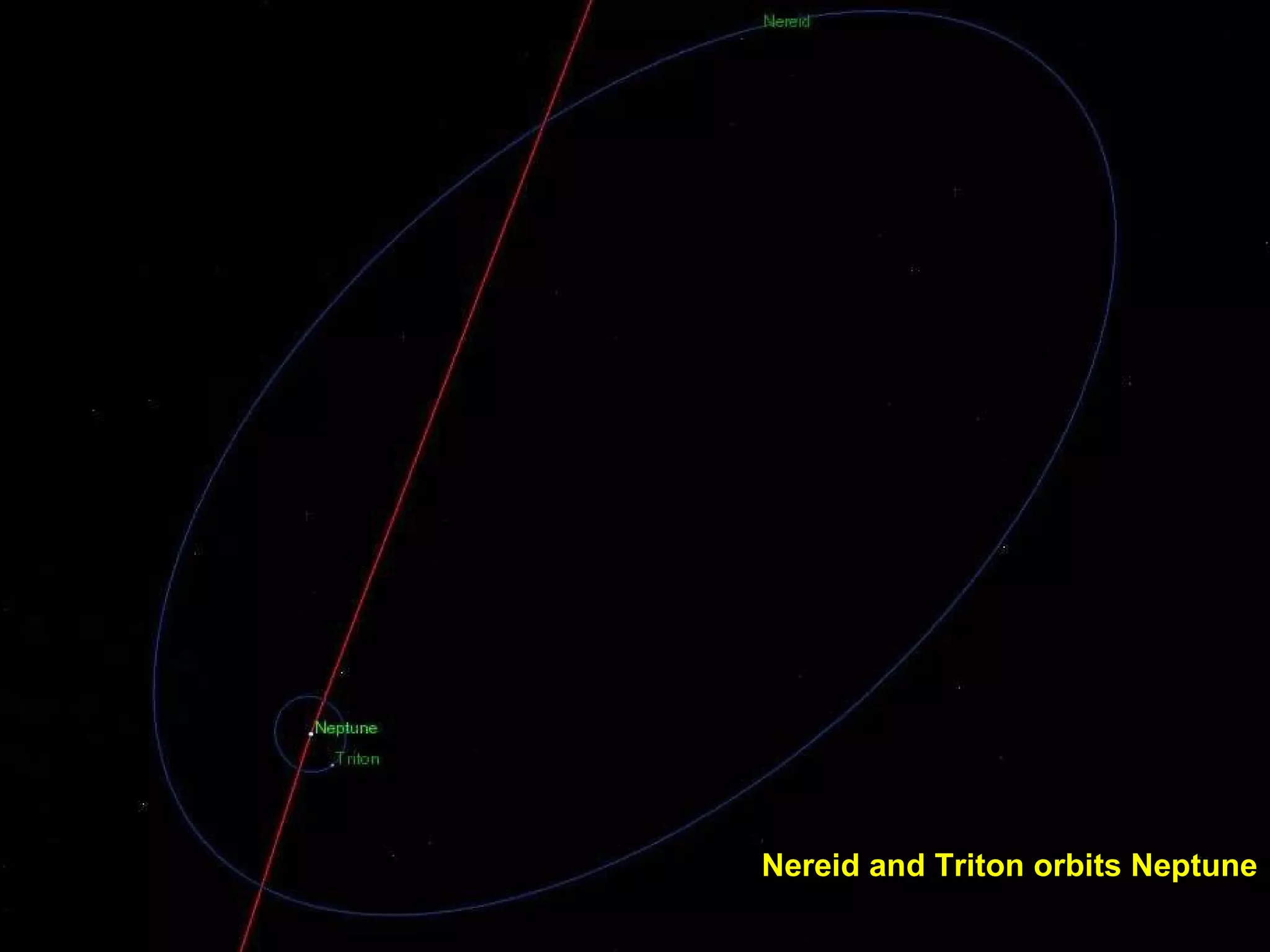
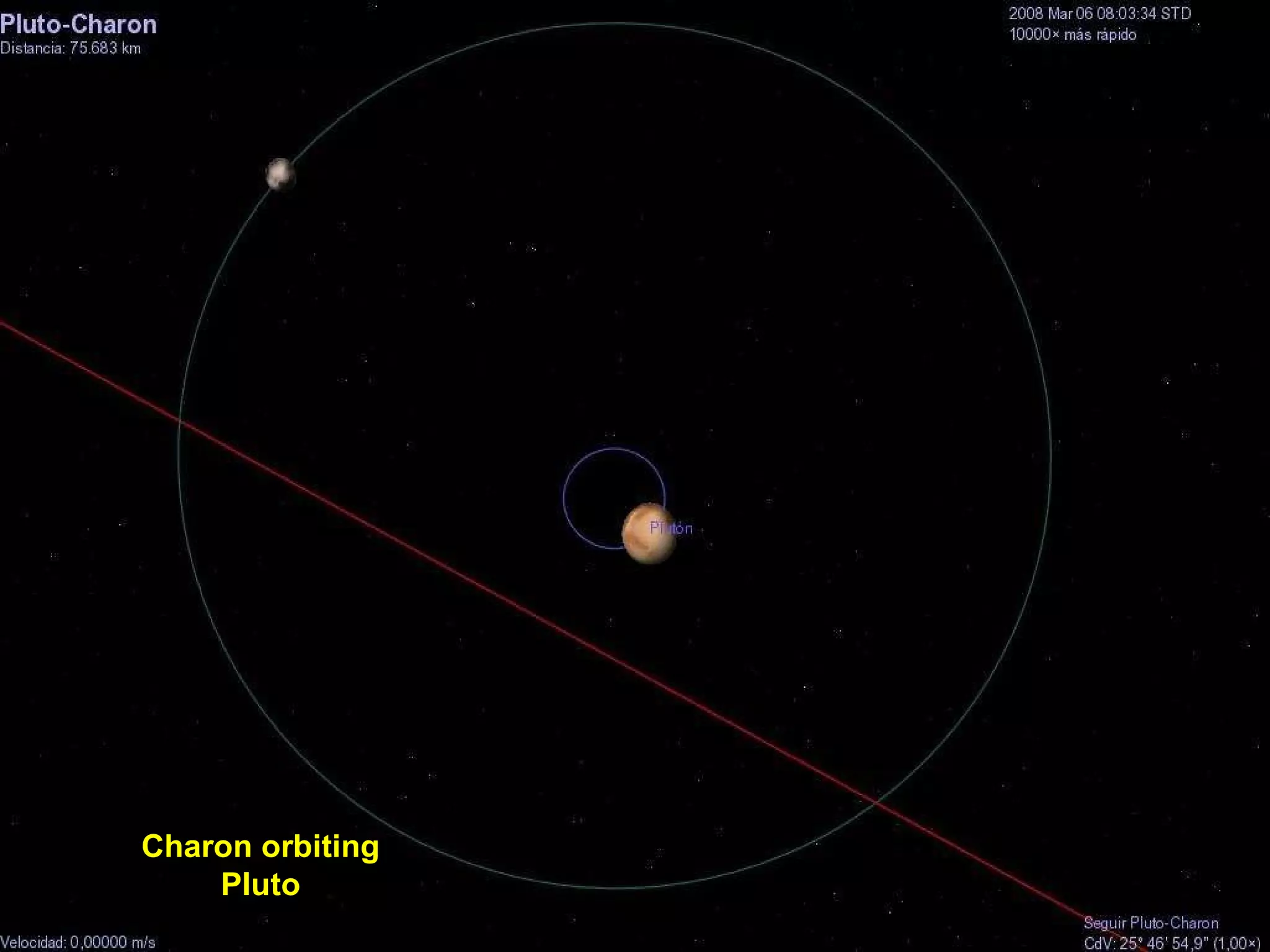
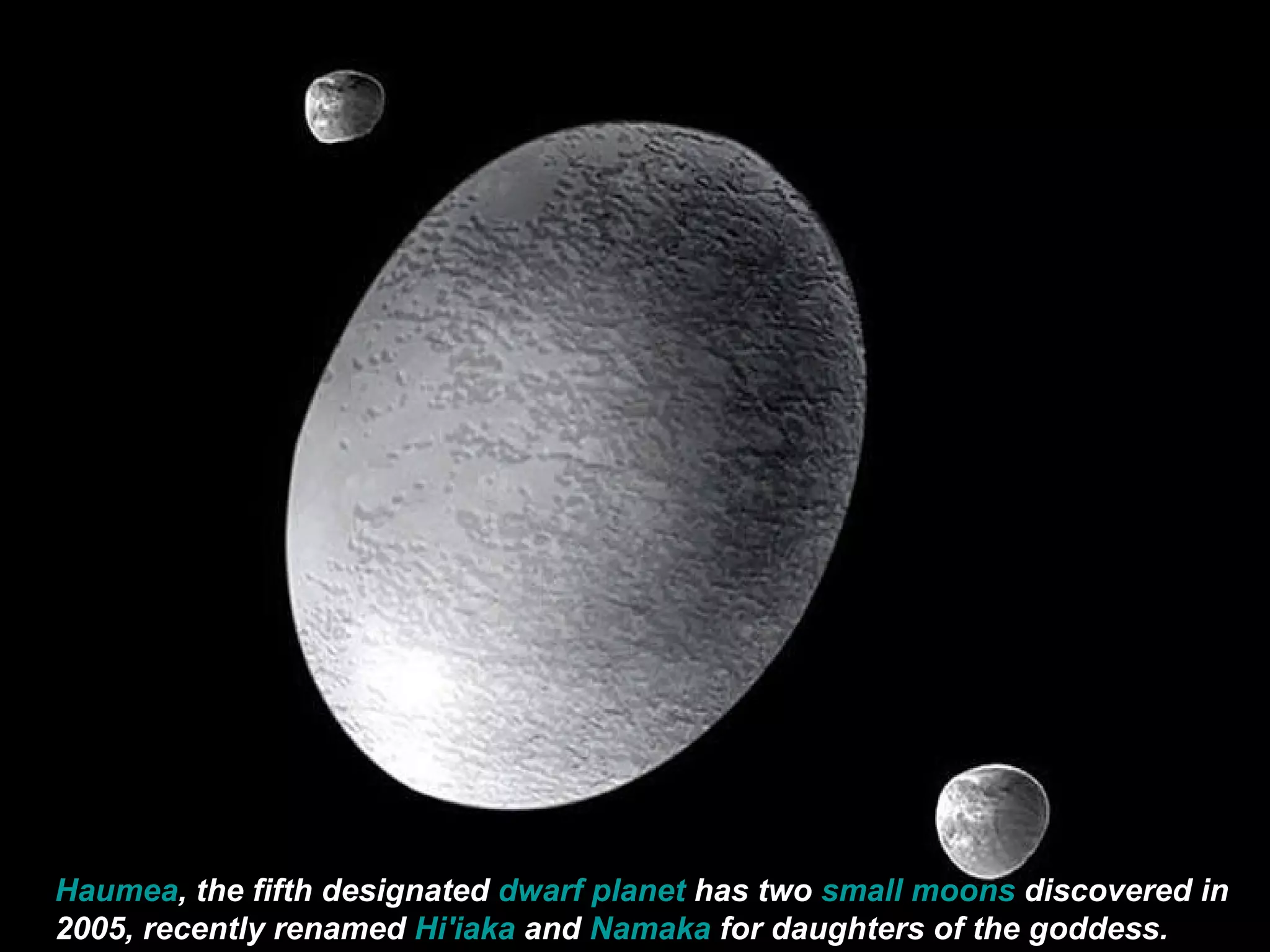
The Hubble Space Telescope is a large space-based observatory named after astronomer Edwin Hubble that has provided unprecedented views of the universe. Hubble orbits Earth every 96 minutes and has taken many famous images including pillars of creation in the Eagle Nebula and the Crab Nebula. Some of Hubble's images show planetary nebulae, star clusters, galaxies and more distant objects in the universe.